Sắp xếp các tỉ số lượng giác sau theo thứ tự từ bé đến lớn:
a, tan 12 0 , cot 61 0 , tan 28 0 , cot 79 0 15 ' , tan 58 0
b, cos 67 0 , sin 56 0 , cos 63 0 41 ' , sin 74 0 , cos 85 0
Sắp xếp các tỉ số lượng giác sau theo thứ tự từ bé đến lớn:
a, tan 12 0 , cot 61 0 , tan 28 0 , cot 79 0 15 ' , tan 58 0
b, cos 67 0 , sin 56 0 , cos 63 0 41 ' , sin 74 0 , cos 85 0
a,
Đổi `tan 12^o = cot 78^o ; tan 28^o = cot 62^o ; tan 58^o = cot 32^o`
Vì `32^o<61^o<62^o<78^o<79^15'`
`->cot 32^o>cot 61^o>cot 62^o > cot 78^o > cot 79^o15'`
`->tan 58^o>cot 61^o > tan 28^o > tan 12^o > cot 79^o15'`
b,
Đổi `sin 56^o = cos 34^o ; sin 74^o=cos 16^o`
Vì `16^o<24^o<63^o41'<67^o<85 ^o`
`->cos 16^o>cos 34^o>cos 63^o41'>cos 67^o>cos 85 ^o`
`->sin 74^o>sin 56^o>cos 63^o41'>cos 67^o>cos 85 ^o`
Tìm nghiệm của phương trình lượng giác cos 2 x - cos x = 0 thỏa mãn điều kiện 0 < x < π
A. x = π 2
B. x=0
C. x= π
D. x=2
Đáp án A
Giải phương trình lượng giác sau đó kết hợp vào điều kiện của đầu bài để tìm ra nghiệm thỏa mãn.
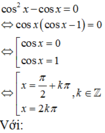
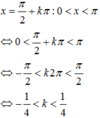
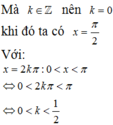
Mà k ∈ ℤ nên không có giá trị k nào thỏa mãn.
Sai lầm và chú ý: Đối với những bài toán giải phương trình lượng giác thỏa mãn điều kiện cho trước, ta cần tìm được x sau đó cho x thỏa mãn điều kiện đầu bài và cô lập được k khi đó ta sẽ tìm được giá trị nguyên k thỏa mãn và sẽ tìm đc x.
cho góc α thoả mãn\(\dfrac{3\pi}{2}< \alpha< 2\pi\). Mệnh đề nào sau đây đúng?
A. \(tan\)α > 0 B. \(cot\)α > 0 C. \(sin\)α > 0 D. \(cos\)α > 0
Giải các pt sau:
a) \(\cos^2x-\cos x=0\)
b) \(2\sin2x\) + \(\sqrt{2}\sin4x=0\)
c) \(8\cos^2x+2\sin x-7=0\)
d) \(4\cos^4x+\cos^2x-3=0\)
e) \(\sqrt{3}\tan x-6\cot x+\left(2\sqrt{3}-3\right)=0\)
a, \(cos^2x-cosx=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cosx\left(cosx-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}cosx=0\\cosx=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k\pi\\x=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
b, \(2sin2x+\sqrt{2}sin4x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2sin2x+2\sqrt{2}sin2x.cos2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sin2x\left(1+\sqrt{2}cos2x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}sin2x=0\\1+\sqrt{2}cos2x=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=k\pi\\cos2x=-\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\\2x=\dfrac{3\pi}{4}+k2\pi\\2x=\dfrac{\pi}{4}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\\x=\dfrac{3\pi}{8}+k\pi\\x=\dfrac{\pi}{8}+k\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
a, \(cos^2x-cosx=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cosx\left(cosx-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}cosx=0\\cosx=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k\pi\\x=k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\) (k ∈ Z)
Vậy...
