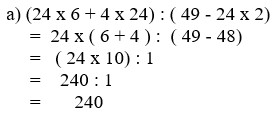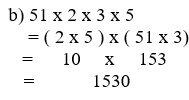x:3-24=4

Những câu hỏi liên quan
1) 54 : x - x : x = 3 x 2 - 1
2) 42 : x + x - x = 4 x 3 - 4
3) 24 : x - 2 x 4 = 24 - 2 x 3 x 4
1, 54 : x - 1 = 5
54 : x = 5+1 = 6
x = 54 : 6 = 9
2, 42 : x + 0 = 8
x = 42 : 8 = 21/4
3, 24 : x - 8 = 0
24 : x = 0 + 8 = 8
x = 24 : 8 = 3
Tk mk nha
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
1) 54:x-x:x=3x2-1
54:x- 1 =6-1
54:x- 1=5
54:x =6
x=54:6=9
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
X + 3 1/4 + x = 24 1/4
3 1/4 , 24 1/4 là hỗn số
Trả lời :
\(x+3\frac{1}{4}+x=24\frac{1}{4}\)
\(x+\frac{13}{4}+x=\frac{97}{4}\)
\(x\text{ x 2 }+\frac{13}{4}=\frac{97}{4}\)
\(x\text{ x 2 }=\frac{97}{4}-\frac{13}{4}\)
\(x\text{ x 2 }=\frac{84}{4}=21\)
\(x=21:2\)
\(x=10,5\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
\(x+3\frac{1}{4}+x=24\frac{1}{4}\)
\(\Rightarrow2x+\frac{13}{4}=\frac{97}{4}\)
\(\Rightarrow2x=21\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\frac{21}{2}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
\(x+3\frac{1}{4}+x=24\frac{1}{4}\)
\(2\times x+\frac{13}{4}=\frac{97}{4}\)
\(2\times x=\frac{97}{4}-\frac{13}{4}\)
\(2\times x=21\)
\(x=21:2\)
\(x=10,5\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
24/x:8/3=3/5
x+3 1/2+x=24 1/4
\(\dfrac{24}{x}:\dfrac{8}{3}=\dfrac{3}{5}\)
\(\dfrac{24}{x}=\dfrac{3}{5}.\dfrac{8}{3}\)
\(\dfrac{24}{x}=\dfrac{8}{5}\)
\(\dfrac{24}{x}=\dfrac{24}{15}\)
=>x=5
Vậy x=5
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
\(x+3\dfrac{1}{2}+x=24\dfrac{1}{4}\)
\(\left(x+x\right)+3\dfrac{1}{2}=24\dfrac{1}{4}\)
\(x.2+\dfrac{7}{2}=\dfrac{97}{4}\)
\(x.2=\dfrac{97}{4}-\dfrac{7}{2}\)
\(x.2=\dfrac{97}{4}-\dfrac{14}{4}\)
\(x.2=\dfrac{83}{4}\)
\(x=\dfrac{83}{4}:2\)
\(x=\dfrac{83}{4}.\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(x=\dfrac{83}{8}\)
\(x=10\dfrac{3}{8}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tính nhanh
a) (24 x 6 + 4 x 24) : ( 49 - 24 x 2)
b) 51 x 2 x 3 x 5
Tính nhẩm
5 x 6 = ..... 2 x 6 = ..... 3 x 6 = ..... 4 x 6 = .....
6 x 5 = ..... 6 x 2 = ..... 6 x 3 = ..... 6 x 4 = .....
30 : 6 = ..... 12 : 6 = ..... 18 : 6 = ..... 24 : 6 = .....
30 : 5 = ..... 12 : 2 = ..... 18 : 3 = ..... 24 : 4 = .....
