Giải phương trình
a, (x^2-2)(x^2+x+1)=0
b, 16x^2 - 8x + 5=0
c, 2x^3 - x^2 - 8x + 4=0
d, 3x^3+6x^2 - 75x -150 = 0
e, 2x^5-3x^4+6x^3-8x^2+3=0
Hỏi đáp
Giải phương trình
a, (x^2-2)(x^2+x+1)=0
b, 16x^2 - 8x + 5=0
c, 2x^3 - x^2 - 8x + 4=0
d, 3x^3+6x^2 - 75x -150 = 0
e, 2x^5-3x^4+6x^3-8x^2+3=0
*vn:vô nghiệm.
a. \(\left(x^2-2\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2-2=0\\x^2+x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left(x-\sqrt{2}\right)\left(x+\sqrt{2}\right)=0\\\left(x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}=0\left(vn\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\pm\sqrt{2}\)
-Vậy \(S=\left\{\pm\sqrt{2}\right\}\).
b. \(16x^2-8x+5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow16x^2-8x+1+4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4x-1\right)^2+4=0\) (vô lí)
-Vậy S=∅.
c. \(2x^3-x^2-8x+4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(2x-1\right)-4\left(2x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-1\right)\left(x^2-4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{1}{2}\\x=\pm2\end{matrix}\right.\)
-Vậy \(S=\left\{\dfrac{1}{2};\pm2\right\}\).
d. \(3x^3+6x^2-75x-150=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2\left(x+2\right)-75\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-25\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3\left(x+2\right)\left(x+5\right)\left(x-5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-2\\x=\pm5\end{matrix}\right.\)
-Vậy \(S=\left\{-2;\pm5\right\}\)
 giup em bai 1 cau c,d vÀ bài 2 câu b ạh....Cảm ơn ạ
giup em bai 1 cau c,d vÀ bài 2 câu b ạh....Cảm ơn ạ
1c.
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-1991}{9}-1+\dfrac{x-1993}{7}-1+...=\dfrac{x-9}{1991}-1+\dfrac{x-7}{1993}-1+...\) (dài quá làm biếng ghi hết, em cứ hiểu là trừ mỗi số hạng 2 vế cho 1)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-2000}{0}+\dfrac{x-2000}{7}+\dfrac{x-2000}{5}+\dfrac{x-2000}{3}+\dfrac{x-2000}{1}=\dfrac{x-2000}{1991}+\dfrac{x-2000}{1993}+\dfrac{x-2000}{1005}+\dfrac{x-2000}{1997}+\dfrac{x-2000}{1999}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2000\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{9}+\dfrac{1}{7}+\dfrac{1}{5}+\dfrac{1}{3}+1-\dfrac{1}{1991}-\dfrac{1}{1993}-\dfrac{1}{1995}-\dfrac{1}{1997}-\dfrac{1}{1999}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=2000\)
(do \(\dfrac{1}{9}+\dfrac{1}{7}+\dfrac{1}{5}+\dfrac{1}{3}+1-\dfrac{1}{1991}-\dfrac{1}{1993}-\dfrac{1}{1995}-\dfrac{1}{1997}-\dfrac{1}{1999}\ne0\))
d.
\(\dfrac{x-85}{15}+\dfrac{x-74}{13}+\dfrac{x-67}{11}+\dfrac{x-64}{9}=10\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-85}{15}-1+\dfrac{x-74}{13}-2+\dfrac{x-67}{11}-3+\dfrac{x-64}{9}-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-100}{15}+\dfrac{x-100}{13}+\dfrac{x-100}{11}+\dfrac{x-100}{9}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-100\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{15}+\dfrac{1}{13}+\dfrac{1}{11}+\dfrac{1}{9}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=100\)
(do \(\dfrac{1}{15}+\dfrac{1}{13}+\dfrac{1}{11}+\dfrac{1}{9}\ne0\))
2.
