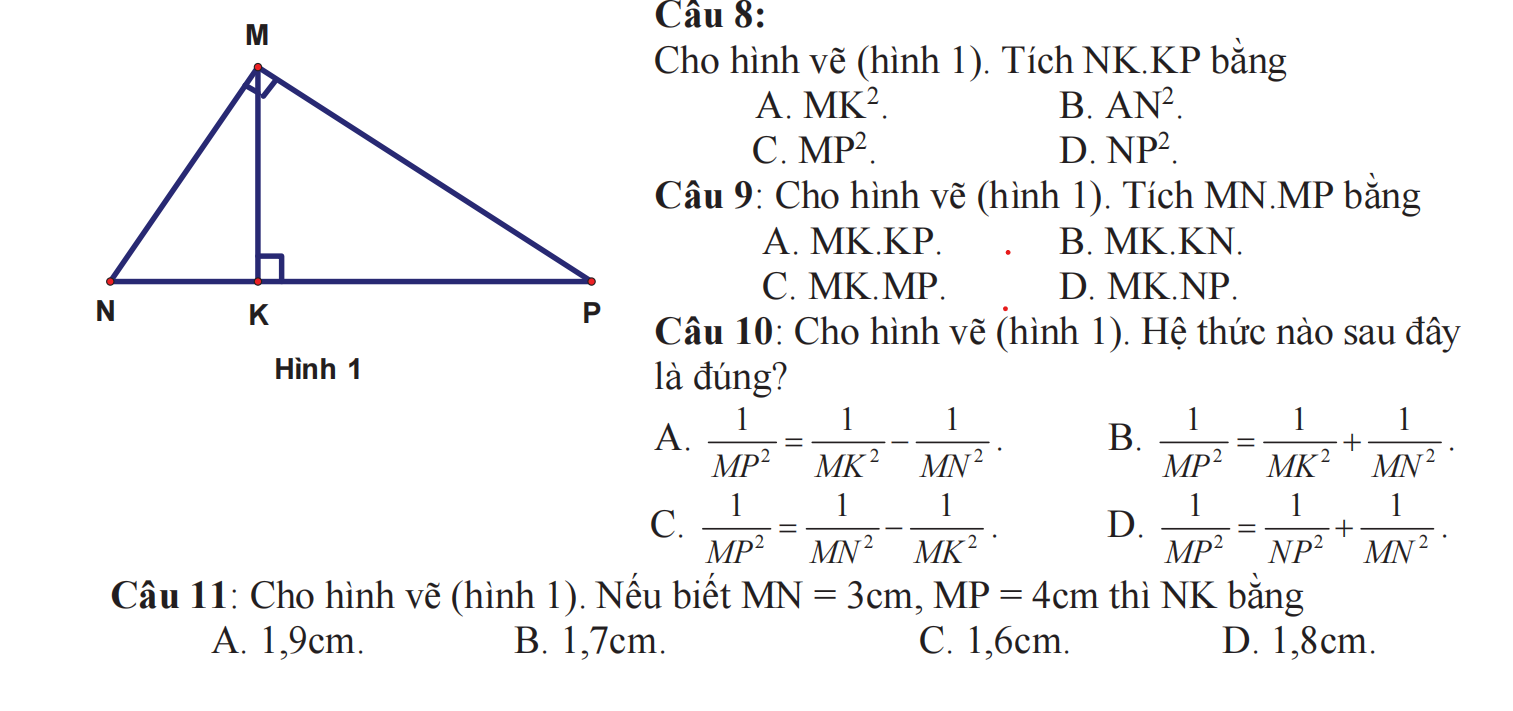
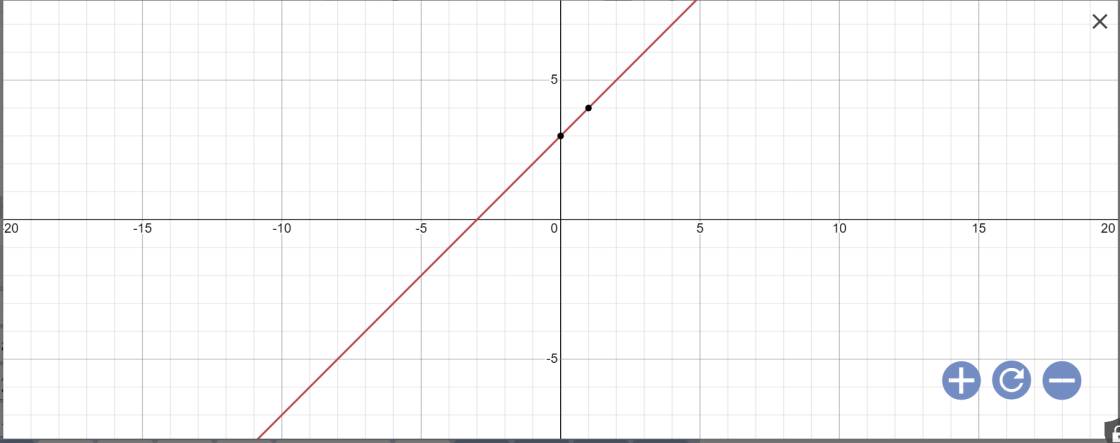
1: Thay m=3 vào y=(m-2)x+3, ta được:
\(y=\left(3-2\right)x+3=x+3\)
Vẽ đồ thị:
2: Để (d1) và (d2) cắt nhau tại một điểm trên trục tung thì:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m-2\ne-1\\m^2+2=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m\ne1\\m^2=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>m=-1
3: (d1): y=(m-2)x+3
=>(m-2)x-y+3=0
\(d\left(O;\left(d1\right)\right)=\dfrac{\left|0\left(m-1\right)+0\left(-1\right)+3\right|}{\sqrt{\left(m-2\right)^2+\left(-1\right)^2}}=\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{\left(m-2\right)^2+1}}\)
Để \(d\left(O;\left(d1\right)\right)=\dfrac{3}{2}\) thì \(\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{\left(m-2\right)^2+1}}=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
=>\(\sqrt{\left(m-2\right)^2+1}=2\)
=>\(\left(m-2\right)^2+1=4\)
=>\(\left(m-2\right)^2=3\)
=>\(m-2=\pm\sqrt{3}\)
=>\(m=2\pm\sqrt{3}\)