giúp mình với. cảm ơn mọi người
giúp mình với. cảm ơn mọi người
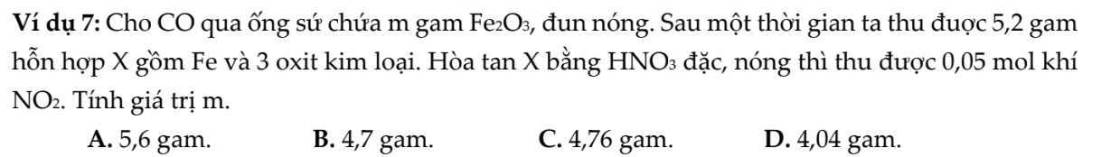
\(m\) \(gam\) \(Fe_2O_3+CO\xrightarrow[]{t^o}5,2g\) \(X\) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}FeO\\Fe_3O_4\\Fe_2O_3\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\xrightarrow[du]{+HNO_3}\) \(Fe\left(NO_3\right)_3+0,05mol\) \(NO+H_2O\)
Bảo toàn electron cho toàn bộ quá trình:\(\rightarrow2n_{CO}=n_{NO_2}\rightarrow n_{CO}=n_{CO_2}=0,025mol\)
Bảo toàn khối lượng: \(\rightarrow m=m_X+m_{CO_2}-m_{CO}=5,2+0,025.44-0,025.28=5,6gam\)
Chọn A
Thổi một luồng khí CO qua hỗn hợp Fe, Fe2O3 nung nóng thu được khí B và hỗn hợp D gồm 4 chất. Cho B qua nước vôi trong dư thấy tạo ra 6 gam kết tủa. Hoà tan D bằng H2SO4 đặc nóng dư thấy tạo ra 0,18 mol SO2 và24gam muối. Xác định % số mol của Fe, Fe2O3 trong hỗn hợp ban đầu?
$CO_2 + Ca(OH)_2 \to CaCO_3 + H_2O$
Theo PTHH :
$n_{CO_2} = n_{CaCO_3} = 0,06(mol)$
$n_{Fe_2(SO_4)_3} = \dfrac{24}{400} = 0,06(mol)$
$\Rightarrow n_{Fe\ trong hh} = 0,06.2 = 0,12(mol)$
Gọi $n_{Fe} = a(mol) ; n_{Fe_2O_3} = b(mol)$
$\Rightarrow a + 2b = 0,12(1)$
$Fe^0 \to Fe^{+3} + 3e$
$C^{+2} \to C^{+4} + 2e$
$S^{+6} + 2e \to S^{+4}$
Bảo toàn electron : $3n_{Fe} + 2n_{CO_2} = 2n_{SO_2}$
$\Rightarrow n_{Fe} = a = 0,08(2)$
Từ (1)(2) suy ra : a = 0,08. ; b = 0,02
$\%n_{Fe} = \dfrac{0,08}{0,08+0,02}.100\% = 80\%$
$\% n_{Fe_2O_3} = 100\% - 80\% = 20\%$
Để a gam bột sắt ngoài không khí, sau một thời gian sẽ chuyển thành hỗn hợp A gồm 4 chất rắn có khối lượng 75,2 gam. Cho hỗn hợp A phản ứng hết với dd H2SO4 đặc nóng dư thấy thoát ra 6,72 lit SO2 (đktc). Tính a ?
Coi A gồm $Fe(x\ mol) ; O(b\ mol) \Rightarrow 56x + 16b = 75,2(1)$
Bảo toàn electron : $3n_{Fe} = 2n_O + 2n_{SO_2}$
$\Rightarrow 3x = 2b + 0,3.2(2)$
Từ (1)(2) suy ra : x = 1 ; b = 1,2
Ta có : $n_{Fe} = 1(mol) \Rightarrow a = 1.56 = 56(gam)$
Hỗn hợp X gồm 2 kim loại A, B đứng trước hiđro và có hoá trị không đổi trong hợp chất. Chia m gam hỗn hợp X thành 2 phần bằng nhau. Phần 1 tan hoàn toàn trong dd gồm HCl, H2SO4 loãng tạo thành 2,24 lít H2 (đktc). Phần 2 tác dụng hết với dd HNO3 dư thu được V lít khí NO duy nhất (đktc). Tính V.
