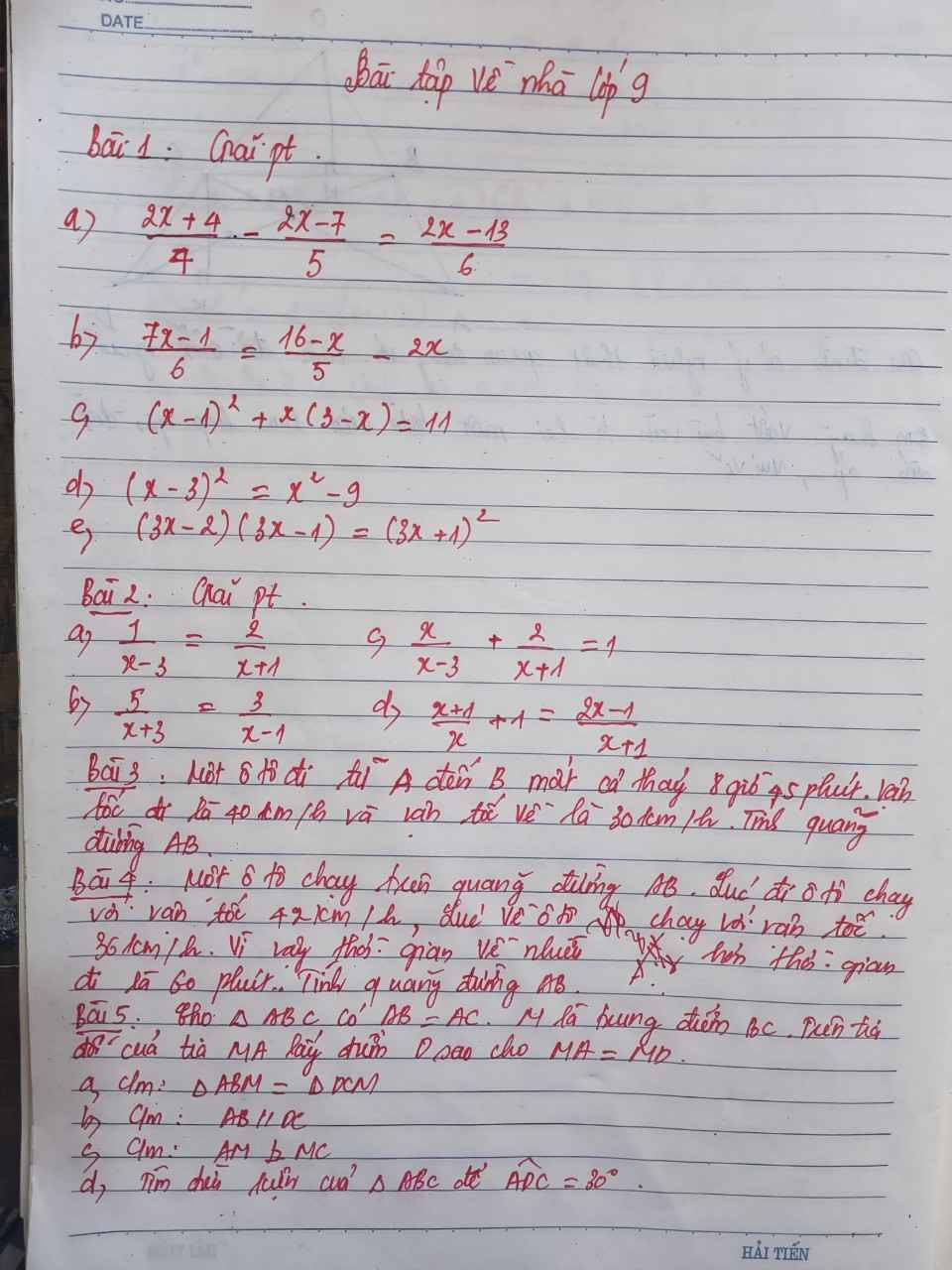Bài 1
a) \(\dfrac{2x+4}{4}-\dfrac{2x-7}{5}=\dfrac{2x-13}{6}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow15.\left(2x+4\right)-12.\left(2x-7\right)=10.\left(2x-13\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow30x+60-24x+84=20x-130\)
\(\Leftrightarrow30x-24x-20x=-130-60-84\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-14x=-274\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{274}{14}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{137}{7}\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{\dfrac{137}{7}\right\}\)
b) \(\dfrac{7x-1}{6}=\dfrac{16-x}{5}-2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5.\left(7x-1\right)=6.\left(16-x\right)-30.2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow35x-5=96-6x-60x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow35x+6x+60x=96+5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow101x=101\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{101}{101}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=1\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{1\right\}\)
c) \(\left(x-1\right)^2+x\left(3-x\right)=11\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x+1+3x-x^2=11\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=11-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=10\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{10\right\}\)
d) \(\left(x-3\right)^2=x^2-9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-6x+9=x^2-9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-6x-x^2=-9-9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-6x=-18\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{18}{6}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=3\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{3\right\}\)
e) \(\left(3x-2\right)\left(3x-1\right)=\left(3x+1\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x^2-3x-6x+2=9x^2+6x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x^2-3x-6x-9x^2-6x=1-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-15x=-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{15}\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{\dfrac{1}{15}\right\}\)
Bài 2:
a) \(\dfrac{1}{x-3}=\dfrac{2}{x+1}\) (1)
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne3;x\ne-1\)
