Tứ giác DNHM là hình chữ nhật \(\Rightarrow\widehat{DMN}=\widehat{DHN}\)
Mà \(\widehat{DHN}=\widehat{DCA}\) (cùng phụ \(\widehat{HDN}\))
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{DMN}=\widehat{DCA}\)
\(\Rightarrow\Delta_VMDN\sim\Delta_VCDA\left(g.g\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{DM}{DC}=\dfrac{DN}{DA}=\dfrac{DH}{AC}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{S_{BAC}}{S_{DMN}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}AB.BC}{\dfrac{1}{2}DM.DN}=\dfrac{DC.DA}{DM.DN}=\left(\dfrac{AC}{DH}\right)^2=\dfrac{AC^2}{DH^2}\)
Trong tam giác vuông ADC với đường cao DH, áp dụng hệ thức lượng:
\(\dfrac{1}{DH^2}=\dfrac{1}{DA^2}+\dfrac{1}{DC^2}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{S_{BAC}}{S_{DMN}}=AC^2\left(\dfrac{1}{DA^2}+\dfrac{1}{DC^2}\right)\) (1)
Lại có: \(\widehat{HDC}=\widehat{DAC}\) (cùng phụ \(\widehat{DCA}\))
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{sin^2\widehat{DAC}}+\dfrac{1}{cos^2\widehat{HDC}}=\dfrac{1}{sin^2\widehat{DAC}}+\dfrac{1}{cos^2\widehat{DAC}}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{\left(\dfrac{DC}{AC}\right)^2}+\dfrac{1}{\left(\dfrac{DA}{AC}\right)^2}=AC^2\left(\dfrac{1}{DC^2}+\dfrac{1}{DA^2}\right)\) (2)
(1);'(2) \(\Rightarrow\dfrac{S_{BAC}}{S_{DMN}}=\dfrac{1}{sin^2\widehat{DAC}}+\dfrac{1}{cos^2\widehat{HDC}}\)






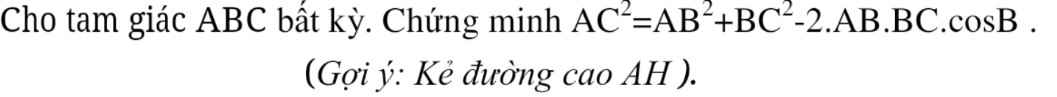

 Ai chỉ em với câu c với khó quá huhu
Ai chỉ em với câu c với khó quá huhu 


 bài 4 câu c thôi ạ
bài 4 câu c thôi ạ

 Mn giúp có thể giúp mình câu C bài 4 và bài 5 được ko ạ, giải chi tiết 1 chút với ạ. Mình cảm ơn
Mn giúp có thể giúp mình câu C bài 4 và bài 5 được ko ạ, giải chi tiết 1 chút với ạ. Mình cảm ơn