b, \(2sin2x+\sqrt{2}sin4x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2sin2x+2\sqrt{2}sin2x.cos2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2sin2x\left(1+\sqrt{2}cos2x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}sin2x=0\\cos2x=\dfrac{-\sqrt{2}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=k\pi\\2x=\pm\dfrac{3\pi}{4}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\\x=\pm\dfrac{3\pi}{8}+k\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy...
c, \(8cos^2x+2sinx-7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8\left(1-sin^2x\right)+2sinx-7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8sin^2x-2sinx-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}sinx=\dfrac{1}{2}\\sinx=-\dfrac{1}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\pi}{6}+k2\pi\\x=\dfrac{5\pi}{6}+k2\pi\\x=arcsin\left(-\dfrac{1}{4}\right)+k2\pi\\x=\pi-arcsin\left(-\dfrac{1}{4}\right)+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy...
d, \(4cos^4x+cos^2x-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}cos^2x=\dfrac{3}{4}\\cos^2x=-1\left(loai\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{cos2x+1}{2}=\dfrac{3}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos2x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=\pm\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k2\pi\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\pm\dfrac{\pi}{6}+k\pi\)
Vậy...
e, \(\sqrt{3}tanx-6cotx+\left(2\sqrt{3}-3\right)=0\) (ĐK: \(x\ne\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\))
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{3}tanx-\dfrac{6}{tanx}+\left(2\sqrt{3}-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{3}tan^2x+\left(2\sqrt{3}-3\right)tanx-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}tanx=\sqrt{3}\\tanx=-2\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k\pi\left(tm\right)\\x=arctan\left(-2\right)+k\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy...
c, \(8cos^2x+2sinx-7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-8sin^2x+2sinx+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}sinx=\dfrac{1}{2}\\sinx=-\dfrac{1}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Với \(sinx=\dfrac{1}{2}\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\pi}{6}+k2\pi\\x=\dfrac{5\pi}{6}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
Với \(sinx=-\dfrac{1}{4}\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=arcsin\left(-\dfrac{1}{4}\right)+k2\pi\\x=\pi-arcsin\left(-\dfrac{1}{4}\right)+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
d, \(4cos^4x+cos^2x-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4cos^2x-3\right)\left(cos^2x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4cos^2x-3=0\left(\text{Vì }cos^2x+1>0\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos^2x=\dfrac{3}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cosx=\pm\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\)
Với \(cosx=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\Leftrightarrow x=\pm\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k2\pi\)
Với \(cosx=-\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\Leftrightarrow x=\pm\dfrac{5\pi}{6}+k2\pi\)
tính \(\sin x.\cos x+\frac{\sin^2x}{1+\cot x}+\frac{\cos^2x}{1+\tan x}\) với \(0^0< x< 90^0\)
1. Cho góc \(\alpha\) thỏa mãn \(60^0\le\alpha< 90^0.\) Tìm GTNN của \(\left(\tan\alpha-1\right)^2+\left(\frac{1}{\tan\alpha}-1\right)^2\)
2. Với giá trị nào của góc nhọn x thì \(P\left(x\right)=3\sin x+\sqrt{3}\cos x\) có GTNN? Tìm GTNN đó.
Câu 2 đề sai, phải là tìm \(max\) bạn nhé.
Đặt \(a=\sin x,b=\cos x\) thì \(P\left(x\right)=3a+\sqrt{3}b\) với \(a^2+b^2=1\)
(Tư tưởng Cauchy-Schwarz quá rõ)
Ta có \(\left(a^2+b^2\right)\left(9+3\right)\ge\left(3a+\sqrt{3}b\right)^2=P^2\left(x\right)\)
Suy ra \(P\left(x\right)\le2\sqrt{3}\). Đẳng thức xảy ra tại \(x=60\) độ.
Câu 1 để mình suy nghĩ sau.
1. Giải các phương trình sau:
a) \(\cos\left(x+15^0\right)=\dfrac{2}{5}\)
b) \(\cot\left(2x-10^0\right)=4\)
c) \(\cos\left(x+12^0\right)+\sin\left(78^0-x\right)=1\)
2. Định m để các phương trình sau có nghiệm:
\(\sin\left(3x-27^0\right)=2m^2+m\)
c.
