TÌM MMAX
-X2-4X-Y2+2Y
tìm GTLN của biểu thức
C=-x2-4x-y2+8y+2
D=2023-8x+2y+4xy-y2-5x2
\(C=-\left(x^2+4x+4\right)-\left(y^2-8y+16\right)+22\\ =-\left(x^2+2x.2+2^2\right)-\left(y^2-2.y.4+4^2\right)+22\\ =-\left(x+2\right)^2-\left(y-4\right)^2+22\\ Vậy:max_C=22.khi.x=-2.và.y=4\)
Tìm GTNN của các biểu thức sau:
a. A= 2a2 + 3ab + b22
b. x2 - 4x + y2 - 6y + 1
c. x2 - 4xy + 5y2 -2y + 5
a, xem lại đề
\(b,x^2-4x+y^2-6y+1\\ =\left(x^2-4x+4\right)+\left(y^2-6y+9\right)-12\\ =\left(x-2\right)^2+\left(y-3\right)^2-12\ge-12\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\y=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy ...
\(c,x^2-4xy+5y^2-2y+5\\ =\left(x^2-4xy+4y^2\right)+\left(y^2-2y+1\right)+4\\ =\left(x-2y\right)^2+\left(y-1\right)^2+4\ge4\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy ...
a,
b,x2−4x+y2−6y+1=(x2−4x+4)+(y2−6y+9)−12=(x−2)2+(y−3)2−12≥−12b,x2−4x+y2−6y+1=(x2−4x+4)+(y2−6y+9)−12=(x−2)2+(y−3)2−12≥−12
Dấu "=" xảy ra⇔{x=2y=3⇔{x=2y=3
Vậy ...
c,x2−4xy+5y2−2y+5=(x2−4xy+4y2)+(y2−2y+1)+4=(x−2y)2+(y−1)2+4≥4c,x2−4xy+5y2−2y+5=(x2−4xy+4y2)+(y2−2y+1)+4=(x−2y)2+(y−1)2+4≥4
Dấu "=" xảy ra⇔{x=2y=1⇔{x=2y=1
Vậy ...
Tìm tâm và bán kính của các đường tròn sau:
a, x2 + y2– 2x – 2y - 2 = 0
b, 16x2 + 16y2 + 16x – 8y -11 = 0
c, x2 + y2 - 4x + 6y – 3 = 0
Cách 1 : Xác định các hệ số a, b, c.
a) x2 + y2 – 2x – 2y – 2 = 0 có hệ số a = 1 ; b = 1 ; c = –2
⇒ tâm I (1; 1) và bán kính 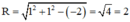
b) 16x2 + 16y2 + 16x – 8y –11 = 0
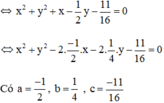
⇒ Đường tròn có tâm 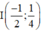 , bán kính
, bán kính 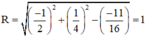
c) x2 + y2 - 4x + 6y - 3 = 0
⇔ x2 + y2 - 2.2x - 2.(-3).y - 3 = 0
có hệ số a = 2, b = -3,c = -3
⇒ Đường tròn có tâm I(2 ; –3), bán kính 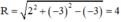
Cách 2 : Đưa về phương trình chính tắc :
a) x2 + y2 - 2x - 2y - 2 = 0
⇔ (x2 - 2x + 1) + (y2 - 2y +1) = 4
⇔(x-1)2 + (y-1)2 = 4
Vậy đường tròn có tâm I(1 ; 1) và bán kính R = 2.
b) 16x2 + 16y2 + 16x - 8y - 11 = 0
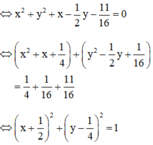
Vậy đường tròn có tâm 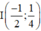 và bán kính R = 1.
và bán kính R = 1.
c) x2 + y2 - 4x + 6y -3 = 0
⇔ (x2 - 4x + 4) + (y2 + 6y + 9) = 4 + 9 + 3
⇔ (x - 2)2 + (y + 3)2 = 16
Vậy đường tròn có tâm I( 2 ; –3) và bán kính R = 4.
