a) 5x - 3 = 7 +3x
⇔ 5x - 3x = 7 + 3
⇔ 2x = 10
⇔ x = 5
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S = {5}
b) \(\dfrac{2}{x-1}\) - \(\dfrac{3x+1}{x^2-x}\) = \(\dfrac{1}{x}\) ĐKXĐ: x ≠ 1 và x ≠ 0
⇔ \(\dfrac{2}{x-1}\) - \(\dfrac{3x+1}{x\left(x-1\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{1}{x}\)
⇔ \(\dfrac{2x}{x\left(x-1\right)}\) - \(\dfrac{3x+1}{x\left(x-1\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{x-1}{x\left(x-1\right)}\)
⇒ 2x - 3x - 1 = x - 1
⇔ 2x - 3x - x = -1 + 1
⇔ -2x = 0
⇔ x = 0 (Loại)
Vậy phương trình vô nghiệm
c) | x - 5 | = 2x + 3 ĐKXĐ: 2x + 3 ≥ 0 ⇔ 2x ≥ -3 ⇔x ≥ \(\dfrac{-3}{2}\)
⇔ x - 5 = 2x +3 ⇔ x - 2x = 3 + 5 ⇔ -x = 8 ⇔ x = -8 (Loại)
hoặc
⇔ x - 5 = -2x -3 ⇔ x +2x = -3 + 5 ⇔ 3x = 2 ⇔ x = \(\dfrac{2}{3}\)(TM)
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S = {\(\dfrac{2}{3}\)}

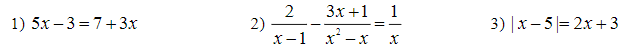












 giúp mình với ạ, mình cần gấp lắm ạ
giúp mình với ạ, mình cần gấp lắm ạ