\(A=\dfrac{x-1}{x+1}=\dfrac{x+1-2}{x+1}=1-\dfrac{2}{x+1}\)
Do 1 nguyên nên A nguyên khi \(\dfrac{2}{x+1}\) nguyên
\(\Rightarrow x+1=Ư\left(2\right)=\left\{-2;-1;1;2\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\left\{-3;-2;0;1\right\}\)
Kết hợp ĐKXĐ \(\Rightarrow x=\left\{-3;-2;0\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{x-1}{x+2}-\dfrac{x}{x-2}+\dfrac{8}{x^2-4}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)-x\left(x+2\right)+8}{x^2-4}\left(đk:x\ne\pm2\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2-2x-x+2-x^2-2x+8}{x^2-4}\)
\(=\dfrac{-5x+10}{x^2-4}=\dfrac{-5\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=-\dfrac{5}{x+2}\)
\(\dfrac{x-1}{x+2}-\dfrac{x}{x-2}+\dfrac{8}{x^2-4}=0\left(x\ne\pm2\right)\) (do ko có kết quả nên mik nghĩ là 0)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)}{x^2-4}-\dfrac{x\left(x+2\right)}{x^2-4}+\dfrac{8}{x^4-4}=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2-2x-x+2-x^2-2x+8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-5x=-10\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=2\left(loại\right)\)
Vậy pt có \(S=\varnothing\)
giúp em với aa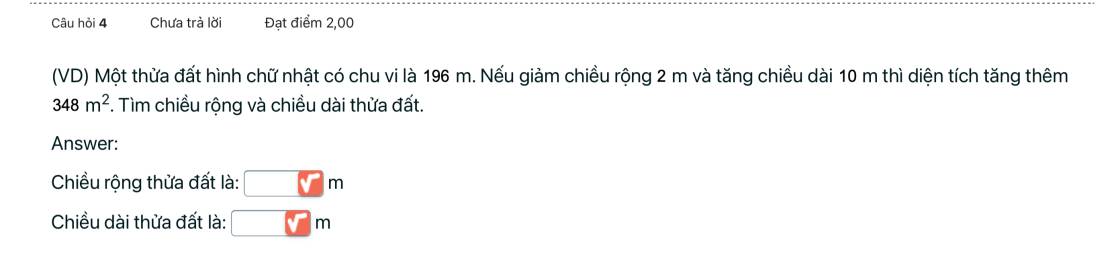
Gọi chiều rộng và chiều dài lần lượt là a,b
Theo đề, ta có: a+b=98 và (a-2)(b+10)=ab+348
=>a+b=98 và 10a-2b=368
=>a=47 và b=51
a
\(\sqrt{6}x+\sqrt{6}=\sqrt{54}+\sqrt{24}\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{6}\left(x+1\right)=\sqrt{3^2.6}+\sqrt{2^2.6}\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{6}\left(x+1\right)=3\sqrt{6}+2\sqrt{6}\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{6}\left(x+1\right)=5\sqrt{6}\\ \Leftrightarrow x+1=5\\ \Leftrightarrow x=4\)
b
\(\dfrac{x^2}{10}-\sqrt{1,21}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2}{10}-\sqrt{\left(1,1\right)^2}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2}{10}-\sqrt{\left(\dfrac{11}{10}\right)^2}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2}{10}-\dfrac{11}{10}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-11=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2=11\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\pm\sqrt{11}\)
c
ĐK: \(x\ne-1,x\ge-\dfrac{3}{4}\)
\(\sqrt{\dfrac{4x+3}{x+1}}=3\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4x+3}{x+1}=3^2=9\\ \Leftrightarrow9x+9-4x-3=0\\ \Leftrightarrow5x+6=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{6}{5}\left(nhận\right)\)
d
ĐK: \(x\ge\dfrac{3}{2}\)
\(\dfrac{\sqrt{2x-3}}{\sqrt{x-1}}=2\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\dfrac{2x-3}{x-1}}=2\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x-3}{x-1}=2^2=4\\ \Leftrightarrow4x-4-2x+3=0\\ \Leftrightarrow2x-1=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{2}\left(loại\right)\)
