Giải phương trình sau: l3x+1l + (2x-3y-1)2014=0

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Giải phương trình 1,l1-5xl-1=3
2,4l2x-1l+3=15
3,lx+4l=2x+1
4,l3x-4l=x-3
5,l2x-3l=3-2x
6,l3x-1l=x+4
7,lx^2-2x+1l=4
8,l1-xl+l4-xl=3
1: |1-5x|-1=3
=>|5x-1|=4
=>5x-1=4 hoặc 5x-1=-4
=>5x=5 hoặc 5x=-3
=>x=1 hoặc x=-3/5
2: 4|2x-1|+3=15
=>4|2x-1|=12
=>|2x-1|=3
=>2x-1=3 hoặc 2x-1=-3
=>x=2 hoặc x=-1
Đúng 3
Bình luận (0)
3,\(\left|x+4\right|=2x+1\)
TH1: x+4≥0⇔x≥-4,pt có dạng:
x+4=2x+1⇔-x=-3⇔x=3(t/m)
TH2:x+4<0⇔x<-4,pt có dạng:
-x-4=2x+1⇔-3x=5⇔x=\(\dfrac{-5}{3}\)(loại)
Vậy pt đã cho có tập nghiệm S=\(\left\{3\right\}\)
4,\(\left|3x+4\right|=x-3\)
TH1: 3x-4≥0⇔3x≥4⇔x≥\(\dfrac{4}{3}\),pt có dạng:
3x-4=x-3⇔2x=1⇔x=\(\dfrac{1}{2}\)(loại)
TH2: 3x-4<0⇔3x<4⇔x<\(\dfrac{4}{3}\),pt có dạng:
-3x+4=x-3⇔-4x=-7 ⇔x=1,75(loại)
Vậy pt đã cho vô nghiệm
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Tìm x
a) 3(2x-1) -5(x+1)-4.l-5l=0
b)5.l3x+1l-15=4.l3x+1l+4
Giúp mình vs
a, <=> 6x-3-5x-5-4.5=0
<=> x=28
b, 5|3x+1|-4|3x+1|=19
<=> |3x+1|=19
<=>\(\orbr{\begin{cases}3x+1=19\\3x+1=-19\end{cases}}\)
<=>\(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=6\\x=\frac{-20}{3}\end{cases}}\)
Chúc hok tốt!!
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải hệ phương trình sau:
a) { 2x + 5y=11
{2x - 3y =0
B) { 4x + 3y = 6
{ 2x + y = 4
Ai giải bài toán này hộ mình với ạ , mình cảm ơn
Xem chi tiết
`2x+5y=11(1)`
`2x-3y=0(2)`
Lấy (1) trừ (2)
`=>8y=11`
`<=>y=11/8`
`<=>x=(3y)/2=33/16`
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
a) Ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+5y=11\\2x-3y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}8y=11\\2x-3y=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{11}{8}\\2x=3y=3\cdot\dfrac{11}{8}=\dfrac{33}{8}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{33}{16}\\y=\dfrac{11}{8}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: Hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất là \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{33}{16}\\y=\dfrac{11}{8}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) Ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4x+3y=6\\2x+y=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4x+3y=6\\4x+2y=8\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-2\\2x+y=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-2=4\\y=-2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x=6\\y=-2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\y=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: Hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất là (x,y)=(3;-2)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
`b)4x+3y=6(1)`
`2x+y=4<=>4x+2y=8(2)`
Lấy (1) trừ (2) ta có:
`y=-2`
`<=>x=(4-2y)/2=3`
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
cho mình hỏi
bài 1: Tìm x
a)2l3x-2l+lx-1l=2x-1
b)ll3x+1l+l4-3xll=x+1
bài 2: tìm x;y bt
a)l2x+3l+(y-1)^2018=0
b)l3x-1l+(x-y^2=0
c)lx-2yl+x^2-2x=-1
d)l3x-2l^2018+(y-2019)^2018< hoặc bằng 0
mình đang cần gấp mai mình nộp rồicho mình hỏi
a) giải hệ phương trình {x+y=3 {2x-3y=1 b) giải phương trình x^ -7x +10=0
\(a,\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+y=3\\2x-3y=1\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+2y=6\\2x-3y=1\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5y=5\\2x-3y=1\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=1\\2x-3.1=1\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(2;1\right)\)
b, \(x^2-7x+10=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-5x-2x+10=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x\left(x-5\right)-2\left(x-5\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x-5\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\x-5=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
\(a,\)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+y=3\\2x-3y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x+3y=9\\2x-3y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5x=10\\2x-3y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\2.2-3y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy hệ pt có nghiệm duy nhất \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(2;1\right)\)
\(b,x^2-7x+10=0\)
\(\Delta=b^2-4ac=\left(-7\right)^2-4.10=9>0\)
\(\Rightarrow\) Pt có 2 nghiệm \(x_1,x_2\)
Ta có :
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{-b+\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\dfrac{7+3}{2}=5\\x_2=\dfrac{-b-\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\dfrac{7-3}{2}=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{5;2\right\}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải các hệ phương trình sau bằng phương pháp cộng đại số:
2
x
+
5
y
8
2
x
-
3
y...
