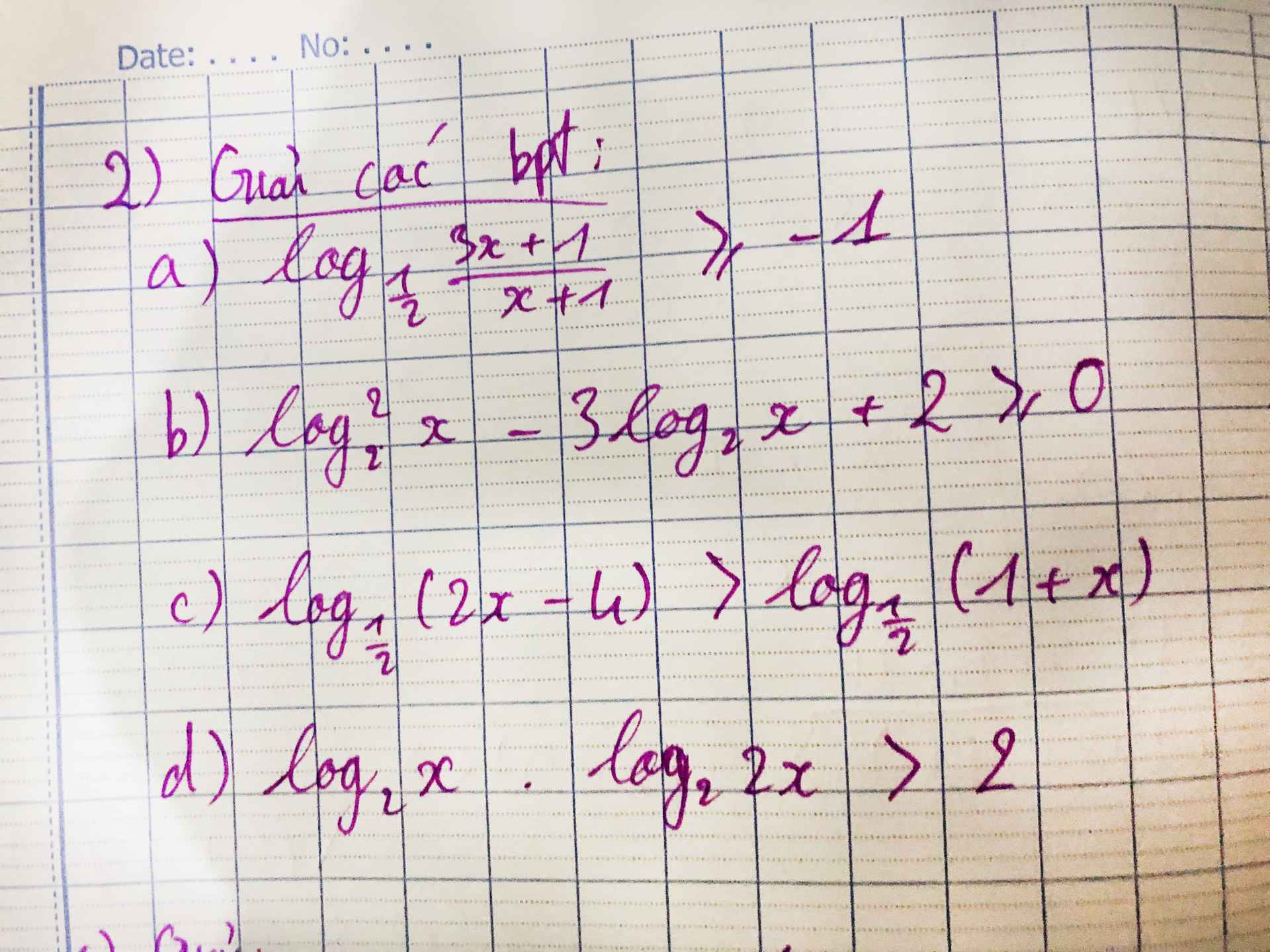Bài 6: Bất phương trình mũ và logarit
1. ĐKXĐ: \(x>\dfrac{4}{3}\)
\(log_2\left(3x-4\right)< 2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow log_2\left(3x-4\right)< log_24\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-4< 4\)
\(\Rightarrow x< \dfrac{8}{3}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{4}{3}< x< \dfrac{8}{3}\)
b.
ĐKXĐ: \(x>\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(log_{0,3}\left(x+1\right)>log_{0,3}\left(4x-2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+1< 4x-2\) (do \(0,3< 1\) )
\(\Leftrightarrow x>1\)
Vậy \(x>1\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
3.
ĐKXĐ: \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}-3< x< 1\\x>3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(log\left(x^2-4x+3\right)>log\left(x+3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-4x+3>x+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-5x>0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>5\\x< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Kết hợp ĐKXĐ: \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}-3< x< 0\\x>5\end{matrix}\right.\)
4.
ĐKXĐ: \(\dfrac{3}{2}< x< 2\)
\(ln\left(4-x^2\right)\le ln\left(2x-3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4-x^2\le2x-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x-7\ge0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\ge-1+2\sqrt{2}\\x\le-1-2\sqrt{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Kết hợp ĐKXĐ: \(\Rightarrow-1+2\sqrt{2}\le x< 2\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
\(\log_3^2x^5-25log_3x^2-750\le0\)
ĐKXĐ: \(x>0\)
\(\left(log_3x^5\right)^2-25.2.log_3x-750\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(5log_3x\right)^2-50log_3x-750\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow25log_3^2x-50log_3x-750\le0\)
Đặt \(log_3x=t\)
\(\Rightarrow25t^2-50t-750\le0\)
\(\Rightarrow1-\sqrt{31}\le t\le1+\sqrt{31}\)
\(\Rightarrow1-\sqrt{31}\le log_3x\le1+\sqrt{31}\)
\(\Rightarrow3^{1-\sqrt{31}}\le x\le3^{1+\sqrt{31}}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
log3x < 2
ĐKXĐ: \(x>0\)
\(log_3x< 2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow log_3x< log_39\)
\(\Rightarrow x< 9\)
Kết hợp ĐKXĐ ta được: \(0< x< 9\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải bất phương trình: \(x\left(3log_2x-2\right)>9log_2x-2\)
Tập nghiệm của bất pt \(\log_{\dfrac{1}{2}}\left(x+1\right)-log_{\dfrac{1}{2}}\left(2x-1\right)< 2\)
ĐKXĐ: \(x>\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(log_{\dfrac{1}{2}}\left(\dfrac{x+1}{2x-1}\right)< 2\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{x+1}{2x-1}>\dfrac{1}{4}\)
\(\Rightarrow x>-\dfrac{5}{2}\)
Kết hợp ĐKXĐ: \(\Rightarrow x>\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải pt \(\log_2^2x-log_24x+2=0\)
ĐKXĐ: \(x>0\)
\(log_2^2x-log_2x-log_24+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow log_2^2x-log_2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow log_2x\left(log_2x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}log_2x=0\\log_2x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)