Vậy PT vô nghiệm
e
ĐK: \(x\ge0\)
Đặt \(t=\sqrt{x}\left(t\ge0\right)\)
Khi đó PT trở thành:
\(t^2-3t-5=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=\dfrac{\sqrt{29}+3}{2}\left(nhận\right)\\t=\dfrac{-\sqrt{29}+3}{2}\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Với \(t=\dfrac{\sqrt{29}+3}{2}\Rightarrow x=\left(\dfrac{\sqrt{29}+3}{2}\right)^2=\dfrac{19+3\sqrt{29}}{2}\) (nhận)
a: \(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{6}\left(x+1\right)=5\sqrt{6}\)
=>x+1=5
=>x=4
b: =>x^2/10=1,1
=>x^2=11
=>x=căn 11 hoặc x=-căn 11
c: =>(4x+3)/(x+1)=9 và (4x+3)/(x+1)>=0
=>4x+3=9x+9
=>-5x=6
=>x=-6/5
d: =>(2x-3)/(x-1)=4 và x-1>0 và 2x-3>=0
=>2x-3=4x-4 và x>=3/2
=->-2x=-1 và x>=3/2
=>x=1/2 và x>=3/2
=>Ko có x thỏa mãn
e: Đặt căn x=a(a>=0)
PT sẽ là a^2-a-5=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}a=\dfrac{1+\sqrt{21}}{2}\left(nhận\right)\\a=\dfrac{1-\sqrt{21}}{2}\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>x=(1+căn 21)^2/4=(11+căn 21)/2
a)(x^2 +2x+1)-x-1 trên 3=6(x+1)^2-5x-5 trên 6
b)(x-1)-2(x-1) trên 3-1 + (2x-2) trên 2
c)(x-2)^2=(2x-3)^2-(x+1)^2
d)(x-2)(x^2-3x+5)=x^2-2x^2
giúp mik nhanh vs đc mấy câu vs ak
a: \(\dfrac{\left(x^2+2x+1\right)-x-1}{3}=\dfrac{6\left(x+1\right)^2-5x-5}{6}\)
=>\(\dfrac{x^2+x}{3}=\dfrac{6\left(x^2+2x+1\right)-5x-5}{6}\)
=>\(\dfrac{2x^2+2x}{6}=\dfrac{6x^2+12x+6-5x-5}{6}\)
=>\(\dfrac{6x^2+7x+1}{6}=\dfrac{2x^2+2x}{6}\)
=>\(6x^2+7x+1=2x^2+2x\)
=>\(4x^2+5x+1=0\)
=>(x+1)(4x+1)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=-\dfrac{1}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: Đề thiếu vế phải rồi bạn
c: \(\left(x-2\right)^2=\left(2x-3\right)^2-\left(x+1\right)^2\)
=>\(\left(x-2\right)^2=\left(2x-3-x-1\right)\left(2x-3+x+1\right)\)
=>\(\left(x-2\right)^2=\left(x-4\right)\left(3x-2\right)\)
=>\(3x^2-2x-12x+8=x^2-4x+4\)
=>\(3x^2-14x+8-x^2+4x-4=0\)
=>\(2x^2-10x+4=0\)
=>\(x^2-5x+2=0\)
=>\(x=\dfrac{5\pm\sqrt{17}}{2}\)
d: Sửa đề: \(\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2-3x+5\right)=x^3-2x^2\)
=>\(\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2-3x+5\right)-x^2\left(x-2\right)=0\)
=>\(\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2-3x+5-x^2\right)=0\)
=>\(\left(x-2\right)\left(-3x+5\right)=0\)
=>(x-2)(3x-5)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=\dfrac{5}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
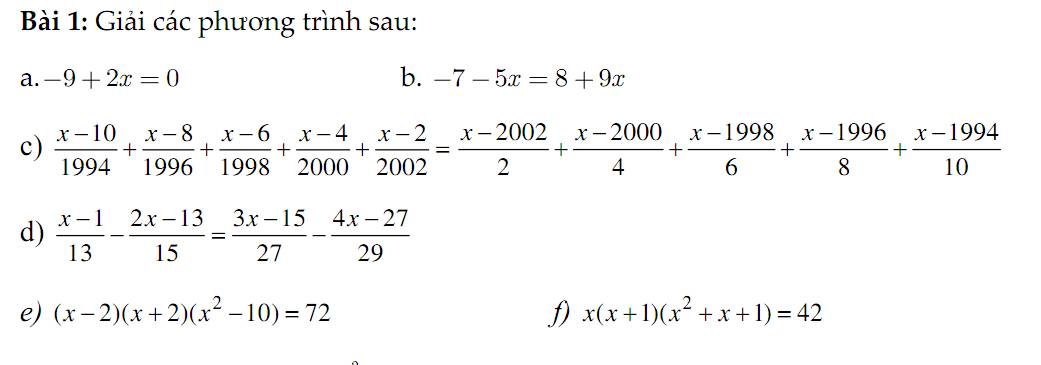 Giup em cau c,d,e và f voi ạh...Em cảm ơn ạh !!