\(\Leftrightarrow cos\left(x+12^0\right)+cos\left(90^0-78^0+x\right)=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2cos\left(x+12^0\right)=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos\left(x+12^0\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+12^0=60^0+k360^0\\x+12^0=-60^0+k360^0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=48^0+k360^0\\x=-72^0+k360^0\end{matrix}\right.\)
2.
Do \(-1\le sin\left(3x-27^0\right)\le1\) nên pt có nghiệm khi:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2m^2+m\ge-1\\2m^2+m\le1\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2m^2+m+1\ge0\left(luôn-đúng\right)\\2m^2+m-1\le0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow-1\le m\le\dfrac{1}{2}\)
a.
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+15^0=arccos\left(\dfrac{2}{5}\right)+k360^0\\x+15^0=-arccos\left(\dfrac{2}{5}\right)+k360^0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-15^0+arccos\left(\dfrac{2}{5}\right)+k360^0\\x=-15^0-arccos\left(\dfrac{2}{5}\right)+k360^0\end{matrix}\right.\)
b.
\(2x-10^0=arccot\left(4\right)+k180^0\)
\(\Rightarrow x=5^0+\dfrac{1}{2}arccot\left(4\right)+k90^0\)
2.
Phương trình \(sin\left(3x-27^o\right)=2m^2+m\) có nghiệm khi:
\(2m^2+m\in\left[-1;1\right]\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2m^2+m\le1\\2m^2+m\ge-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(m+1\right)\left(2m-1\right)\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-1\le m\le\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Trong các khẳng định sau đây, khẳng định nào sai?
A. |x| ≥ 0, ∀ x B. |x| + x ≥ 0, ∀ x
C. |x| ≥ a, ⇒ x ≥ a D. |x| - x ≥ 0, ∀ x
A, B, D đúng theo các tính chất của giá trị tuyệt đối, do đó C sai.
Đáp án: C
Giải các phương trình sau
1) sin3x = 0
2) cos25x = 0
3) tan (x - 15o) = 3tan (x + 15o)
4) cos x + cos 2x + cos 3x = 0
5) sin 2x + sin 4x + sin 6x = 0
6) tan x + tan 2x + tan x.tan 2x = 1
7) tan x + tan 2x + tan 3x = tan x.tan 2x.tan 3x
8) cot2x + \(\frac{\text{3}}{\text{sin x}}\) + 3 = 0
1.
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=k\pi\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{k\pi}{3}\)
2.
\(\Leftrightarrow cos5x=0\Leftrightarrow5x=\frac{\pi}{2}+k\pi\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{\pi}{10}+\frac{k\pi}{5}\)
4.
\(cos3x+cosx+cos2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2cos2x.cosx+cos2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos2x\left(2cosx+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}cos2x=0\\cosx=-\frac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\frac{\pi}{4}+\frac{k\pi}{2}\\x=\pm\frac{2\pi}{3}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
3. ĐKXĐ: ...
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{sin\left(x-15\right)}{cos\left(x-15\right)}=\frac{3sin\left(x+15\right)}{cos\left(x+15\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sin\left(x-15\right)cos\left(x+15\right)=3sin\left(x+15\right)cos\left(x-15\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sin2x-sin30^0=3\left[sin2x+sin30^0\right]\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sin2x-\frac{1}{2}=3sin2x+\frac{3}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sin2x=-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=-\frac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-\frac{\pi}{4}+k\pi\)
5.
\(sin6x+sin2x+sin4x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2sin4x.cos2x+sin4x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sin4x\left(2cos2x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}sin4x=0\\cos2x=-\frac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\frac{k\pi}{4}\\x=\pm\frac{\pi}{3}+k\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
6. ĐKXĐ; ...
