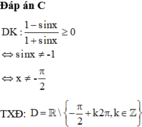Tập xác định của hàm số y = sin(x + pi/4) là

Những câu hỏi liên quan
c1 tập xác định của hàm số \(y=\dfrac{sin2x+cosx}{tanx-sinx}\)
c2 tập xác định của hàm số \(y=\sqrt{1+cot^22x}\)
c3 tập xác định của hàm số \(y=cot\left(x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)+tan\left(x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)\)
1.
ĐKXĐ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}cosx\ne0\\tanx-sinx\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}cosx\ne0\\\dfrac{sinx}{cosx}-sinx\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}cosx\ne0\\sinx\ne0\\cosx\ne1\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow sin2x\ne0\Leftrightarrow x\ne\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\)
2.
ĐKXĐ: \(sin2x\ne0\Leftrightarrow x\ne\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\)
3.
ĐKXĐ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}sin\left(x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)\ne0\\cos\left(x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sin\left(2x-\dfrac{\pi}{2}\right)\ne0\Leftrightarrow cos2x\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{4}+\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (5)
câu 2 ..... \(\dfrac{cos^22x}{sin^22x}=cot^22x\) nên suy ra sin2x khác 0 đúng hơm
còn câu 3, tui ko hiểu chỗ sin(2x-pi/4).. sao ở đây rớt xuống dợ
Đúng 1
Bình luận (2)
tìm tập xác định của hàm số lượng giác saua)ydfrac{tanleft(2x-dfrac{pi}{4}right)}{sqrt{1-sinleft(x-dfrac{pi}{8}right)}}b)ydfrac{tanleft(x-dfrac{pi}{4}right)}{1-cosleft(x+dfrac{pi}{3}right)}c)ydfrac{3}{cosx-cos3x}d)ydfrac{4}{sin^2x-cos^2x}e)ydfrac{1+cotleft(dfrac{pi}{3}+xright)}{tan^2left(3x-dfrac{pi}{4}right)}
Đọc tiếp
tìm tập xác định của hàm số lượng giác sau
a)\(y=\dfrac{tan\left(2x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)}{\sqrt{1-sin\left(x-\dfrac{\pi}{8}\right)}}\)
b)\(y=\dfrac{tan\left(x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)}{1-cos\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)}\)
c)\(y=\dfrac{3}{cosx-cos3x}\)
d)\(y=\dfrac{4}{sin^2x-cos^2x}\)
e)\(y=\dfrac{1+cot\left(\dfrac{\pi}{3}+x\right)}{tan^2\left(3x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)}\)
Tập xác định của hàm số y=x+ pi/4 là là
Tập xác định của hàm số y frac{{cos x}}{{sin x - 1}} làA. mathbb{R}backslash { k2pi {rm{|}}k; in ;mathbb{Z}{rm{} }} B. mathbb{R};backslash left{ {frac{pi }{2} + k2pi {rm{|}}k; in ;mathbb{Z}} right}C. mathbb{R}backslash left{ {frac{pi }{2} + kpi {rm{|}}k; in ;mathbb{Z}} right} D. mathbb{R}backslash { kpi {rm{|}}k; in ;mathbb{Z}{rm{} }}
Đọc tiếp
Tập xác định của hàm số \(y = \frac{{\cos x}}{{\sin x - 1}}\) là
A. \(\mathbb{R}\backslash \{ k2\pi {\rm{|}}k\; \in \;\mathbb{Z}{\rm{\} }}\)
B. \(\mathbb{R}\;\backslash \left\{ {\frac{\pi }{2} + k2\pi {\rm{|}}k\; \in \;\mathbb{Z}} \right\}\)
C. \(\mathbb{R}\backslash \left\{ {\frac{\pi }{2} + k\pi {\rm{|}}k\; \in \;\mathbb{Z}} \right\}\)
D. \(\mathbb{R}\backslash \{ k\pi {\rm{|}}k\; \in \;\mathbb{Z}{\rm{\} }}\)
Hàm số xác định khi: \(\sin x - 1\; \ne 0\; \Leftrightarrow \sin x \ne 1\; \Leftrightarrow x \ne \frac{\pi }{2} + k2\pi ,\;\;k \in \mathbb{Z}\)
Vậy ta chọn đáp án B
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tập xác định của hàm số
y=\(\dfrac{cot\left(x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)}{sin^4x-cos^4x}\)
ĐK: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}sin\left(x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)\ne0\\sin^4x-cos^4x\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}\ne k\pi\\\left(cos^2x-sin^2x\right)\left(cos^2x+sin^2x\right)\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{4}+k\pi\\cos2x\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{4}+k\pi\\2x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{4}+k\pi\\x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{4}+\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{4}+\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tìm tập xác định D của hàm số
y
1
-
sin
x
1
+
sin
x
Đọc tiếp
Tìm tập xác định D của hàm số y = 1 - sin x 1 + sin x
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Trong các hàm số sau, có bao nhiêu hàm số là hàm chẵn trên tập xác định của nó? y cot 2x; y cos(x + π); y 1 – sin x; y tan2016x A. 1. B. 2 C. 3 D. 4
Đọc tiếp
Trong các hàm số sau, có bao nhiêu hàm số là hàm chẵn trên tập xác định của nó?
y = cot 2x; y = cos(x + π); y = 1 – sin x; y = tan2016x
A. 1.
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
Đáp án B
+ Xét hàm y = f(x) = cos (x + π)
TXĐ: D = R
Với mọi x ∈ D, ta có: -x ∈ D và f(-x) = cos (-x + π) = -cos x = cos (x + π) = f(x)
Do đó y = cos (x + π) là hàm số chẵn .
+ Xét hàm y = g(x) = tan2016x
TXĐ: D = R\{π/2 + kπ, k ∈ Z}
Với mọi x ∈ D, ta có: -x ∈ D và g(-x) = tan2016(-x) = (-tan x)2016 = tan2016x = g(x)
Do đó: y = tan2016x là hàm chẵn trên tập xác định của nó.
+Xét hàm y = cot2x
f(-x) = cot(-2x) = - cot 2x = -f(x) nên đây là hàm số lẻ.
+ Xét hàm số y = 1-sinx
f(-x) = 1- sin(-x) = 1+ sin x
Nên hàm số không chẵn không lẻ
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Tìm m để hàm số \(y=\sqrt{\dfrac{m-\sin x-\cos x-2\sin x\cos x}{\sin^{2017}x-\cos^{2019}x+\sqrt{2}}}\) xác định với mọi \(x\in[-\dfrac{\pi}{2};\dfrac{\pi}{2}]\)
Bạn tham khảo:
Tìm m để hàm số : \(y=\sqrt{\frac{m-\sin x-\cos x-2\sin x\cos x}{\sin^{2017}x-\cos^{2019}x \sqrt{2}}}\) xác định với mọi... - Hoc24
Đúng 0
Bình luận (5)
Tìm tập xác định của hàm số sau đây
a)y=2tanx+3
b)y=2tan2x-4sinx
c)y=cot(x+\(\dfrac{\pi}{4}\))+1
ĐKXĐ:
a. \(cosx\ne0\Leftrightarrow x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k\pi\)
b. \(cos2x\ne0\Leftrightarrow x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{4}+\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\)
c. \(sin\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)\ne0\Leftrightarrow x+\dfrac{\pi}{4}\ne k\pi\Leftrightarrow x\ne-\dfrac{\pi}{4}+k\pi\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)