Giup em cau c,d,e và f voi ạh...Em cảm ơn ạh !!
Câu c giống câu hồi nãy, em lần lượt trừ từng số hạng 2 vế cho 1 sẽ ra tử số giống nhau là \(x-2004\)
d.
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-1}{13}-1+\left(\dfrac{2x-13}{15}+1\right)=\dfrac{3x-15}{27}-1-\left(\dfrac{4x-27}{29}+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-14}{13}-\dfrac{2\left(x-14\right)}{15}=\dfrac{3\left(x-14\right)}{27}-\dfrac{4\left(x-14\right)}{29}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-14\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{13}-\dfrac{2}{15}-\dfrac{3}{27}+\dfrac{4}{29}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=14\)
e.
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-4\right)\left(x^2-10\right)=72\)
Đặt \(x^2-10=t\Rightarrow x^2-4=t+6\)
Pt trở thành:
\(t\left(t+6\right)=72\Leftrightarrow t^2+6t-72=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow t^2-6t+12t-72=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow t\left(t-6\right)+12\left(t-6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(t-6\right)\left(t+12\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=6\\t=-12\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2-10=6\\x^2-10=-12\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2=16\\x^2=-2\left(vô-nghiệm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\pm4\)
Câu f tương tự câu e, biến đổi thành:
\(\left(x^2+x\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)-42=0\)
Đặt \(x^2+x=t\) pt thành:
\(t\left(t+1\right)-42=0\Leftrightarrow t^2+t-42=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(t+7\right)\left(t-6\right)=0\)
Tới đây em tự giải quyết nốt
Giải phương trình \((m^2-1)x+1=m\) khi \(m=-1\)
Ta có phương trình:
\(\left(m^2-1\right)x+1=m\) (1)
Khi \(m=-1\) thì phương trình (1) trở thành:
\(\left[\left(-1\right)^2-1\right]x+1=-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(1-1\right)x+1=-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow0x+1=-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow1=-1\) (vô lý)
⇒ Phương trình vô nghiệm
Vậy: khi \(m=-1\) thì phương trình (1) vô nghiệm
Khi m=-1 thì phương trình sẽ là:
[(-1)^2-1]x+1=-1
=>0x+1=-1
=>1=-1(vô lý)
=>Phương trình vô nghiệm
y^2+5y+6=0
\(y^2+5y+6=0\\ \Leftrightarrow y^2+2y+3y+6=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(y^2+2y\right)+\left(3y+6\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow y\left(y+2\right)+3\left(y+2\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(y+3\right)\left(y+2\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}y+3=0\\y+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}y=-3\\y=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm \(S=\left\{-3;-2\right\}.\)
\(y^2+5y+6=0\\ \Leftrightarrow y^2+3y+2y+6=0\\ \Leftrightarrow y\left(y+3\right)+2\left(y+3\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(y+2\right).\left(y+3\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}y+2=0\\y+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}y=-2\\y=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy pt có tập nghiệm A={-2;-3}
c: =>4y^2-4y+1=0
=>(2y-1)^2=0
=>2y-1=0
=>y=1/2
d: =>y^2-2y-80=0
=>(y-10)(y+8)=0
=>y=10 hoặc y=-8