Giải phương trình: (√25 - x^2) - (√10 - x^2) = 3

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Giải phương trình \(\sqrt{25-x^2}-\sqrt{10-x^2}=3\)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
giải phương trình :x^2 +(10/x) ^2 =25
Giải phương trình:
A/ 2×-5=-x+4. B/(4x-10)(25+5x)=0.
c/1+ x/3-x=5x/(x+2)(3-x)+2/x+2.
D/ x/3 -2x+1/2 =x/6-x
\(a,2x-5=-x+4\\ \Leftrightarrow3x=9\\ \Leftrightarrow x=3\\ b,\left(4x-10\right)\left(25+5x\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}4x-10=0\\25+5x=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{5}{2}\\x=-5\end{matrix}\right.\\ c,\dfrac{x}{3}-\dfrac{2x+1}{2}=\dfrac{x}{6}-x\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x}{6}-\dfrac{3\left(2x+1\right)}{6}-\dfrac{x}{6}+\dfrac{6x}{6}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow2x-6x-3-x+6x=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x-3=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x=3\)
d, ĐKXĐ:\(x\ne-2,x\ne3\)
\(1+\dfrac{x}{3-x}=\dfrac{5x}{\left(x+2\right)\left(3-x\right)}+\dfrac{2}{x+2}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x+2\right)\left(3-x\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left(3-x\right)}+\dfrac{x\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left(3-x\right)}-\dfrac{5x}{\left(x+2\right)\left(3-x\right)}-\dfrac{2\left(3-x\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left(3-x\right)}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{-x^2+x+6}{\left(x+2\right)\left(3-x\right)}+\dfrac{x^2+2x}{\left(x+2\right)\left(3-x\right)}-\dfrac{5x}{\left(x+2\right)\left(3-x\right)}-\dfrac{6-2x}{\left(x+2\right)\left(3-x\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{-x^2+x+6+x^2+2x-5x-6+2x}{\left(x+2\right)\left(3-x\right)}=0\\ \Rightarrow0=0\left(luôn.đúng\right)\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình \(\sqrt{25-x^2}-\sqrt{10-x^2}=3\)
\(DK:x\in\left[-\sqrt{10};\sqrt{10}\right]\)
PT\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{25-x^2}-4\right)+\left(1-\sqrt{10-x^2}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{9-x^2}{\sqrt{25-x^2}+4}-\frac{9-x^2}{1+\sqrt{10-x^2}}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(9-x^2\right)\left(\frac{1}{\sqrt{25-x^2}+4}-\frac{1}{1+\sqrt{10-x^2}}\right)=0\)
Ta di chung minh:
\(\sqrt{25-x^2}+4>1+\sqrt{10-x^2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow41-x^2+8\sqrt{25-x^2}>11-x^2+2\sqrt{10-x^2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow15+4\sqrt{25-x^2}>\sqrt{10-x^2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow325-x^2+120\sqrt{25-x^2}>10-x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow315+120\sqrt{25-x^2}>0\left(True\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{1}{\sqrt{25-x^2}+4}-\frac{1}{1+\sqrt{10-x^2}}< 0\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=3\left(n\right)\\x=-3\left(n\right)\end{cases}}\)
Vay PT co nghiem la \(x=3\)va \(x=-3\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải các bất phương trình sau:
a) \(7{x^2} - 19x - 6 \ge 0\)
b) \( - 6{x^2} + 11x > 10\)
c) \(3{x^2} - 4x + 7 > {x^2} + 2x + 1\)
d) \({x^2} - 10x + 25 \le 0\)
a) Xét tam thức \(f\left( x \right) = 7{x^2} - 19x - 6\) có \(\Delta = 529 > 0\), có hai nghiệm phân biệt \({x_1} = - \frac{2}{7},{x_2} = 3\) và có \(a = 7 > 0\)
Ta có bảng xét dấu như sau
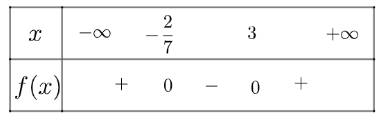
Vậy nghiệm của bất phương trình là đoạn \(\left[ { - \frac{2}{7};3} \right]\)
b) \( - 6{x^2} + 11x > 10 \Leftrightarrow - 6{x^2} + 11x - 10 > 0\)
Xét tam thức \(f\left( x \right) = - 6{x^2} + 11x - 10\) có \(\Delta = - 119 < 0\)và có \(a = - 6 < 0\)
Ta có bảng xét dấu như sau

Vậy bất phương trình vô nghiệm
c) \(3{x^2} - 4x + 7 > {x^2} + 2x + 1 \Leftrightarrow 2{x^2} - 6x + 6 > 0\)
