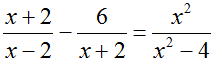\(a,3x-12=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=12\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=4\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{4\right\}\)
\(b,\left(x-2\right)\left(3x+3\right)=0\)
\(\cdot TH1:x-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
\(\cdot TH2:3x+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-1\)
vậy \(S=\left\{-1;2\right\}\)
\(c,\dfrac{x+2}{x-2}-\dfrac{6}{x+2}=\dfrac{x^2}{x^2-4}\left(ĐKXĐ:x\ne2;x\ne-2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(x+2\right)-6\left(x-2\right)=x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x+2x+4-6x+12=x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-x^2+2x+2x-6x+4+12=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x+16=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x=-16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=8\left(nhận\right)\)
Vậy S\(S=\left\{8\right\}\)
a) 3x-12=0
⟺3x=12⟺x=4
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là S={4}
b) (x-2)(3x+3)=0
⟺ x-2=0 ⟺x=2 ⟺x=2
3x+3=0 ⟺3x=-3 ⟺x=-1
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là S={2;-1}
c)
x-2≠0 x-2≠0 x≠2
ĐKXĐ x+2≠0 ⟺ x+2≠0 ⟺ x ≠-2
x2-4=(x-2)(x+2)≠0
x+2/x-2 - 6/x+2 = x2/x2-4
⟺ (x+2)(x+2)/(x-2)(x+2) - 6(x-2)/(x-2)(x+2) = x2/(x-2)(x+2)
⟺(x+2)(x+2) - 6(x-2)=x2
⟺(x+2)(x+2-6)=x2
⟺(x+2)(x-4)-x2=0
⟺x2-4x+2x-8-x2=0
⟺-2x-8=0
⟺-2x=8
⟺x=-4
Vập tập nghiệm của phương trình là S={-4}