1:
a: Khi m=-2 thì phương trình sẽ trở thành:
\(x^2+2x-2-1=0\)
=>\(x^2+2x-3=0\)
=>(x+3)(x-1)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+3=0\\x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: \(x^2+2x+m-1=0\)
\(\text{Δ}=2^2-4\left(m-1\right)=4-4m+4=-4m+8\)
Để phương trình có hai nghiệm thì -4m+8>=0
=>-4m>=-8
=>m<=2
Theo Vi-et, ta có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-2\\x_1\cdot x_2=m-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
mà \(x_1+2x_2=1\)
nên ta có hệ phương trình:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-2\\x_1+2x_2=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-x_2=-3\\x_1+x_2=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_2=3\\x_1=-2-x_2=-2-3=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x_1\cdot x_2=m-1\)
=>\(m-1=3\cdot\left(-5\right)=-15\)
=>m=-15+1=-14

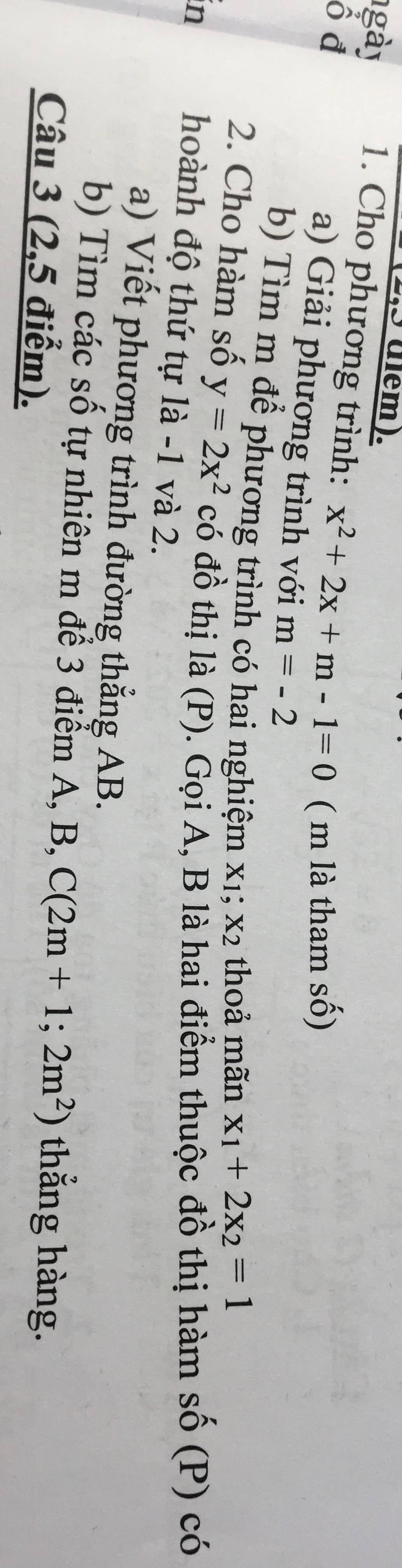












 Giúp em giải bài tập này với ạ. Em cảm ơn.
Giúp em giải bài tập này với ạ. Em cảm ơn.