Tìm tọa độ tâm I của mặt cầu S : x 2 + y 2 + z 2 + 4 x - 2 y + 6 z + 5 = 0
A. I(1;-3;-2)
B. I(-3;-2;1)
C. I(2;-1;3)
D. I(-2;1;-3)
a,A=x2+x-2 b,B=4x-x2+5 c,C=9x2-6x+3 d,D=3x+x2-7 e,E=x2+y2-3x+2y+3 f,F=x2+y2-x+4y+5
Lần sau bạn chú ý viết đầy đủ yêu cầu của đề bài.
a) \(A=x^2+x-2=\left(x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)\)
b) \(B=-x^2+4x+5=-\left(x^2-4x-5\right)=-\left(x-5\right)\left(x+1\right)\)
c) \(C=9x^2-6x+3=3\left(3x^2-2x+1\right)\)
Phân tích các đa thức sau thành nhân tử:
a,x3+4x-5
b,x3-3x2+4
c,x3+2x2+3x+2
d,x2+2xy+y2+2x-2y-3
e,(x2+3x)2-2(x2+3x)-8
f,(x2+4x+10)2-7(x2+4x+11)+7
a) x3+4x-5 = x3-x2+x2+4x-5=(x3-x2)+(x2-x)+(5x-5)=x2(x-1)+x(x-1)+5(x-1)=(x2+x+5)(x-1)
b) x3-3x2+4=x3-2x2-x2+4=(x3-2x2)-(x2-4)=x2(x-2)-(x-2)(x+2)=(x2-x+2)(x-2)
c) x3+2x2+3x+2=x3+x2+x2+x+2x+2=(x3+x2)+(x2+x)+(2x+2)=x2(x+1)+x(x+1)+2(x+1)=(x2+x+2)(x+1)
d) bạn xem lại đề đúng ko
e) (x2+3x)2-2(x2+3x)-8=x4+6x3+9x2-2x2-6x-8=x4+6x3+7x2-6x-8=x4-x3+7x3-7x2+14x2-14x+8x-8=(x4-x3)+(7x3-7x2)+(14x2-14x)+(8x-8)=x3(x-1)+7x2(x-1)+14x(x-1)+8(x-1)=(x3+7x2+14x+8)(x-1)=(x3+x2+6x2+6x+8x+8)(x-1)=\(\left[\left(x^3+x^2\right)+\left(6x^2+6x\right)+\left(8x+8\right)\right]\left(x-1\right)\)\(=\left[x^2\left(x+1\right)+6x\left(x+1\right)+8\left(x+1\right)\right]\left(x-1\right)\)\(=\left(x^2+6x+8\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)\)\(=\left(x^2+2x+4x+8\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)\)\(=\left[\left(x^2+2x\right)+\left(4x+8\right)\right]\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)\)\(=\left[x\left(x+2\right)+4\left(x+2\right)\right]\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)\)=\(\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x+4\right)\)
f) (x2+4x+10)2-7(x2+4x+11)+7=(x2+4x+10)2-\(\left[7\left(x^2+4x+11\right)-7\right]\)\(=\left(x^2+4x+10\right)^2-7\left(x^2+4x+10\right)\)\(=\left(x^2+4x+10\right)\left(x^2+4x+3\right)\)
a) Ta có: \(x^3+4x-5\)
\(=x^3-x+5x-5\)
\(=x\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)+5\left(x-1\right)\)
\(=\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+5\right)\)
b) Ta có: \(x^3-3x^2+4\)
\(=x^3+x^2-4x^2+4\)
\(=x^2\left(x+1\right)-4\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\)
\(=\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-4x+4\right)\)
\(=\left(x+1\right)\cdot\left(x-2\right)^2\)
c) Ta có: \(x^3+2x^2+3x+2\)
\(=x^3+x^2+x^2+x+2x+2\)
\(=x^2\left(x+1\right)+x\left(x+1\right)+2\left(x+1\right)\)
\(=\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2+x+2\right)\)
