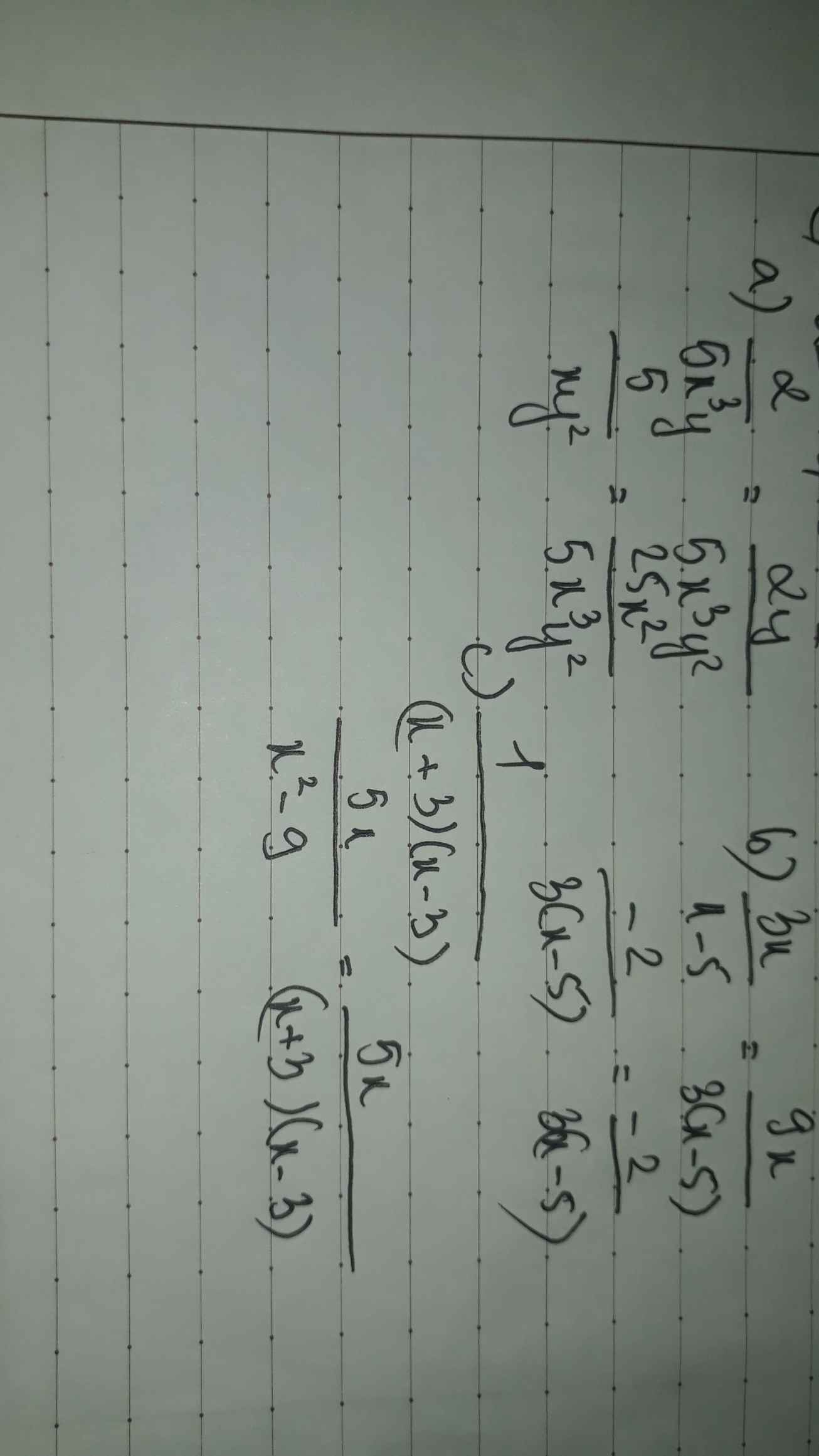\(\dfrac{x-x^2}{5x^2-5}=\dfrac{x}{A}\)

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Rút gọn: A= \(\dfrac{x}{5-x}+\left(\dfrac{x}{x^2-25}+\dfrac{5-x}{5x+x^2}\right):\dfrac{2x-5}{x^2+5x}\)
\(A=\dfrac{x}{5-x}+\left(\dfrac{x}{x^2-25}+\dfrac{5-x}{5x+x^2}\right):\dfrac{2x-5}{x^2+5x}=\dfrac{x}{5-x}+\left[\dfrac{x^2}{x\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)}-\dfrac{\left(x-5\right)^2}{x\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)}\right].\dfrac{x^2+5x}{2x-5}=\dfrac{x}{5-x}+\dfrac{x^2-\left(x-5\right)^2}{x\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)}.\dfrac{x\left(x+5\right)}{2x-5}=\dfrac{x}{5-x}+\dfrac{\left(x^2-x^2+10x-25\right)x\left(x+5\right)}{x\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)\left(2x-5\right)}=\dfrac{x}{5-x}+\dfrac{5\left(2x-5\right)x\left(x+5\right)}{x\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)\left(2x-5\right)}=\dfrac{x}{5-x}+\dfrac{5}{x-5}=\dfrac{x}{5-x}-\dfrac{5}{5-x}=\dfrac{x-5}{5-x}=\dfrac{-\left(5-x\right)}{5-x}=-1\)
Vậy A=-1
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
quy đồng mẫu thức của các phân tử
a, \(\dfrac{2}{5x^3y};\dfrac{5}{xy^2}\)
b, \(\dfrac{3x}{x-5};\dfrac{-2}{3\left(x-5\right)}\)
c, \(\dfrac{1}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)};\dfrac{5x}{x^2-9}\)
Rút gọn biểu thức
\(A=\dfrac{x^2}{5x+25}+\dfrac{2\left(x-5\right)}{x}+\dfrac{50+5x}{x\left(x+5\right)}\)
ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{0;-5\right\}\)
\(A=\dfrac{x^2}{5x+25}+\dfrac{2\left(x-5\right)}{x}+\dfrac{50+5x}{x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2}{5\left(x+5\right)}+\dfrac{2\left(x-5\right)}{x}+\dfrac{5x+50}{x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^3+2\cdot5\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)+5\left(5x+50\right)}{5x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^3+10x^2-250+25x+250}{5x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^3+10x^2+25x}{5x\left(x+5\right)}=\dfrac{x\left(x^2+10x+25\right)}{5x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x+5\right)^2}{5\left(x+5\right)}=\dfrac{x+5}{5}\)
Đúng 3
Bình luận (0)
\(A=\dfrac{x^2}{5x+25}+\dfrac{2\left(x-5\right)}{x}+\dfrac{50+5x}{x\left(x+5\right)}\left(ĐKXĐ:x\ne0;x\ne-5\right)\)
\(A=\dfrac{x^2}{5\left(x+5\right)}+\dfrac{2\left(x-5\right)}{x}+\dfrac{50+5x}{x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(A=\dfrac{x^2.x}{5x\left(x+5\right)}+\dfrac{2.5\left(x+5\right)\left(x-5\right)}{5x\left(x+5\right)}+\dfrac{5\left(50+5x\right)}{5x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(A=\dfrac{x^3}{5x\left(x+5\right)}+\dfrac{10.