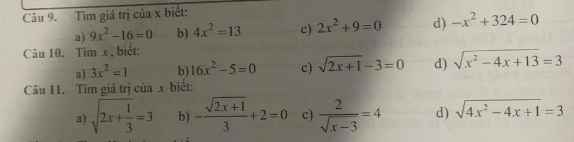Câu I:
1) Khi x = 9 => A = \(\dfrac{\sqrt{9}+3}{\sqrt{9}-4}=\dfrac{3+3}{3-4}=\dfrac{6}{-1}=-6\)
2) B = \(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+3}{\sqrt{x}+4}+\dfrac{5\sqrt{x}+12}{x-16}\) = \(\dfrac{x-\sqrt{x}-12+5\sqrt{x}+12}{x-16}\)
\(=\dfrac{x+4\sqrt{x}}{x-16}\)
= \(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-4}\)
3) Ta có: A.B = \(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+3}{\sqrt{x}-4}\).\(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-4}\)= \(\dfrac{x+3\sqrt{x}}{x-8\sqrt{x}+16}\) = m + 1
=> (m + 1)x - 8(m + 1)\(\sqrt{x}\) + 16(m + 1) = x + 3\(\sqrt{x}\)
⇔ mx - 8(m - 2)\(\sqrt{x}\) + 16(m + 1) = 0
Phương trình có nghiệm ⇔ △' ≥ 0
⇔ 16(m - 2)2 - 16m(m + 1) ≥ 0
⇔ 16m2 - 64m + 64 - 16m2 - 16m ≥ 0
⇔ 64 - 80m ≥ 0 ⇔ x ≤ 0,8
Câu II:
1) a) Với x = 1 => 1 - 2 - m2 + 2m = 0 ⇔ m = 1
Với m = 1, phương trình trở thành: x2 - 2x + 1 = 0
Ta có: △' = 1 - 1 = 0 => phương trình có nghiệm kép x1 = x2 = 1
b) Xét phương trình x2 - 2x - m2 + 2m = 0
Phương trình có 2 nghiệm phân biệt ⇔ △' > 0
⇔ 1 + m2 - 2m > 0
⇔ (m - 1)2 > 0 ⇔ m \(\ne\) 1
Theo hệ thức Viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2\left(1\right)\\x_1.x_2=-m^2+2m\end{matrix}\right.\)
=> x12 - x22 = (x1 - x2)(x1 + x2) = 6
=> 2(x1 - x2) = 6 => x1 - x2 = 3 (2)
Cộng các vế của (1) và (2) => 2x1 = 5 => x1 = 2,5 => x2 = -0,5
=> x1.x2 = -m2 + 2m = -0,5.2,5 = -1,25
=> m2 - 2m - 1,25 = 0
=> m ∈ {\(\dfrac{5}{2};\dfrac{-1}{2}\)} (t/m)
2) a) Xét phương tình hoành độ giao điểm của (d) và (d'):
x + 1 = 2x - 2m - 1
⇔ x = 2m + 2 => y = 2m + 3
Do (d) cắt (d') tại điểm thuộc góc phần tư thứ II
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2m+2< 0\\2m+3>0\end{matrix}\right.\)⇔\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m< -1\\m>-\dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\) ⇔ \(-\dfrac{3}{2}\) < m < -1
b) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(x+1\right)\left(y-1\right)=xy+4\\\left(2x-4\right)\left(y+1\right)=2xy+5\end{matrix}\right.\) ⇔ \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}xy-x+y-1=xy+4\\2xy+2x-4y-4=2xy+5\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇔ \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-x+y=5\\2x-4y=9\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇔ \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-2x+2y=10\\2x-4y=9\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇔ \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-x+y=5\\-2y=19\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{29}{2}\\y=-\dfrac{19}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy (x, y) ∈ {(\(\dfrac{-29}{2},\dfrac{-19}{2}\))}