Coi hai kim loại là R có hóa trị n
Phần 1 : $n_{H_2} = 0,1(mol)$
$R^0 \to R^{+n} + ne$
$2H^+ + 2e \to H_2$
Bảo toàn electron : $n_R = \dfrac{0,1.2}{n} = \dfrac{0,2}{n}(mol)$
Phần 2 :
$R^0 \to R^{+n} + ne$
$N^{+5} + 3e \to N^{+2}$
Bảo toàn electron : $n.n_R = 3n_{NO} \Rightarrow n_{NO} = \dfrac{0,2}{3}(mol)$
$V = \dfrac{0,2}{3}.22,4 = 1,493(lít)$
Trộn 84 gam bột Fe với 32 gam bột S rồi đun nóng (không có không khí). Hoà tan chất rắn A sau khi nung bằng dd HCl dư được dd B và khí C. Đốt cháy khí C cần V lít oxi (đktc). Các phản ứng xảy ra hoàn toàn. Tính V.
$n_{Fe} = \dfrac{84}{56} = 1,5(mol)$
$n_S = \dfrac{32}{32} = 1(mol)$
Quá trình oxi hóa - khử :
$Fe^0 \to Fe^{+2} + 2e$
$S^0 \to S^{+4} + 4e$
$O_2 + 4e \to 2O^{-2}$
Bảo toàn electron : $2n_{Fe} + 4n_S = 4n_{O_2}$
$\Rightarrow n_{O_2} = \dfrac{1,5.2 + 1.4}{4} = 1,75( mol)$
$V = 1,75.22,4 = 39,2(lít)$
Chia m gam hỗn hợp 2 kim loại A, B có hoá trị không đổi, đứng trước hiđro thành 2 phần bằng nhau. Phần 1 tan hết trong dd HCl dư tạo thành 1,792 lit H2 (đktc). Phần 2 nung trong oxi dư thu được 2,84 gam hỗn hợp oxit. Giá trị của m là?
Gọi hai kim loại A,B là R có hóa trị n
Phần 1 : $n_{H_2} = \dfrac{1,792}{22,4} = 0,08(mol)$
$2R + 2nHCl \to 2RCl_n + nH_2$
Theo PTHH : $n_R = \dfrac{2}{n}.n_{H_2} = \dfrac{0,16}{n}(mol)$
Phần 2 :
$4R + nO_2 \xrightarrow{t^o}2R_2O_n$
Theo PTHH : $n_{O_2} = \dfrac{n}{4}.n_R = 0,04(mol$
$\Rightarrow m = m_{oxit} -m_{O_2} = 2,84 -0,04.32 = 1,56(gam)$
Nung nóng 16,8 gam bột sắt trong không khí thu được m gam hỗn hợp X gồm 4 chất rắn. Hoà tan hết m gam X bằng H2SO4 đặc nóng dư thoát ra 5,6 lit SO2 (đktc). Giá trị của m?
Coi hỗn hợp X gồm Fe và O
$n_{Fe} = \dfrac{16,8}{56} = 0,3(mol)$
$n_{SO_2} = \dfrac{5,6}{22,4} = 0,25(mol)$
Bảo toàn electron : $3n_{Fe} = 2n_O + 2n_{SO_2}$
$\Rightarrow n_O = \dfrac{0,3.3 - 0,25.2}{2} = 0,2(mol)$
$m = m_{Fe} + m_O = 16,8 + 0,2.16 = 20(gam)$
Hỗn hợp A gồm Al và Fe. Nếu hoà tan hết 11 gam A trong dd H2SO4 loãng dư thu được 8,96 lít khí (đktc) còn khi hoà tan hết 5,5 gam A trong H2SO4 đặc nóng dư thì thu được V lít khí SO2(đktc, spk duy nhất). Xác định V.