\left(x^2-25\right)}{5x\left(x+5\right)}+\dfrac{250+25x}{5x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(A=\dfrac{x^3}{5x\left(x+5\right)}+\dfrac{10x^2-250}{5x\left(x+5\right)}+\dfrac{250+25x}{5x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(A=\dfrac{x^3+10x^2-250+250+25x}{5x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(A=\dfrac{x^3+10x^2+25x}{5x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(A=\dfrac{x\left(x^2+10x+25\right)}{5x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(A=\dfrac{\left(x+5\right)^2}{5\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(A=\dfrac{x+5}{5}\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
giải các phương trình sau
1, \(\dfrac{5x^2-12}{x^2-1}+\dfrac{3}{x-1}=\dfrac{5x}{x+1}\)
2, \(\dfrac{3}{x-5}-\dfrac{15-3x}{x^2-25}=\dfrac{3}{x+5}\)
3, \(\dfrac{-3}{x-4}-\dfrac{3-5x}{x^2-16}=\dfrac{1}{x+4}\)
1: Ta có: \(\dfrac{5x^2-12}{x^2-1}+\dfrac{3}{x-1}=\dfrac{5x}{x+1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{5x^2-12}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}+\dfrac{3x+3}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{5x^2-5x}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}\)
Suy ra: \(5x^2+3x-9=5x^2-5x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8x=9\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{9}{8}\left(tm\right)\)
2: Ta có: \(\dfrac{3}{x-5}-\dfrac{15-3x}{x^2-25}=\dfrac{3}{x+5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3x+15}{\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)}+\dfrac{3x-15}{\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)}=\dfrac{3x-15}{\left(x+5\right)\left(x-5\right)}\)
Suy ra: \(6x=3x-15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=-15\)
hay \(x=-5\left(loại\right)\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
2. ĐKXĐ: $x\neq \pm 5$
PT \(\Leftrightarrow \frac{3}{x-5}+\frac{3x-15}{x^2-25}=\frac{3}{x+5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \frac{3}{x-5}+\frac{3(x-5)}{(x-5)(x+5)}=\frac{3}{x+5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \frac{3}{x-5}+\frac{3}{x+5}=\frac{3}{x+5}\Leftrightarrow \frac{3}{x-5}=0\) (vô lý)
Vậy pt vô nghiệm.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
3. ĐKXĐ: $x\neq \pm 4$
PT \(\Leftrightarrow \frac{-3(x+4)}{(x-4)(x+4)}-\frac{3-5x}{(x-4)(x+4)}=\frac{x-4}{(x-4)(x+4)}\)
\(\Rightarrow -3(x+4)-(3-5x)=x-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow 2x-15=x-4\Leftrightarrow x=11\) (thỏa mãn)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
a) \(\dfrac{5x-2}{3}+x=1+\dfrac{5-3x}{2}\)
b) \(\dfrac{\left(3x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)}{3}-\dfrac{2x^2+1}{2}=\dfrac{11}{2}\)
c) \(x-\dfrac{5x+2}{6}=\dfrac{7-3x}{4}\)
d) \(\dfrac{x-1}{2}+\dfrac{x-1}{3}-\dfrac{x-1}{6}=2\)
a, \(\Rightarrow10x-4+6x=6+15-9x\Leftrightarrow7x=25\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{25}{7}\)
