Tính đạo hàm của hàm số y = 3 1 + x
A. y ' = 1 + x .3 x
B. y ' = 3.3 x . ln 3
C. y ' = 3 ln 3 .3 x
D. y ' = 3 1 + x . ln 3 1 + x
Bài 1: Xét tính đơn điệu của hàm số \(y=f(x)\) khi biết đạo hàm của hàm số là:
a) \(f'(x)=(x+1)(1-x^2)(2x-1)^3\)
b) \(f'(x)=(x+2)(x-3)^2(x-4)^3\)
Bài 2: Cho hàm số \(y=f(x)\) có đạo hàm \(f'(x)=x(x+1)(x-2)\). Xét tính biến thiên của hàm số:
a) \(y=f(2-3x)\)
b) \(y=f(x^2+1)\)
c) \(y=f(3x+1)\)
a) Tính đạo hàm của hàm số \(y = {x^3}\) tại điểm x bất kì.
b) Dự đoán công thức đạo hàm của hàm số \(y = {x^n}\left( {n \in {\mathbb{N}^*}} \right)\)
a) Với \({x_0}\) bất kì, ta có:
\(f'\left( {{x_0}} \right) = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {x_0}} \frac{{f\left( x \right) - f\left( {{x_0}} \right)}}{{x - {x_0}}} = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {x_0}} \frac{{{x^3} - x_0^3}}{{x - {x_0}}}\\ = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {x_0}} \frac{{\left( {x - {x_0}} \right)\left( {{x^2} + x{x_0} + x_0^2} \right)}}{{x - {x_0}}} = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {x_0}} \left( {{x^2} + x{x_0} + x_0^2} \right) = 3x_0^2\)
Vậy hàm số \(y = {x^3}\) có đạo hàm là hàm số \(y' = 3{x^2}\)
b) \(y' = \left( {{x^n}} \right)' = n{x^{n - 1}}\)
Cho hàm số \(y = {x^{22}}\)
a) Tính đạo hàm của hàm số trên tại điểm x bất kì
b) Tính đạo hàm của hàm số trên tại điểm \({x_0} = - 1\)
a) Ta có: \(f'\left( x \right) = \left( {{x^{22}}} \right)' = 22.{x^{21}}\)
b) Đạo hàm của hàm số tại điểm \({x_0} = - 1\) là: \(f'\left( { - 1} \right) = 22.{\left( { - 1} \right)^{21}} = - 22\)
Cho hàm số \(u = \sin x\) và hàm số \(y = {u^2}\).
a) Tính \(y\) theo \(x\).
b) Tính \(y{'_x}\) (đạo hàm của \(y\) theo biến \(x\)), \(y{'_u}\) (đạo hàm của \(y\) theo biến \(u\)) và \(u{'_x}\) (đạo hàm của \(u\) theo biến \(x\)) rồi so sánh \(y{'_x}\) với \(y{'_u}.u{'_x}\).
