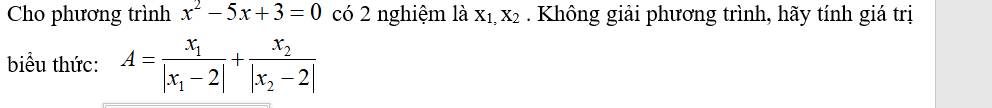Lời giải:
Áp dụng định lý Viet:
$x_1+x_2=5$
$x_1x_2=3$
Nếu cả hai số $x_1,x_2$ đều lớn hơn 2 thì $x_1x_2>4$ (vô lý)
Nếu cả hai số $x_1,x_2$ đều nhỏ hơn 2 thì $x_1+x_2< 4$ (vô lý)
Vậy trong 2 số $x_1,x_2$ tồn tại một số nhỏ hơn 2 và 1 số lớn hơn 2. Không mất tính tổng quát giả sử $x_1> 2> x_2$
Khi đó:
\(A=\frac{x_1}{x_1-2}-\frac{x_2}{x_2-2}=\frac{x_1x_2-2x_1-x_1x_2+2x_2}{(x_1-2)(x_2-2)}\\ =\frac{-2(x_1-x_2)}{x_1x_2-2(x_1+x_2)+4}\\ =\frac{-2\sqrt{(x_1+x_2)^2-4x_1x_2}}{x_1x_2-2(x_1+x_2)+4}\\ =\frac{-2\sqrt{5^2-4.3}}{3-2.5+4}=\frac{2\sqrt{13}}{3}\)
Theo hệ thức Viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=5>0\\x_1x_2=3>0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1>0\\x_2>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow A>0\)
\(x_1^2+x_2^2=\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2=19\)
\(A^2=\dfrac{x_1^2}{\left(x_1-2\right)^2}+\dfrac{x_2^2}{\left(x_2-2\right)^2}+\dfrac{2x_1x_2}{\left|\left(x_1-2\right)\left(x_2-2\right)\right|}\)
\(=\dfrac{x_1^2\left(x_2^2-4x_2+4\right)+x_2^2\left(x_1^2-4x_1+4\right)}{\left[\left(x_1-2\right)\left(x_2-2\right)\right]^2}+\dfrac{2x_1x_2}{\left|x_1x_2-2\left(x_1+x_2\right)+4\right|}\)
\(=\dfrac{2\left(x_1x_2\right)^2-4x_1x_2\left(x_1+x_2\right)+4\left(x_1^2+x_2^2\right)}{\left[x_1x_2-2\left(x_1+x_2\right)+4\right]^2}+\dfrac{2x_1x_2}{\left|x_1x_2-2\left(x_1+x_2\right)+4\right|}\)
\(=\dfrac{2.3^2-4.3.5+4.19}{\left(3-10+4\right)^2}+\dfrac{2.3}{\left|3-10+4\right|}=\dfrac{52}{9}\)
\(\Rightarrow A=\sqrt{\dfrac{52}{9}}=\dfrac{2\sqrt{13}}{3}\)