\(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow x+1=2.\left(x-3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+1=2x-6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-2x=-6-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x=-7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=7\) (nhận)
Vậy \(S=\left\{7\right\}\)
b) \(\dfrac{5}{x+3}=\dfrac{3}{x-1}\) (2)
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne-3;x\ne1\)
\(\left(2\right)\Leftrightarrow5.\left(x-1\right)=3.\left(x+3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x-5=3x+9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x-3x=9+5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=14\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{14}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=7\) (nhận)
Vậy \(S=\left\{7\right\}\)
c) \(\dfrac{x}{x-3}+\dfrac{2}{x+1}=1\) (3)
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne3;x\ne-1\)
\(\left(3\right)\Leftrightarrow x.\left(x+1\right)+2.\left(x-3\right)=\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x+2x-6=x^2-3x+x-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x+2x-x^2+3x-x=-3+6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{3}{5}\) (nhận)
Vậy \(S=\left\{\dfrac{3}{5}\right\}\)
d) \(\dfrac{x+1}{x}+1=\dfrac{2x-1}{x+1}\) (4)
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne0;x\ne-1\)
\(\left(4\right)\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x+1\right)+x\left(x+1\right)=\left(2x-1\right).x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x+1+x^2+x=2x^2-x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x+x^2+x-2x^2+x=-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{4}\) (nhận)
Vậy \(S=\left\{-\dfrac{1}{4}\right\}\)
Bài 3:
Gọi \(x\left(km\right)\) là độ dài quãng đường AB \(\left(x>0\right)\)
Thời gian lúc đi: \(\dfrac{x}{42}\left(h\right)\)
Thời gian lúc về: \(\dfrac{x}{30}\left(h\right)\)
Đổi \(8h45'=\dfrac{35}{4}\left(h\right)\)
Theo đề bài, ta có phương trình:
\(\dfrac{x}{42}+\dfrac{x}{30}=\dfrac{35}{4}\)
\(10x+14x=35.105\)
\(24x=3675\)
\(x=\dfrac{3675}{24}\)
\(x=153,125\) (nhận)
Vậy độ dài quãng đường AB là 153,125 km
Bài 4:
Gọi \(x\left(km\right)\) là độ dài quãng đường AB \(\left(x>0\right)\)
Thời gian lúc đi: \(\dfrac{x}{42}\left(h\right)\)
Thời gian lúc về: \(\dfrac{x}{36}\left(h\right)\)
Đổi 60 phút = 1 giờ
Theo đề bài, ta có phương trình:
\(\dfrac{x}{36}-\dfrac{x}{42}=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow7x-6x=252\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=252\) (nhận)
Vậy quãng đường AB dài 252 km