5 x 6 = 30 2 x 6 = 12 3 x 6 = 18 4 x 6 = 24
6 x 5 = 30 6 x 2 = 12 6 x 3 = 18 6 x 4 = 24
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tính nhẩm:
5 x 6 = 30 2 x 6 = 12 3 x 6 = 18 4 x 6 = 24
6 x 5 = 30 6 x 2 = 12 6 x 3 = 18 6 x 4 = 24
30 : 6 = 5 12 : 6 = 2 18 : 6 = 3 24 : 6 = 4
30 : 5 = 6 12 : 2 = 6 18 : 3 = 6 24 : 4 = 6
Học tốt <3
5 x 6 = 30 2 x 6 = 12 3 x 6 = 18 4 x 6 = 24
6 x 6 = 30 6 x 2 = 12 6 x 3 = 18 6 x 4 = 24
30 : 6 = 5 12 : 6 = 2 18 : 6 = 3 24 : 6 = 4
30 : 5 = 6 12 : 2 = 6 18 : 3 = 6 24 : 4 = 6
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
a,24/x:8/3=3/5
b,x+3 1/2+x=24 1/4
a.24/x:8/3=3/5
suy ra :24/x=8/5
suy ra:x=15
b. x=35/8
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
a) \(\frac{24}{x}:\frac{8}{3}=\frac{3}{5}\) \(\frac{24}{x}=\frac{3}{5}.\frac{8}{3}\) \(\frac{24}{x}=\frac{8}{5}\) \(x=24.5:8\) \(x=15\)
b) Đề bài sai rồi
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tính nhẩm:
8 x 5 =
8 x 4 =
8 x 6 =
8 x 3 =
40 : 8 =
32 : 8 =
48 : 8 =
24 : 8 =
40 : 5 =
32 : 4 =
48 : 6 =
24 : 3 =
Học sinh nhẩm và ghi:
8 x 5 = 40
8 x 4 = 32
8 x 6 = 48
8 x 3 = 24
40 : 8 = 5
32 : 8 = 4
48 : 8 = 6
24 : 8 = 3
40 : 5 = 8
32 : 4 = 8
48 : 6 = 8
24 : 3 = 8
(chú ý: mối quan hệ giữa nhân và chia)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Tính nhẩm:
8 x 5 = 40
8 x 4 = 32
8 x 6 = 48
8 x 3 = 24
40 : 8 = 5
32 : 8 = 4
48 : 8 = 6
24 : 8 = 3
40 : 5 = 8
32 : 4 = 8
48 : 6 = 8
24 : 3 = 8
24 mũ 4 x 3 mũ 4-32 mũ 12:4 mũ 24
mong cac ban tra loi chu minh cung muon tim ket qua cua cau nay lam
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử
a,(x+1).(x+2).(x+3).(x+4)+1
b,(x+1).(x+2).(x+3).(x+4)-24
c,(x+1).(x+3).(x+5).(x+7)+15
d,.(x+2).(x+3).(x+4).(x+5)-24
Bài làm:
a) \(\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)\left(x+4\right)+1\)
\(=\left[\left(x+1\right)\left(x+4\right)\right]\left[\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)\right]+1\)
\(=\left(x^2+5x+4\right)\left(x^2+5x+6\right)+1\)
Đặt \(x^2+5x+5=t\)\(\Rightarrow\left(t-1\right)\left(t+1\right)+1=t^2-1+1=t^2\)
\(=\left(x^2+5x+5\right)^2\)
b) Tương tự như a phân tích và đặt ra được: \(t^2-1-24=t^2-25=\left(t-5\right)\left(t+5\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2+5x\right)\left(x^2+5x+10\right)=x\left(x+5\right)\left(x^2+5x+10\right)\)
c) \(\left(x+1\right)\left(x+3\right)\left(x+5\right)\left(x+7\right)+15\)
\(=\left[\left(x+1\right)\left(x+7\right)\right]\left[\left(x+3\right)\left(x+5\right)\right]+15\)
\(=\left(x^2+8x+7\right)\left(x^2+8x+15\right)+15\)
Đặt \(x^2+8x+11=t\)\(\Rightarrow\left(t-4\right)\left(t+4\right)+15=t^2-16+15=t^2-1\)
\(=\left(t-1\right)\left(t+1\right)=\left(x^2+8x+10\right)\left(x^2+8x+12\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2+8x+10\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x+6\right)\)
d) \(\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)\left(x+4\right)\left(x+5\right)-24\)
\(=\left[\left(x+2\right)\left(x+5\right)\right]\left[\left(x+3\right)\left(x+4\right)\right]-24\)
\(=\left(x^2+7x+10\right)\left(x^2+7x+12\right)-24\)
Đặt \(x^2+7x+11=t\)\(\Rightarrow\left(t-1\right)\left(t+1\right)-24=t^2-1-24=t^2-25\)
\(=\left(t-5\right)\left(t+5\right)=\left(x^2+7x+6\right)\left(x^2+7x+16\right)\)
\(=\left(x+1\right)\left(x+6\right)\left(x^2+7x+16\right)\)