a: \(y=u^2=\left(sinx\right)^2\)
b: \(y'\left(x\right)=\left(sin^2x\right)'=2\cdot sinx\cdot cosx\)
\(y'\left(u\right)=\left(u^2\right)'=2\cdot u\)
\(u'\left(x\right)=\left(sinx\right)'=cosx\)
=>\(y'\left(x\right)=y'\left(u\right)\cdot u'\left(x\right)\)
1. Tính đạo hàm của các hàm số sau:
a, \(y=\dfrac{2x-1}{x-1}\)
b, \(y=\dfrac{2x+1}{1-3x}\)
c, \(y=\dfrac{x^2+2x+2}{x+1}\)
d, \(y=\dfrac{2x^2}{x^2-2x-3}\)
e, \(y=x+1-\dfrac{2}{x-1}\)
g, \(y=\dfrac{2x^2-4x+5}{2x+1}\)
2. Tính đạo hàm của các hàm số sau:
a, \(y=\left(x^2+x+1\right)^4\)
b, y= (1-2x2)5
c, \(y=\left(\dfrac{2x+1}{x-1}\right)^3\)
d, \(y=\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)^3}\)
e, \(y=\dfrac{1}{\left(x^2-2x+5\right)^2}\)
f, \(y=\left(3-2x^2\right)^4\)
a. \(y'=\dfrac{-1}{\left(x-1\right)}\)
b. \(y'=\dfrac{5}{\left(1-3x\right)^2}\)
c. \(y=\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2+1}{x+1}=x+1+\dfrac{1}{x+1}\Rightarrow y'=1-\dfrac{1}{\left(x+1\right)^2}=\dfrac{x^2+2x}{\left(x+1\right)^2}\)
d. \(y'=\dfrac{4x\left(x^2-2x-3\right)-2x^2\left(2x-2\right)}{\left(x^2-2x-3\right)^2}=\dfrac{-4x^2-12x}{\left(x^2-2x-3\right)^2}\)
e. \(y'=1+\dfrac{2}{\left(x-1\right)^2}=\dfrac{x^2-2x+3}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\)
g. \(y'=\dfrac{\left(4x-4\right)\left(2x+1\right)-2\left(2x^2-4x+5\right)}{\left(2x+1\right)^2}=\dfrac{4x^2+4x-14}{\left(2x+1\right)^2}\)
2.
a. \(y'=4\left(x^2+x+1\right)^3.\left(x^2+x+1\right)'=4\left(x^2+x+1\right)^3\left(2x+1\right)\)
b. \(y'=5\left(1-2x^2\right)^4.\left(1-2x^2\right)'=-20x\left(1-2x^2\right)^4\)
c. \(y'=3\left(\dfrac{2x+1}{x-1}\right)^2.\left(\dfrac{2x+1}{x-1}\right)'=3\left(\dfrac{2x+1}{x-1}\right)^2.\left(\dfrac{-3}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\right)=\dfrac{-9\left(2x+1\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)^4}\)
d. \(y'=\dfrac{2\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)^3-3\left(x-1\right)^2\left(x+1\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)^6}=\dfrac{-x^2-6x-5}{\left(x-1\right)^4}\)
e. \(y'=-\dfrac{\left[\left(x^2-2x+5\right)^2\right]'}{\left(x^2-2x+5\right)^4}=-\dfrac{2\left(x^2-2x+5\right)\left(2x-2\right)}{\left(x^2-2x+5\right)^4}=-\dfrac{4\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x^2-2x+5\right)^3}\)
f. \(y'=4\left(3-2x^2\right)^3.\left(3-2x^2\right)'=-16x\left(3-2x^2\right)^3\)
1. Đạo hàm của hàm số y= \(\left(x^3-5\right).\sqrt{x}\) bằng bao nhiêu?
2. Đạo hàm của hàm số y= \(\dfrac{1}{2}x^6-\dfrac{3}{x}+2\sqrt{x}\) là?
3. Hàm số y= \(2x+1+\dfrac{2}{x-2}\) có đạo hàm bằng?
1. \(y'=3x^2\sqrt{x}+\dfrac{x^3-5}{2\sqrt{x}}=\dfrac{7x^3-5}{2\sqrt{x}}\)
2. \(y'=3x^5+\dfrac{3}{x^2}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}}\)
3. \(y'=2-\dfrac{2}{\left(x-2\right)^2}\)
Tính đạo hàm của hàm số y= (x2-x+1)1/3
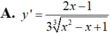
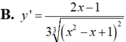
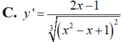
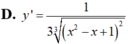
a) Dùng định nghĩa tỉnh đạo hàm của hàm số \(y = x\) tại điểm \(x = {x_0}\).
b) Nhắc lại đạo hàm của các hàm số \(y = {x^2},y = {x^3}\) đã tìm được ở bài học trước. Từ đó, dự đoán đạo hàm của hàm số \(y = {x^n}\) với \(n \in {\mathbb{N}^*}\).