Xét tam thức \(f\left( x \right) = 2{x^2} - 6x + 6\) có \(\Delta = - 12 < 0\)và có \(a = 2 > 0\)
Ta có bảng xét dấu như sau
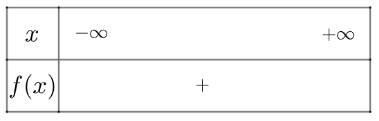
Vậy bất phương trình có vô số nghiệm
d) Xét tam thức \(f\left( x \right) = {x^2} - 10x + 25\) có \(\Delta = 0\), có nghiệm kép \({x_1} = {x_2} = 5\) và có \(a = 1 > 0\)
Ta có bảng xét dấu như sau
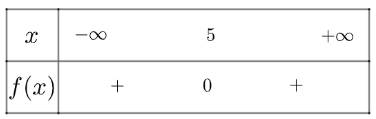
Vậy nghiệm của bất phương trình là \(x = 5\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải bất phương trình sau: \(\dfrac{x^2-26}{10}\)+\(\dfrac{x^2-25}{11}\) \(\ge\) \(\dfrac{x^2-24}{12}\)+\(\dfrac{x^2-23}{13}\)
\(\dfrac{x^2-26}{10}+\dfrac{x^2-25}{11}\ge\dfrac{x^2-24}{12}+\dfrac{x^2-23}{13}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\dfrac{x^2-26}{10}-1\right)+\left(\dfrac{x^2-25}{11}-1\right)\ge\left(\dfrac{x^2-24}{12}-1\right)+\left(\dfrac{x^2-23}{13}-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2-36}{10}+\dfrac{x^2-36}{11}\ge\dfrac{x^2-36}{12}+\dfrac{x^2-36}{13}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2-36}{10}+\dfrac{x^2-36}{11}-\dfrac{x^2-36}{12}-\dfrac{x^2-36}{13}\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-36\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{10}+\dfrac{1}{11}-\dfrac{1}{12}-\dfrac{1}{13}\right)\ge0\)
Vì \(\dfrac{1}{10}+\dfrac{1}{11}-\dfrac{1}{12}-\dfrac{1}{13}>0\Rightarrow x^2-36\ge0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\le-6\\x\ge6\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Bất phương trình đó tương đương với:
\(\left(\dfrac{x^2-26}{10}-1\right)+\left(\dfrac{x^2-25}{11}-1\right)\ge\left(\dfrac{x^2-24}{12}-1\right)+\left(\dfrac{x^2-23}{13}-1\right)\)
⇔ \(\dfrac{x^2-36}{10}+\dfrac{x^2-36}{11}\ge\dfrac{x^2-36}{12}+\dfrac{x^2-36}{13}\)
⇔ \(\dfrac{x^2-36}{10}+\dfrac{x^2-36}{11}-\dfrac{x^2-36}{12}-\dfrac{x^2-36}{13}\ge0\)
⇔ \(\left(x^2-36\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{10}+\dfrac{1}{11}-\dfrac{1}{12}-\dfrac{1}{13}\right)\ge0\)
+)Vì \(\dfrac{1}{10}>\dfrac{1}{11}>\dfrac{1}{12}>\dfrac{1}{13}\) nên \(\dfrac{1}{10}+\dfrac{1}{11}-\dfrac{1}{12}-\dfrac{1}{13}>0\)
⇔ \(x^2-36\ge0\)
⇔ \(x^2\ge36\)
⇔ \(\sqrt{x^2}\ge6\)
⇔ \(\left|x\right|\ge6\)
⇔ \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\ge6\\x\le-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
➤ Vậy \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\ge6\\x\le-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
giải phương trình \(\frac{3}{2x+10}-\frac{2x}{^{x^2-25}}+\frac{3}{x-5}=0\)
giải phương trình tích :
a) ( 2x - 10 ) ( 5x + 25) = 0
b) ( x + 15) ( x - 2 ) = 0
c) x2 - 7x =0
a: (2x-10)(5x+25)=0
=>2x-10=0 hoặc 5x+25=0
=>x=5 hoặc x=-5
b: (x+15)(x-2)=0
=>x+15=0 hoặc x-2=0
=>x=-15 hoặc x=2
c: =>x(x-7)=0
=>x=0 hoặc x=7
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
a, (2x - 10) (5x + 25) = 0
⇒ 2x - 10 = 0 hoặc 5x + 25 = 0
⇒ x = 5 hoặc x = -5
b, (x + 15) (x - 2) = 0
⇒ x + 15 = 0 hoặc x - 2 = 0
⇒ x = -15 hoặc x = 2
c: =>x(x-7)=0
=>x=0 hoặc x=7
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
giải phương trình
a)\(\sqrt{x-1}+\sqrt{4x-4}-\sqrt{25x-25}+2=0\)
b) \(\dfrac{1}{3}\sqrt{2x}-\sqrt{8x}+\sqrt{18x}-10=2\)
\(a,ĐK:x\ge1\\ PT\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x-1}+2\sqrt{x-1}-5\sqrt{x-1}=-2\\ \Leftrightarrow-2\sqrt{x-1}=-2\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x-1}=1\\ \Leftrightarrow x-1=1\Leftrightarrow x=2\left(tm\right)\\ b,ĐK:x\ge0\\ PT\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{3}\sqrt{2x}-2\sqrt{2x}+3\sqrt{2x}=12\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4}{3}\sqrt{2x}=12\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2x}=9\\ \Leftrightarrow2x=81\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{81}{2}\left(tm\right)\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)


























