Điều kiện: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+y\ne0\\x-y\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đặt: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x+y}=a\\\dfrac{1}{x-y}=b\end{matrix}\right.\), ta được:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a+b=\dfrac{5}{8}\\a-b=-\dfrac{3}{8}\end{matrix}\right.=>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2b=1\\a+b=\dfrac{5}{8}\end{matrix}\right.=>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}b=\dfrac{1}{2}\\a=\dfrac{1}{8}\end{matrix}\right.\)
`=> ` \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x+y}=\dfrac{1}{8}\\\dfrac{1}{x-y}=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\) => \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+y=8\\x-y=2\end{matrix}\right.=>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x=10\\x+y=8\end{matrix}\right.=>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\y=3\end{matrix}\right.\) (Tm)
Vậy `(x;y) = (5;3)`

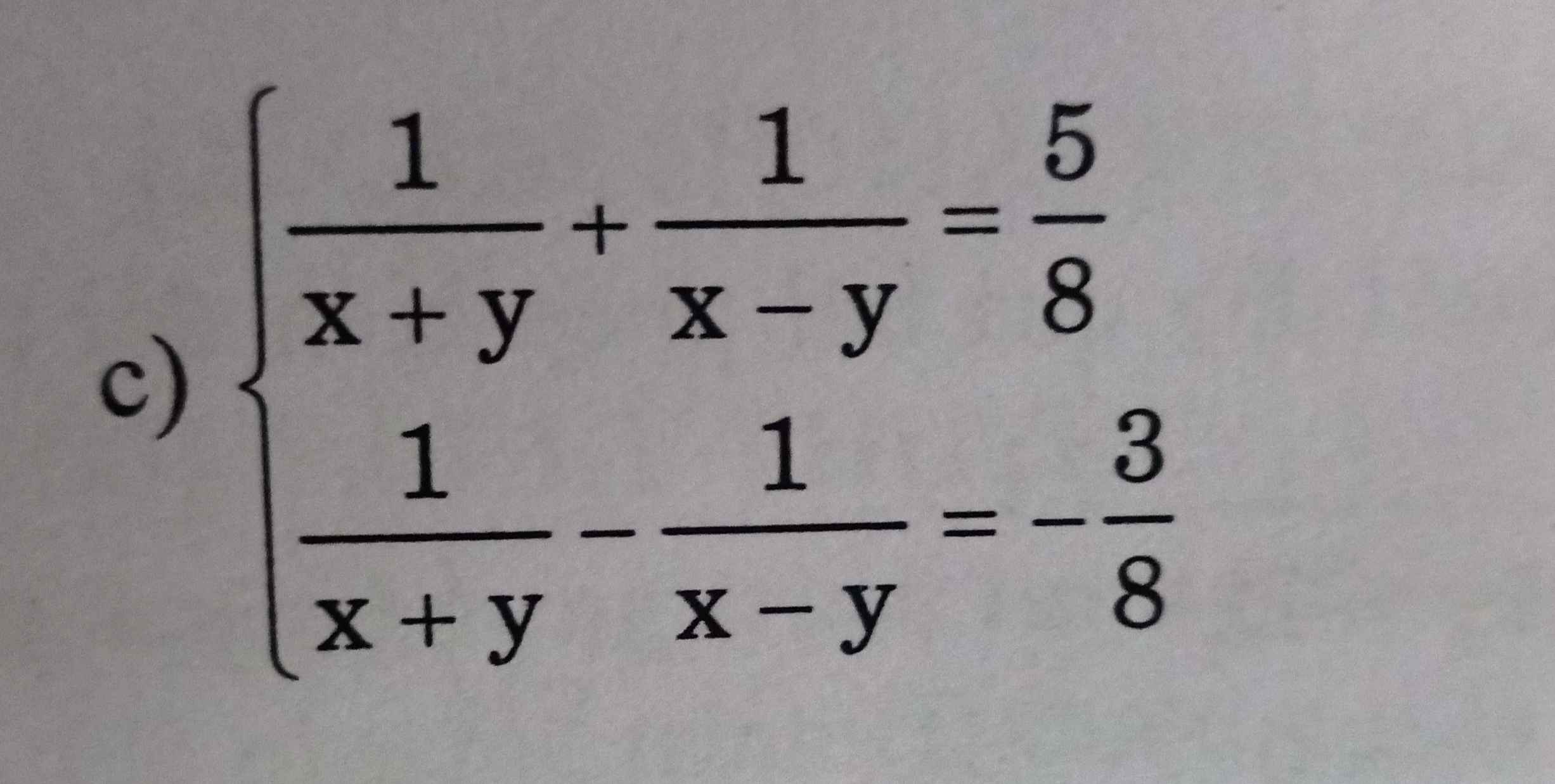




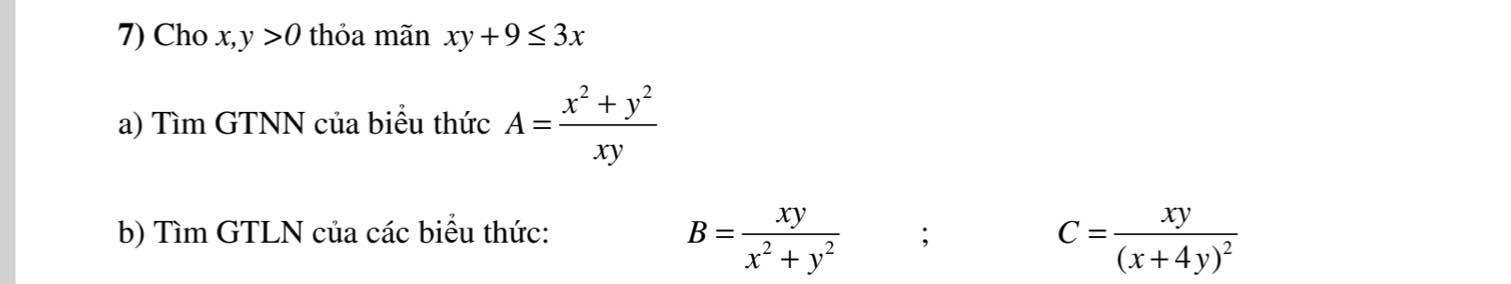 mọi người giúp em 2 ý này với ạ, em rất cảm ơn ạ 🥺
mọi người giúp em 2 ý này với ạ, em rất cảm ơn ạ 🥺