\(\Leftrightarrow tanx+tan2x=1-tanx.tan2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{tanx+tan2x}{1-tanx.tan2x}=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow tan3x=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{\pi}{12}+\frac{k\pi}{3}\)
1.Cho \(\alpha,\beta\left(\alpha\ne\beta\right)\in\left(0;\dfrac{\pi}{2}\right)\)và thỏa mãn điều kiện \(\dfrac{cosx-cos\alpha}{cosx-cos\beta}=\dfrac{sin^2\alpha cos\beta}{sin^2\beta cos\alpha}\)
(giả sử \(x\) xác định). Chứng minh\(tan^2\dfrac{x}{2}=tan^2\dfrac{\alpha}{2}tan^2\dfrac{\beta}{2}\)
2. Giải hệ phương trình \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}xy-2y-3=\sqrt{y-x-1}+\sqrt{y-3x+5}\\\left(1-y\right)\sqrt{2x-y}+2\left(x-1\right)=\left(2x-y-1\right)\sqrt{y}\end{matrix}\right.\)
3. Cho ba số thực dương a, b, c thỏa mãn \(\dfrac{1}{a+2}+\dfrac{1}{b+3}+\dfrac{1}{c+4}=1\). Tìm Min của biểu thức \(P=a+b+c+\dfrac{4}{\sqrt[3]{a\left(b+1\right)\left(c+2\right)}}+3\)
4. Tìm m để hệ bất phương trình \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2-5x+9\le\left|x-6\right|\\x^2+2x-3m^2+4\left|m\right|-4\le0\end{matrix}\right.\)
2.
ĐK: \(2x-y\ge0;y\ge0;y-x-1\ge0;y-3x+5\ge0\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}xy-2y-3=\sqrt{y-x-1}+\sqrt{y-3x+5}\left(1\right)\\\left(1-y\right)\sqrt{2x-y}+2\left(x-1\right)=\left(2x-y-1\right)\sqrt{y}\left(2\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left(2\right)\Leftrightarrow\left(1-y\right)\sqrt{2x-y}+y-1+2x-y-1-\left(2x-y-1\right)\sqrt{y}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(1-y\right)\left(\sqrt{2x-y}-1\right)+\left(2x-y-1\right)\left(1-\sqrt{y}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(1-\sqrt{y}\right)\left(\sqrt{2x-y}-1\right)\left(1+\sqrt{y}\right)+\left(\sqrt{2x-y}-1\right)\left(1-\sqrt{y}\right)\left(\sqrt{2x-y}+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(1-\sqrt{y}\right)\left(\sqrt{2x-y}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{y}+\sqrt{2x-y}+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}y=1\\y=2x-1\end{matrix}\right.\) (Vì \(\sqrt{y}+\sqrt{2x-y}+2>0\))
Nếu \(y=1\), khi đó:
\(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow x-5=\sqrt{-x}+\sqrt{-3x+6}\)
Phương trình này vô nghiệm
Nếu \(y=2x-1\), khi đó:
\(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow2x^2-5x-1=\sqrt{x-2}+\sqrt{4-x}\) (Điều kiện: \(2\le x\le4\))
\(\Leftrightarrow2x\left(x-3\right)+x-3+1-\sqrt{x-2}+1-\sqrt{4-x}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{1+\sqrt{4-x}}-\dfrac{1}{1+\sqrt{x-2}}+2x+1\right)=0\)
Ta thấy: \(1+\sqrt{x-2}\ge1\Rightarrow-\dfrac{1}{1+\sqrt{x-2}}\ge-1\Rightarrow1-\dfrac{1}{1+\sqrt{x-2}}\ge0\)
Lại có: \(\dfrac{1}{1+\sqrt{4-x}}>0\); \(2x>0\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{1+\sqrt{4-x}}-\dfrac{1}{1+\sqrt{x-2}}+2x+1>0\)
Nên phương trình \(\left(1\right)\) tương đương \(x-3=0\Leftrightarrow x=3\Rightarrow y=5\)
Ta thấy \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(3;5\right)\) thỏa mãn điều kiện ban đầu.
Vậy hệ phương trình đã cho có nghiệm \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(3;5\right)\)