b, \(\Rightarrow2\left(3x^2+5x-2\right)-6x^2-3=33\Leftrightarrow10x-7=33\Leftrightarrow x=4\)
c, \(\Rightarrow12x-10x-4=21-9x\Leftrightarrow11x=25\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{25}{11}\)
d, \(\Rightarrow3x-3+2x-2-x+1=12\Leftrightarrow4x=16\Leftrightarrow x=4\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
\(\dfrac{5x-2}{3}+x=1+\dfrac{5-3x}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{5x-2+3x}{3}=\dfrac{2+5-3x}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{8x-2}{3}=\dfrac{7-3x}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow16x-4=21-9x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow16x+9x=21+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow25x=25\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=1\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
\(a,\dfrac{5x-2}{3}+x=1+\dfrac{-3x+5}{2}\)
\(2\left(5x-2\right)+6x=-9x+21\)
\(16x+9x=21+4\)
\(25x=25\)
\(x=1\)
\(b,\dfrac{3x^2+5x-2}{3}-\dfrac{2x^2+1}{2}=\dfrac{11}{2}\)
\(\dfrac{6x^2=10x-4-6x^2-3}{6}=\dfrac{11}{2}\)
\(\dfrac{10x-4-3}{6}=\dfrac{11}{2}\)
\(\dfrac{10x-7}{6}=\dfrac{11}{2}\)
\(10x=33+7\)
\(x=4\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình
a) \(\dfrac{3}{5x-1}\)+ \(\dfrac{2}{3-5x}\)=\(\dfrac{4}{\left(1-5x\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
b) \(\dfrac{5-x}{4x^2-8x}\)+\(\dfrac{7}{8x}\)=\(\dfrac{x-1}{2x\left(x-2\right)}\)+\(\dfrac{1}{8x-16}\)
a:Sửa đề: \(\dfrac{3}{5x-1}+\dfrac{2}{3-x}=\dfrac{4}{\left(1-5x\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
=>3x-9-10x+2=-4
=>-7x-7=-4
=>-7x=3
=>x=-3/7
b: =>\(\dfrac{5-x}{4x\left(x-2\right)}+\dfrac{7}{8x}=\dfrac{x-1}{2x\left(x-2\right)}+\dfrac{1}{8\left(x-2\right)}\)
=>\(2\left(5-x\right)+7\left(x-2\right)=4\left(x-1\right)+x\)
=>10-2x+7x-14=4x-4+x
=>5x-4=5x-4
=>0x=0(luôn đúng)
Vậy: S=R\{0;2}
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
a, \(\dfrac{x^2}{5x-x^2}-\dfrac{3}{x}=\dfrac{4-x}{x-5}\)
b, \(\dfrac{x+1}{x-2}+\dfrac{x-1}{x+2}=\dfrac{2\left(x^2+2\right)}{x^2-4^{ }}\)
a: \(\Leftrightarrow-x^2-3\left(x-5\right)=x\left(4-x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x^2-3x+15=4x-x^2\)
=>-3x+15=4x
=>-7x=-15
hay x=15/7(nhận)
b: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)+\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)=2x^2+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+3x+2+x^2-3x+2=2x^2+4\)
=>4=4(luôn đúng)
Vậy: S={x|\(x\notin\left\{2;-2\right\}\)}
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
1/ \(\dfrac{5x+1}{8}-\dfrac{x-2}{4}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
2/ \(\dfrac{x+3}{4}+\dfrac{1-3x}{3}=\dfrac{-x+1}{18}\)
3/ \(\dfrac{x+2}{4}-\dfrac{5x}{6}=\dfrac{1-x}{3}\)
4/ \(\dfrac{x-3}{2}-\dfrac{x+1}{10}=\dfrac{x-2}{5}\)