Làm mẫu cho 1 vd:
a, (x+1)(x+2)(x+3)(x+4)+1
\(=\left(x+1\right)\left(x+4\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)+1\)
\(=\left(x^2+5x+4\right)\left(x^2+5x+6\right)+1\)(1)
Đặt \(y=x^2+5x+5\)
Khi đó ::
(1) = \(\left(y-1\right)\left(y+1\right)+1\)
\(=y^2-1+1=y^2\)
Thay vào ta được: \(\left(x^2+5x+5\right)^2\)
a) (x+1)(x+2)(x+3)(x+4)+1=[(x+1)(x+4)].[(x+2)(x+3)]+1=(x2+5x+4)(x2+5x+6)+1
đặt t=x2+5x+5 ta có đa thức (t-1)(t+1)+1=t2-1+1=t2. mà t=x2+5x+5
=> (x+1)(x+2)(x+3)(x+4)+1=(x2+5x+5)2
b) (x+1)(x+2)(x+3)(x+4)-24. theo kết quả câu (a) ta được (x+1)(x+2)(x+3)(x+4)=(x2+5x+4)(x2+5x+6)
đặt t=x2+5x+5 ta có đa thức (t-1)(t+1)-24=t2-1-24=t2-25=(t-5)(t+5)
mà t=x2+5x+5 => (t-5)(t+5)=(x2+5x)(x2+5x+10)
c) (x+1)(x+3)(x+5)(x+7)+15=[(x+1)(x+7)].[(x+3)(x+5)]+15=(x2+8x+7)(x2+8x+15)+15
đặt x2+8x+11=t ta có đa thức (t-4)(t+4)+15=t2-16+15=t2-1=(t-1)(t+1)
mà t=x2+8x+11 => (t-1)(t+1)=(x2+8x-10)(x2+8x+12)
d) (x+2)(x+3)(x+4)(x+5)-24=[(x+2)(x+5)][(x+3)(x+4)]-24=(x2+7x+12)(x2+7x+10)-24
đặt t=x2+7x+11 ta có đa thức (t-1)(t+1)-24=t2-1-24=t2-25=(t+5)(t-5)
mà t=x2+7x+11 => (t-5)(t+5)=(x2+7x+6)(x2+7x+16)
giải pt
a 4(x+3)^2=(2x+6)^2
b (3x+4)^2=4(x+3)
c (6x+3)^2=(x-4)^2
d (x^2+3x+2)(x^2+3x+3)-2=0
e(x^2-5x)+10(x^2-5x)+24=0
f(x^2+x+1)(x^2+x+2)=12
gx(x+1)(x-1)(x+2)=24
h(x+1)(x+2)(x+3)(x+4)-24=0
lm giúp mik nha các bn
a) \(4\left(x+3\right)^2=\left(2x+6\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2^2\left(x+3\right)^2=\left(2x+6\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+6\right)^2=\left(2x+6\right)^2\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là \(S=ℝ\)
b) \(\left(3x+4\right)^2=4\left(x+3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x^2+24x+16=4x+12\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x^2+20x+4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(9x+2\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}9x+2=0\\x+2=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-\frac{2}{9}\\x=-2\end{cases}}\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là \(S=\left\{-\frac{2}{9};-2\right\}\)
c) \(\left(6x+3\right)^2=\left(x-4\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}6x+3=x-4\\6x+3=4-x\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}5x+7=0\\7x-1=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-\frac{7}{5}\\x=\frac{1}{7}\end{cases}}\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là \(S=\left\{-\frac{7}{5};\frac{1}{7}\right\}\)
d) \(\left(x^2+3x+2\right)\left(x^2+3x+3\right)-2=0\)
Đặt \(t=x^2+3x+2\), ta có :
\(t\left(t+1\right)-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow t^2+t-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(t+2\right)\left(t-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}t+2=0\\t-1=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x^2+3x+4=0\\x^2+3x+1=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}\left(x+\frac{3}{2}\right)^2+\frac{7}{4}=0\left(ktm\right)\\\left(x+\frac{3}{2}\right)^2-1,25=0\left(tm\right)\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\pm\sqrt{1,25}-\frac{3}{2}=-\frac{3\pm\sqrt{5}}{2}\)(tm)
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là \(S=\left\{-\frac{3\pm\sqrt{5}}{2}\right\}\)
e)Đề bài sai ! Mik sửa :
\(\left(x^2-5x\right)^2+10\left(x^2-5x\right)+24=0\)
Đặt \(t=x^2-5x\), ta có :
