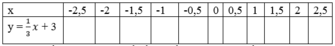
Bài 1:
Hàm số y=(m-3)x+4 đồng biến trên R khi m-3>0
=>m>3
Hàm số y=(m-3)x+4 nghịch biến trên R khi m-3<0
=>m<3
Bài 4:
a: Vì \(a=3-\sqrt{2}>0\)
nên hàm số \(y=\left(3-\sqrt{2}\right)x+1\) đồng biến trên R
b: Khi x=0 thì \(y=0\left(3-\sqrt{2}\right)+1=1\)
Khi x=1 thì \(y=\left(3-\sqrt{2}\right)\cdot1+1=3-\sqrt{2}+1=4-\sqrt{2}\)
Khi \(x=\sqrt{2}\) thì \(y=\left(3-\sqrt{2}\right)\cdot\sqrt{2}+1=3\sqrt{2}-2+1=3\sqrt{2}-1\)
Khi \(x=3+\sqrt{2}\) thì \(y=\left(3-\sqrt{2}\right)\left(3+\sqrt{2}\right)-1\)
=9-4-1
=9-5
=4
Khi \(x=3-\sqrt{2}\) thì \(y=\left(3-\sqrt{2}\right)^2-1\)
\(=11-6\sqrt{2}-1=10-6\sqrt{2}\)