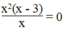Giai phương trình: (x2+4x+8)2 +3x(x2+4x+8)+2x2=0
Mọi người giúp mình với!
Hãy giải các phương trình sau đây :
1, x2 - 4x + 4 = 0
2, 2x - y = 5
3, x + 5y = - 3
4, x2 - 2x - 8 = 0
5, 6x2 - 5x - 6 = 0
6,( x2 - 2x )2 - 6 (x2 - 2x ) + 5 = 0
7, x2 - 20x + 96 = 0
8, 2x - y = 3
9, 3x + 2y = 8
10, 2x2 + 5x - 3 = 0
11, 3x - 6 = 0
1) Ta có: \(x^2-4x+4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-2=0\)
hay x=2
Vậy: S={2}
Phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử bằng phương pháp đặt ẩn phụ
(x2+4x+8)2+3x(x2+4x+8)+2x2
\(\left(x^2+4x+8\right)^2+3x\left(x^2+4x+8\right)+2x^2=\left(x^2+4x+8+\dfrac{3}{2}x\right)^2-\dfrac{1}{4}x^2=\left(x^2+\dfrac{11}{2}x+8\right)^2-\left(\dfrac{1}{2}x\right)^2=\left(x^2+\dfrac{11}{2}x+8-\dfrac{1}{2}x\right)\left(x^2+\dfrac{11}{2}x+8+\dfrac{1}{2}x\right)=\left(x^2+5x+8\right)\left(x^2+6x+8\right)=\left(x+2\right)\left(x+4\right)\left(x^2+5x+8\right)\)
\(\left(x^2+4x+8\right)^2+3x\left(x^2+4x+8\right)+2x^2\)
\(=\left(x^2+4x+8\right)^2+x\left(x^2+4x+8\right)+2x\left(x^2+4x+8\right)+2x^2\)
\(=\left(x^2+4x+8\right)\left(x^2+5x+8\right)+2x\left(x^2+5x+8\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2+5x+8\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x+4\right)\)
giải phương trình (x2+4x+8)(x2+5x+8)=2x2
\(\left(x^2+4x+8\right)\left(x^2+5x+8\right)=2x^2\left(1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^4+5x^3+8x^2+4x^3+20x^2+32x+8x^2+40x+64-2x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^4+5x^3+4x^3+8x^2+20x^2+8x^2-2x^2+40x+32x+64=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^4+9x^3+34x^2+72x+64=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^4+2x^3+7x^3+14x^2+20x^2+40x+32x+64=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3\left(x+2\right)+7x^2\left(x+2\right)+20x\left(x+2\right)+32\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(x^3+7x^2+20x+32\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(x^3+4x^2+3x^2+12x+8x+32\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left[x^2\left(x+4\right)+3x\left(x+4\right)+8\left(x+4\right)\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(x+4\right)\left(x^2+3x+8\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+2=0\\x+4=0\\x^2+3x+8=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-2\\x=-4\\vô.nghiệm\left(\Delta=9-32=-23< 0\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-2\\x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\) là nghiệm của phương trình \(\left(1\right)\)
Phương trình nào sau đây là phương trình của đường tròn?
(I) x2+ y2 – 4x +15y -12= 0.
(II) x2+ y2 – 3x +4y +20= 0.
(III) 2x2+ 2y2- 4x + 6y +1= 0 .
A. Chỉ (I).
B. Chỉ (II).
C. Chỉ (III).
D. Chỉ (I) và (III).
Ta xét các phương án:
(I) có:
![]()
(II) có:
![]()
(III) tương đương : x2+ y2 – 2x - 3y + 0,5= 0.
phương trình này có:
![]()
Vậy chỉ (I) và (III) là phương trình đường tròn.
Chọn D.
Giải các phương trình sau:
g/ x(x + 3)(x – 3) – (x + 2)(x2 – 2x + 4) = 0
h/ (3x – 1)(x2 + 2) = (3x – 1)(7x – 10)
i/ (x + 2)(3 – 4x) = x2 + 4x + 4
k/ x(2x – 7) – 4x + 14 = 0
m/ x2 + 6x – 16 = 0
n/ 2x2 + 5x – 3 = 0
\(m,x^2+6x-16=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x+8x-16=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-2\right)+8\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+8\right)\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+8=0\\x-2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-8\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(n,2x^2+5x-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-x+6x-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(2x-1\right)+3\left(2x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+3\right)\left(2x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+3=0\\2x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\x=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(k,x\left(2x-7\right)-4x+14=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-4x-7x+14=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x\left(x-2\right)-7\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-7\right)\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-7=0\\x-2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{7}{2}\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
1) Tìm nghiệm nguyên của phương trình : x2= 2y2+2013
2) Giải phương trình x3+2x2- 4x +\(\dfrac{8}{3}\)=0
Ta có \(2y^2⋮2\Rightarrow x^2\equiv1\left(mod2\right)\Rightarrow x^2\equiv1\left(mod4\right)\Rightarrow2y^2⋮4\Rightarrow y⋮2\Rightarrow x^2\equiv5\left(mod8\right)\) (vô lí).