a) Với bất kì \({x_0} \in \mathbb{R}\), ta có:
\(f'\left( {{x_0}} \right) = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {x_0}} \frac{{f\left( x \right) - f\left( {{x_0}} \right)}}{{x - {x_0}}} = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {x_0}} \frac{{x - {x_0}}}{{x - {x_0}}} = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {x_0}} 1 = 1\)
Vậy \(f'\left( x \right) = {\left( x \right)^\prime } = 1\) trên \(\mathbb{R}\).
b) Ta có:
\(\begin{array}{l}{\left( {{x^2}} \right)^\prime } = 2{\rm{x}}\\{\left( {{x^3}} \right)^\prime } = 3{{\rm{x}}^2}\\...\\{\left( {{x^n}} \right)^\prime } = n{{\rm{x}}^{n - 1}}\end{array}\)
a) Tính đạo hàm của hàm số \(y = {x^2}\) tại điểm \({x_0}\) bất kì bằng định nghĩa
b) Dự đoán đạo hàm của hàm số \(y = {x^n}\) tại điểm x bất kì
a)
\(\begin{array}{l}f'({x_0}) = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {x_0}} \frac{{f(x) - f({x_0})}}{{x - {x_0}}} = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {x_0}} \frac{{{x^2} - x_0^2}}{{x - {x_0}}} = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {x_0}} \frac{{{e^{2.\ln x}} - {e^{2.\ln {x_0}}}}}{{x - {x_0}}} = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {x_0}} \frac{{{e^{2.\ln {x_0}}}.\left( {{e^{2\ln x - 2\ln {x_0}}} - 1} \right)}}{{x - {x_0}}} = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {x_0}} \frac{{x_0^2\left( {{e^{2.\ln x - 2\ln {x_0}}} - 1} \right)}}{{x - {x_0}}}\\ = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {x_0}} \frac{{x_0^2\left( {2\ln x - 2\ln {x_0}} \right)}}{{x - {x_0}}} = 2x_0^2\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {x_0}} \frac{{\ln \left( {\frac{x}{{{x_0}}}} \right)}}{{x - {x_0}}} = 2x_0^2\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {x_0}} \frac{{\ln \left( {1 + \frac{x}{{{x_0}}} - 1} \right)}}{{x - {x_0}}} = 2x_0^2\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {x_0}} \frac{{\frac{x}{{{x_0}}} - 1}}{{x - {x_0}}} = 2x_0^2\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {x_0}} \frac{{\frac{{x - {x_0}}}{{{x_0}}}}}{{x - {x_0}}} = 2x_0^2\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {x_0}} \frac{1}{{{x_0}}}\\ = 2x_0^2.\frac{1}{{{x_0}}} = 2x\\ \Rightarrow \left( {{x^2}} \right)' = 2x\end{array}\)
b) Dự đoán đạo hàm của hàm số \(y = {x^n}\) tại điểm x bất kì: \(y' = n.{x^{n - 1}}\)
a) Tính đạo hàm của hàm số \(y=\sqrt{sinx+cosx}\)
b) Hãy viết phương trình tiếp tuyến với đồ thị (C) của hàm số \(y=\dfrac{x+3}{x-1}\) biết tiếp tuyến vuông góc với đường thẳng \(y=\dfrac{1}{4}x+5\)
a.
\(y'=\dfrac{\left(sinx+cosx\right)'}{2\sqrt{sinx+cosx}}=\dfrac{cosx-sinx}{2\sqrt{sinx+cosx}}\)
b.
\(y'=\dfrac{-4}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\)
Tiếp tuyến vuông góc với \(y=\dfrac{1}{4}x+5\) nên có hệ số góc thỏa mãn \(k.\left(\dfrac{1}{4}\right)=-1\Rightarrow k=-4\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{-4}{\left(x-1\right)^2}=-4\Rightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2=1\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\Rightarrow y=-3\\x=2\Rightarrow y=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
Có 2 tiếp tuyến thỏa mãn: \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}y=-4x-3\\y=-4\left(x-2\right)+5\end{matrix}\right.\)