5/ \(\dfrac{4x+1}{4}-\dfrac{9x-5}{12}+\dfrac{x-2}{3}=0\)
1: Ta có: \(\dfrac{5x+1}{8}-\dfrac{x-2}{4}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x+1-2\left(x-2\right)=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x+1-2x+4=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=-1\)
hay \(x=-\dfrac{1}{3}\)
2: Ta có: \(\dfrac{x+3}{4}+\dfrac{1-3x}{3}=\dfrac{-x+1}{18}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x+27+12-36x=-2x+2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-27x+2x=2-39\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{37}{25}\)
3: Ta có: \(\dfrac{x+2}{4}-\dfrac{5x}{6}=\dfrac{1-x}{3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x+6-10x=4-4x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-7x+4x=4-6=-2\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{2}{3}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
4: Ta có: \(\dfrac{x-3}{2}-\dfrac{x+1}{10}=\dfrac{x-2}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x-15-x-1=2x-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x-2x=-4+16=12\)
hay x=6
5: Ta có: \(\dfrac{4x+1}{4}-\dfrac{9x-5}{12}+\dfrac{x-2}{3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x+3-9x+5+4x-8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow7x=0\)
hay x=0
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Rút gọn:
\(A=\dfrac{x}{5-x}+\left(\dfrac{x}{x^2-25}+\dfrac{5-x}{5x+x^2}\right):\dfrac{2x-5}{x^2+5x}\)
\(B=\left[\left(\dfrac{1}{x^2}+1\right)\cdot\dfrac{1}{1+2x+x^2}+\left(1+\dfrac{1}{x}\right)\cdot\dfrac{2}{\left(1+x\right)^3}\right]:\dfrac{x-1}{x^3}\)
a) \(\dfrac{10-2x}{2}=\dfrac{25-5x}{5}\)
b) \(\dfrac{x-3}{x-1}-\dfrac{2x+1}{x+1}=\dfrac{x-x^2}{x^2-1}\)
a, \(\dfrac{10-2x}{2}=\dfrac{25-5x}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2\left(5-x\right)}{2}=\dfrac{5\left(5-x\right)}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5-x=5-x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow0x=0\)
⇒ Có vô số giá trị của x thỏa mãn.
Vậy...
b, ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne\pm1\)
\(\dfrac{x-3}{x-1}-\dfrac{2x+1}{x+1}=\dfrac{x-x^2}{x^2-1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+1\right)-\left(2x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{x-x^2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2-2x-3-2x^2+x+1=x-x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-1\left(ktm\right)\)
Vậy...
Đúng 2
Bình luận (1)
a) Ta có: \(\dfrac{10-2x}{2}=\dfrac{25-5x}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5\left(10-2x\right)=2\left(25-5x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow50-10x=50-10x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow0x=0\)(phương trình có vô số nghiệm)
Vậy: S={x|\(x\in R\)}
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)