Vậy pt vô nghiệm nguyên.
2: \(PT\Leftrightarrow3x^3+6x^2-12x+8=0\Leftrightarrow4x^3=\left(x-2\right)^3\Leftrightarrow\sqrt[3]{4}x=x-2\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{-2}{\sqrt[3]{4}-1}\).
Phân tích đa thức sau thành nhân tử : (x2 + 4x + 8)2 + 3x(x2 + 4x + 8) + 2x2
\(\left(x^2+4x+8\right)^2+3x\left(x^2+4x+8\right)+2x^2=\left(x^2+4x+8\right)^2+2x\left(x^2+4x+8\right)+x\left(x^2+4x+8\right)+2x^2\)
\(=\left(x^2+4x+8\right)\left(x^2+4x+8+2x\right)+x\left(x^2+4x+8+2x\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2+4x+8\right)\left(x^2+6x+8\right)+x\left(x^2+6x+8\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2+4x+8+x\right)\left(x^2+6x+8\right)=\left(x^2+5x+8\right)\left(x^2+6x+8\right)\)
Ta có: \(\left(x^2+4x+8\right)^2+3x\left(x^2+4x+8\right)+2x^2\)
\(=\left(x^2+5x+8\right)\left(x^2+6x+8\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2+5x+8\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x+4\right)\)
Bài 1. Giải các phương trình sau:
a) x2 - 6x + 5 = 0 b) 2x2 + 4x – 8 = 0
c) 4y2 – 4y + 1 = 0 d) 5x2 - x + 2 = 0
\(a,x^2-6x+5=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x^2-5x\right)-\left(x-5\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow x\left(x-5\right)-\left(x-5\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-5\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(b,2x^2+4x-8=0\\ \Rightarrow x^2+2x-4=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x^2+2x+1\right)-5=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x+1\right)^2-\sqrt{5^2}=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x+1+\sqrt{5}\right)\left(x+1-\sqrt{5}\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1-\sqrt{5}\\x=-1+\sqrt{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(c,4y^2-4y+1=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(2y-1\right)^2=0\\ \Rightarrow2y-1=0\\ \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(d,5x^2-x+2=0\)
Ta có:\(\Delta=\left(-1\right)^2-4.5.2=1-40=-39\)
Vì \(\Delta< 0\Rightarrow\) pt vô nghiệm
Cho phương trình (1+4x-x2).52x^2-3x-1 + (2x2-3x-1).51+4x-x^2 = x2+x. Tổng tất cả các nghiệm của phương trình nằm trong khoảng nào dưới đây?
A.(0;4)
B. (4;6)
C.(6;8)
D. (8;12)
Các khẳng định sau đây đúng hay sai:
a. Phương trình 4 x - 8 + 4 - 2 x x 2 + 1 = 0 có nghiệm x = 2.
b. Phương trình x + 2 2 x - 1 - x - 2 x 2 - x + 1 = 0 có tập nghiệm S = {-2; 1}
c. Phương trình x 2 + 2 x + 1 x + 1 = 0 có nghiệm x = - 1
d. Phương trình x 2 x - 3 x = 0 có tập nghiệm S = {0; 3}
a. Đúng
Vì x 2 + 1 > 0 với mọi x nên phương trình đã cho tương đương với phương trình:
4x – 8 + (4 – 2x) = 0 ⇔ 2x – 4 = 0 ⇔ 2x = 4 ⇔ x = 2
b. Đúng
Vì x 2 – x + 1 = x - 1 / 2 2 + 3/4 > 0 với mọi x nên phương trình đã cho tương đương với phương trình:
(x + 2)(2x – 1) – x – 2 = 0 ⇔ (x + 2)(2x – 2) = 0
⇔ x + 2 = 0 hoặc 2x – 2 = 0 ⇔ x = - 2 hoặc x = 1
c. Sai
Vì điều kiện xác định của phương trình là x + 1 ≠ 0 ⇔ x ≠ - 1
Do vậy phương trình 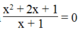 không thể có nghiệm x = - 1
không thể có nghiệm x = - 1
d. Sai
Vì điều kiện xác định của phương trình là x ≠ 0
Do vậy x = 0 không phải là nghiệm của phương trình