d) Ta có: \(x^2+2xy+y^2+2x+2y-3\)
\(=\left(x+y\right)^2+2\left(x+y\right)-3\)
\(=\left(x+y\right)^2+3\left(x+y\right)-\left(x+y\right)-3\)
\(=\left(x+y\right)\left(x+y+3\right)-\left(x+y+3\right)\)
\(=\left(x+y+3\right)\left(x+y-1\right)\)
e) Ta có: \(\left(x^2+3x\right)^2-2\left(x^2+3x\right)-8\)
\(=\left(x^2+3x\right)^2-4\left(x^2+3x\right)+2\left(x^2+3x\right)-8\)
\(=\left(x^2+3x\right)\left(x^2+3x-4\right)+2\left(x^2+3x-4\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2+3x-4\right)\left(x^2+3x+2\right)\)
\(=\left(x+4\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)\)
f) Ta có: \(\left(x^2+4x+10\right)^2-7\left(x^2+4x+11\right)+7\)
\(=\left(x^2+4x+10\right)^2-7\left(x^2+4x+10\right)-7+7\)
\(=\left(x^2+4x+10\right)\left(x^2+4x+10-7\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2+4x+3\right)\left(x^2+4x+10\right)\)
\(=\left(x+1\right)\left(x+3\right)\left(x^2+4x+10\right)\)
Trong tất cả các cặp (x; y) thỏa mãn log x 2 + y 2 + 2 ( 4 x + 4 y - 4 ) ≥ 1 . Tìm m nhỏ nhất để tồn tại duy nhất cặp (x; y) sao cho x 2 + y 2 + 2 x - 2 y + 2 - m = 0
A. ( 10 - 2 ) 2
B. 10 + 2
C. ( 10 + 2 ) 2
D. 10 - 2
Bài 1: Phân tích các đa thức sau thành nhân tử
a)x2-y2-2x+2y e)x4+4y4
b)x2(x-1)+16(1-x) f)x4-13x2+36
c)x2+4x-y2+4 g) (x2+x)2+4x2+4x-12
d)x3-3x2-3x+1 h)x6+2x5+x4-2x3-2x2+1
a.
$x^2-y^2-2x+2y=(x^2-y^2)-(2x-2y)=(x-y)(x+y)-2(x-y)=(x-y)(x+y-2)$
b.
$x^2(x-1)+16(1-x)=x^2(x-1)-16(x-1)=(x-1)(x^2-16)=(x-1)(x-4)(x+4)$
c.
$x^2+4x-y^2+4=(x^2+4x+4)-y^2=(x+2)^2-y^2=(x+2-y)(x+2+y)$
d.
$x^3-3x^2-3x+1=(x^3+1)-(3x^2+3x)=(x+1)(x^2-x+1)-3x(x+1)$
$=(x+1)(x^2-4x+1)$
e.
$x^4+4y^4=(x^2)^2+(2y^2)^2+2.x^2.2y^2-4x^2y^2$
$=(x^2+2y^2)^2-(2xy)^2=(x^2+2y^2-2xy)(x^2+2y^2+2xy)$
f.
$x^4-13x^2+36=(x^4-4x^2)-(9x^2-36)$
$=x^2(x^2-4)-9(x^2-4)=(x^2-9)(x^2-4)=(x-3)(x+3)(x-2)(x+2)$
g.
$(x^2+x)^2+4x^2+4x-12=(x^2+x)^2+4(x^2+x)-12$
$=(x^2+x)^2-2(x^2+x)+6(x^2+x)-12$
$=(x^2+x)(x^2+x-2)+6(x^2+x-2)=(x^2+x-2)(x^2+x+6)$
$=[x(x-1)+2(x-1)](x^2+x+6)=(x-1)(x+2)(x^2+x+6)$
h.
$x^6+2x^5+x^4-2x^3-2x^2+1$
$=(x^6+2x^5+x^4)-(2x^3+2x^2)+1$
$=(x^3+x^2)^2-2(x^3+x^2)+1=(x^3+x^2-1)^2$
Trong không gian Oxyz, cho mặt cầu
S = x 2 + y 2 + z 2 - 4 x - 2 y + 2 z - m 2 - 2 m + 5 = 0
và mặt phẳng α : x + 2 y - 2 z + 3 = 0 . Tìm m để giao tuyến giữa (a) và (S) là một đường tròn
A. m ∈ - 4 ; - 2 ; 2 ; 4
B. m > -2 hoặc m < 4
C. m < -4 hoặc m > -2
D. m < -4 hoặc m > 2
(S) có tâm I(2;1;-1) và bán kính R = m 2 + 2 m + 1 = m + 1
Giao tuyến của (a) và (S) là đường tròn
⇔ d I a < R ⇔ m + 1 > 3 ⇔ m < - 4 m > 2
Đáp án D