Đọc tiếp
Giải các hệ phương trình sau bằng phương pháp cộng đại số:
2 x + 5 y = 8 2 x - 3 y = 0
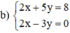 (Hệ số của x ở 2 pt bằng nhau nên ta trừ từng vế của 2pt)
(Hệ số của x ở 2 pt bằng nhau nên ta trừ từng vế của 2pt)
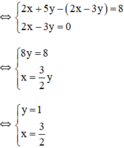
Vậy hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất 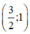
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải hệ phương trình sau:
\(\hept{\begin{cases}x-3y+\sqrt{x^2+3y^2}=0\\\sqrt{2y-1}+2x^2-y^2-3x+1=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\hept{\begin{cases}x-3y+\sqrt{x^2+3y^2}=0\left(1\right)\\\sqrt{2y-1}+2x^2-y^2-3x+1=0\left(2\right)\end{cases}}\) \(\left(ĐKXĐ:y\ge\frac{1}{2}\right)\)
Xét phương trình (1)
\(\sqrt{x^2+3y^2}=3y-x\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2+3y^2=x^2-6xy+9y^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6y^2-6xy=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow y\left(y-x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}y=0\left(ktmđkxđ\right)\\x=y\end{cases}}\)
Thay x=y vào (2) ta đc:
\(\sqrt{2y-1}+2y^2-y^2-3y+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2y-1}+y^2-3y+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{2y-1}-1\right)+\left(y^2-3y+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{2y-1-1}{\sqrt{2y-1}+1}+\left(y-2\right)\left(y-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(y-1\right)\left(\frac{2}{\sqrt{2y-1}+1}+y-2\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow y=1\left(tmđkxđ\right)\)
Vậy nghiệm của hpt trên là (x;y)=(1;1)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Bất phương trình nào sau đây là bất phương trình bậc nhất hai ẩn?
a) \(2x^2+3y>0\)
b) 2x + \(3y^2\le0\)
c) 2x + 3y > 0
d) \(2x^2-y^2+3x-2y< 0\)
e) 3y < 1
f) x - 2y \(\le1\)
g) x \(\le0\)
h) y > 0
i) 4(x-1) + 5(y-3) > 2x - 9
Bất phương trình bậc nhất 2 ẩn :
\(2x+3y>0\Rightarrow Câu\) \(C\)
\(x-2y\le1\Rightarrow Câu\) \(f\)
\(4\left(x-1\right)+5\left(y-3\right)>2x-9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x-4+5y-15-2x+9>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+5y-10>0\) \(\Rightarrow Câu\) \(i\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Bất phương trình nào sau đây là bất phương trình bậc nhất hai ẩn?
a) \(2x - 3y + 1 \le 0\)
b) \(x - 3y + 1 \ge 0\)
c) \(y - 5 > 0\)
d) \(x - {y^2} + 1 > 0\)
Các bất phương trình a), b), c) là các bất phương trình bậc nhất hai ẩn.
Bất phương trình d) không là bất phương trình bậc nhất hai ẩn vì có chứa \({y^2}.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
