\(t^2+10t-24=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(t+12\right)\left(t-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}t+12=0\\t-2=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x^2-5x+12=0\\x^2-5x-2=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}\left(x-\frac{5}{2}\right)^2+\frac{23}{4}=0\left(ktm\right)\\\left(x-\frac{5}{2}\right)^2-\frac{33}{4}=0\left(tm\right)\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\pm\frac{\sqrt{33}}{2}+\frac{5}{2}\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là \(S=\left\{\frac{\sqrt{33}}{2}+\frac{5}{2};-\frac{\sqrt{33}}{2}+\frac{5}{2}\right\}\)
f) \(\left(x^2+x+1\right)\left(x^2+x+2\right)=12\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+x+1\right)\left(x^2+x+2\right)-12=0\)
Đặt \(t=x^2+x+1\), ta có :
\(t\left(t+1\right)-12=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow t^2+t-12=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(t+4\right)\left(t-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}t+4=0\\t-3=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x^2+x+5=0\\x^2+x-2=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}\left(x+\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{19}{4}=0\left(ktm\right)\\\left(x+\frac{1}{2}\right)^2-\frac{9}{4}=0\left(tm\right)\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{3}{2}-\frac{1}{2}=1\left(tm\right)\\x=-\frac{3}{2}-\frac{1}{2}=-2\left(tm\right)\end{cases}}\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là \(S=\left\{1;-2\right\}\)
g) \(x\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)=24\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+x\right)\left(x^2+x-2\right)-24=0\)
Đặt \(t=x^2+x\), ta có :
\(t\left(t-2\right)-24=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow t^2-2t-24=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(t+4\right)\left(t-6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}t+4=0\\t-6=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x^2+x+4=0\\x^2+x-6=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}\left(x+\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{15}{4}=0\left(ktm\right)\\\left(x+\frac{1}{2}\right)^2-\frac{25}{4}=0\left(tm\right)\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{5}{2}-\frac{1}{2}=2\left(tm\right)\\x=-\frac{5}{2}-\frac{1}{2}=-3\left(tm\right)\end{cases}}\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là \(S=\left\{2;-3\right\}\)
h) \(\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)\left(x+4\right)-24=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+5x+4\right)\left(x^2+5x+6\right)-24=0\)
Đặt \(t=x^2+5x+4\), ta có :
\(t\left(t+2\right)-24=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow t^2+2t-24=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(t+6\right)\left(t-4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}t+6=0\\t-4=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x^2+5x+10=0\\x^2+5x=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}\left(x+\frac{5}{2}\right)^2+\frac{15}{4}=0\left(ktm\right)\\x\left(x+5\right)=0\left(tm\right)\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\left(tm\right)\\x=-5\left(tm\right)\end{cases}}\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là \(S=\left\{0;-5\right\}\)