Gọi $n_{Al} = a(mol) ; n_{Fe} = b(mol) \Rightarrow 27a + 56b = 11(1)$
$n_{H_2} = \dfrac{8,96}{22,4} = 0,4(mol)$
Bảo toàn electron :
$3n_{Al} + 2n_{Fe} = 2n_{H_2} \Rightarrow 3a + 2b = 0,4.2(2)$
Từ (1)(2) suy ra a = 0,2 ; 0,1
Suy ra : trong 5,5 gam A có $n_{Al} = 0,2 : 2 = 0,1(mol) ; n_{Fe} = 0,1 : 2 = 0,05(mol)$
Bảo toàn electron :$3n_{Al} + 3n_{Fe} = 2n_{SO_2}$
$\Rightarrow n_{SO_2} = \dfrac{0,1.3 + 0,05.3}{2} = 0,225(mol)$
$\Rightarrow V = 0,225.22,4 = 5,04(lít)$
Đốt cháy 16,2 gam kim loại M (hoá trị không đổi) trong bình khí chứa 0,15 mol oxi. Chất rắn thu được cho tan trong dd HCl dư thấy thoát ra 13,44 lít H2 (đktc). Các phản ứng xảy ra hoàn toàn, xác định M.
Chất rắn thu được cho tan trong HCl dư thấy thoát ra 13,44 lít khí --> có M dư
Gọi n là hóa trị của kim loại M
Ta có hai phương trình
\(4M+nO_2->2M_2O_n\)
0,6/n<--0,15 (mol)
\(2M+2nHCl->2MCl_n+nH_2\)
1,2/n <--0,6 (mol)
--> số mol ban đầu của M là \(\dfrac{0,6}{n}+\dfrac{1,2}{n}=\dfrac{1,8}{n}\left(mol\right)\)
Ta có \(\dfrac{m_M}{n_M}=M_M\)
--> \(\dfrac{16,2}{\dfrac{1,8}{n}}=M_M\Leftrightarrow9n=M_M\)
Khi \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}n=1\\n=2\\n=3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}M=9\\M=18\\M=27\left(Al\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
--> M là kim loại Nhôm (Al)
Khi đốt 37,9 gam hỗn hợp Al, Zn trong bình khí Clo thu được 59,2 gam hỗn hợp chất rắn. Cho hỗn hợp này tan hết trong dd HCl dư thấy thoát ra 11,2 lít khí (đktc). Tính khối lượng mỗi kim loại Al, Zn trong hỗn hợp ban đầu.
Bảo toàn khối lượng : $m_{Cl_2} = 59,2 - 37,9 = 21,3(gam)$
$\Rightarrow n_{Cl_2} = \dfrac{21,3}{71} = 0,3(mol)$
$n_{H_2} = \dfrac{11,2}{22,4} = 0,5(mol)$
Gọi $n_{Al} = a(mol) ; n_{Zn} = b(mol) \Rightarrow 27a + 65b = 37,9(1)$
$Al^0 \to Al^{+3} + 3e$
$Zn^0 \to Zn^{+2} + 2e$
$Cl_2 + 2e \to 2Cl^-$
$2H^+ + 2e \to H_2$
Bảo toàn electron : $3n_{Al} + 2n_{Zn} = 2n_{Cl_2} + 2n_{H_2}$
$\Rightarrow 3a + 2b = 0,3.2 + 0,5.2(2)$
Từ (1)(2) suy ra a = 0,2 ;b = 0,5
$m_{Al} = 0,2.27 = 5,4(gam)$
$m_{Zn} = 0,5.65 = 32,5(gam)$