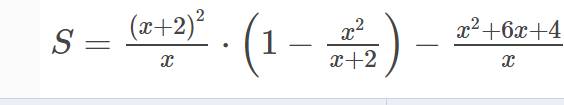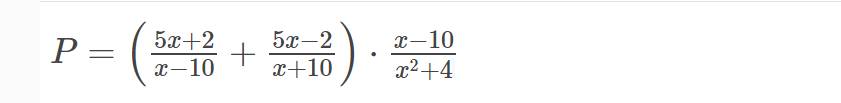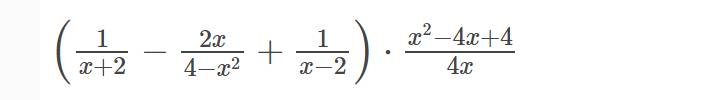a) ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne0;x\ne-2\)
b) \(S=\dfrac{\left(x+2\right)^2}{x}\cdot\left(1-\dfrac{x^2}{x+2}\right)-\dfrac{x^2+6x+4}{x}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x+2\right)^2}{x}\cdot\dfrac{x+2-x^2}{x+2}-\dfrac{x^2+6x+4}{x}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+2-x^2\right)}{x}-\dfrac{x^2+6x+4}{x}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2+2x-x^3+2x+4-2x^2-x^2-6x-4}{x}\)
\(=\dfrac{-x^3-2x^2-2x}{x}\)
\(=\dfrac{x\left(-x^2-2x-2\right)}{x}\)
\(=-x^2-2x-2\)
Với \(x=0\Rightarrow\) loại
Với \(x=1\), thay vào \(S\) ta được
\(S=-1^2-2\cdot1-2=-5\)
c) Có: \(S=-x^2-2x-2\)
\(=-\left(x^2+2x+2\right)\)
\(=-\left(x^2+2x+1\right)-1\)
\(=-\left(x+1\right)^2-1\)
Ta thấy: \(\left(x+1\right)^2\ge0\forall x\ne0;x\ne-2\)
\(\Rightarrow-\left(x+1\right)^2\le0\forall x\ne0;x\ne-2\)
\(\Rightarrow S=-\left(x+1\right)^2-1\le-1\forall x\ne0;x\ne-2\)
Dấu \("="\) xảy ra khi: \(x+1=0\Leftrightarrow x=-1\left(tmdk\right)\)
\(\text{#}\mathit{Toru}\)