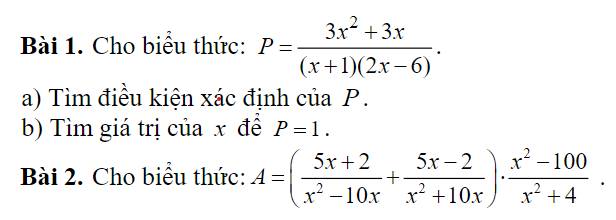Bài 1 :
\(a,P=\dfrac{3x^2+3x}{\left(x+1\right)\left(2x-6\right)}\left(dkxd:x\ne-1;3\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{3x\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x+1\right)\left(2x-6\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{3x}{2x-6}\)
Để P = 1 thì :
\(\dfrac{3x}{2x-6}=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3x-2x+6}{2x-6}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-6\)
Bài 1 :
a) ĐKXĐ : `x \ne -1 ; x \ne 3`
b)
`P = ( 3x^2 + 3x )/((x+1)(2x-6))`
`P=(3x( x + 1 ))/((x+1)(2x-6))`
`P=(3x)/(2x-6)`
Để `P = 1 <=> (3x)/(2x-6)=1`
`<=> 3x=2x-6`
`<=> 2x-3x=6`
`<=> -x=6`
`<=> x=-6` ( tm )
Vậy `x=-6`
a, ĐKXĐ:
x+1≠0 => x≠-1
2x-6≠0 => x≠-3
b, P=\(\dfrac{3x^2+3x}{\left(x+1\right)\left(2x-6\right)}\) => P=\(\dfrac{3x\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x+1\right)\left(2x-6\right)}\)
=>P=\(\dfrac{3x}{2x-6}\)
Ta có: P=1
=>\(\dfrac{3x}{2x-6}\)=1
=>3x=2x-6
=>3x-2x=-6
=>x=-6
Vậy x=-6 để P=1