2: tọa độ A là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\y=2x+m-5=2\cdot0+m-5=m-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: A(0;m-5)
Tọa độ B là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\2x+m-5=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\2x=-m+5\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{-m+5}{2}\\y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(B\left(\dfrac{-m+5}{2};0\right)\)
\(OA=\sqrt{\left(0-0\right)^2+\left(m-5-0\right)^2}=\sqrt{\left(m-5\right)^2}=\left|m-5\right|\)
\(OB=\sqrt{\left(\dfrac{-m+5}{2}-0\right)^2+\left(0-0\right)^2}=\sqrt{\left(\dfrac{m-5}{2}\right)^2}=\dfrac{\left|m-5\right|}{2}\)
Ta có: Ox\(\perp\)Oy
=>OA\(\perp\)OB
=>\(S_{OAB}=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot AO\cdot OB=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot\dfrac{\left|m-5\right|}{2}\cdot\left|m-5\right|=\dfrac{\left(m-5\right)^2}{4}\)
Để \(S_{AOB}=9\) thì \(\dfrac{\left(m-5\right)^2}{4}=9\)
=>\(\left(m-5\right)^2=36\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}m-5=6\\m-5=-6\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=11\\m=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
1:
a: 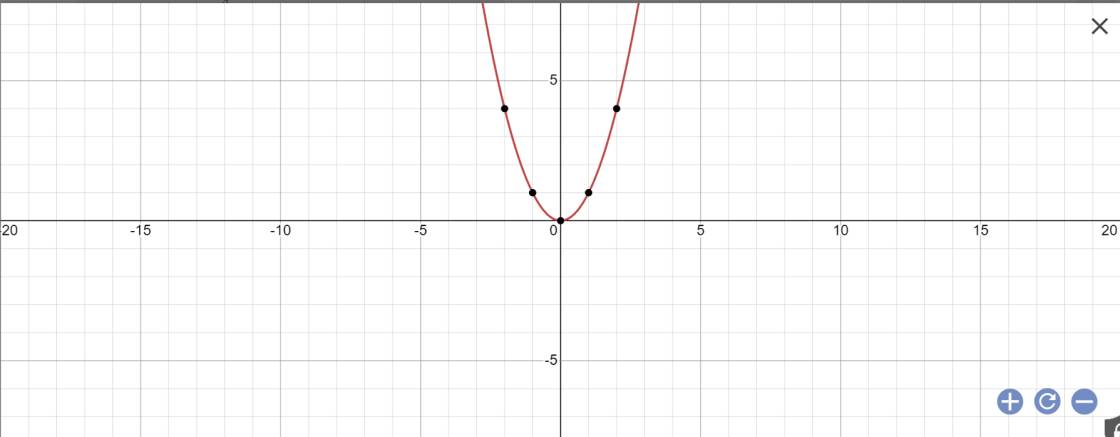
b: Thay x=-5 và y=a vào \(y=x^2\) , ta được:
\(a=\left(-5\right)^2=25\)






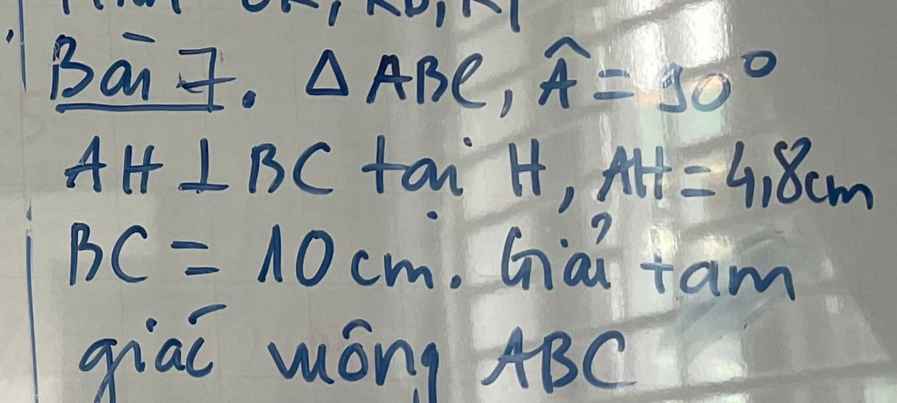













 em cần giải gấp bài 2 ạ, mọi người giúp em với ạ
em cần giải gấp bài 2 ạ, mọi người giúp em với ạ


