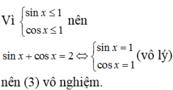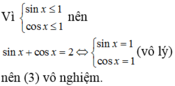Giải phương trình sau: sinx = 1/3

Những câu hỏi liên quan
III. Phương trình bậc nhất đối với sinx và cosx:*Giải các phương trình bậc nhất đối với sinx và cosx sau đây:(2.1)1) 2sinx-2cosxsqrt{2}2) cosx-sqrt{3}sinx13) sqrt{3}sindfrac{x}{3}+cosdfrac{x}{2}sqrt{2}4) cosx-sinx15) 2cosx+2sinxsqrt{6}6) sin3x+sqrt{3}cosxsqrt{2}7) 3sinx-2cosx2(2.3)1) left(sinx-1right)left(1+cosxright)cos^2x2) sinleft(dfrac{pi}{2}+2xright)+sqrt{3}sinleft(pi-2xright)13) sqrt{2}left(cos^4x-sin^4xright)cosx+sinx4) sin2x+cos2xsqrt{2}sin3x5) sinxsqrt{2}sin5x-cosx6) sin8x-cos6xsqrt{3}l...
Đọc tiếp
III. Phương trình bậc nhất đối với sinx và cosx:
*Giải các phương trình bậc nhất đối với sinx và cosx sau đây:
(2.1)
1) \(2sinx-2cosx=\sqrt{2}\)
2) \(cosx-\sqrt{3}sinx=1\)
3) \(\sqrt{3}sin\dfrac{x}{3}+cos\dfrac{x}{2}=\sqrt{2}\)
4) \(cosx-sinx=1\)
5) \(2cosx+2sinx=\sqrt{6}\)
6) \(sin3x+\sqrt{3}cosx=\sqrt{2}\)
7) \(3sinx-2cosx=2\)
(2.3)
1) \(\left(sinx-1\right)\left(1+cosx\right)=cos^2x\)
2) \(sin\left(\dfrac{\pi}{2}+2x\right)+\sqrt{3}sin\left(\pi-2x\right)=1\)
3) \(\sqrt{2}\left(cos^4x-sin^4x\right)=cosx+sinx\)
4) \(sin2x+cos2x=\sqrt{2}sin3x\)
5) \(sinx=\sqrt{2}sin5x-cosx\)
6) \(sin8x-cos6x=\sqrt{3}\left(sin6x+cos8x\right)\)
7) \(cos3x-sinx=\sqrt{3}\left(cosx-sin3x\right)\)
8) \(2sin^2x+\sqrt{3}sin2x=3\)
9) \(sin^4x+cos^4\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)=\dfrac{1}{4}\)
(2.3)
1) \(\dfrac{\sqrt{3}\left(1-cos2x\right)}{2sinx}=cosx\)
2) \(cotx-tanx=\dfrac{cosx-sinx}{sinx.cosx}\)
3) \(\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{cosx}+\dfrac{1}{sinx}=4\)
4) \(\dfrac{1+sinx}{1+cosx}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
5) \(3cosx+4sinx+\dfrac{6}{3cosx+4sinx+1}=6\)
(2.4)
a) Tìm nghiệm \(x\in\left(\dfrac{2\pi}{5};\dfrac{6\pi}{7}\right)\) của phương trình \(cos7x-\sqrt{3}sin7x+\sqrt{2}=0\)
b) Tìm nghiệm \(x\in\left(0;\pi\right)\) của phương trình \(4sin^2\dfrac{x}{2}-\sqrt{3}cos2x=1+2cos^2\left(x-\dfrac{3\pi}{4}\right)\)
(2.5) Xác định tham số m để các phương trình sau đây có nghiệm:
a) \(mcosx-\left(m+1\right)sinx=m\)
b) \(\left(2m-1\right)sinx+\left(m-1\right)cosx=m-3\)
(2.6) Tìm GTLN, GTNN (nếu có) của các hàm số sau đây:
a) \(y=3sinx-4cosx+5\)
b) \(y=cos2x+sin2x-1\)
2.1
a.
\(\Leftrightarrow sinx-cosx=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2}sin\left(x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sin\left(x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}=\dfrac{\pi}{6}+k2\pi\\x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}=\dfrac{5\pi}{6}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{5\pi}{12}+k2\pi\\x=\dfrac{13\pi}{12}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
b.
\(cosx-\sqrt{3}sinx=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}cosx-\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}sinx=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}=\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k2\pi\\x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}=-\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=k2\pi\\x=-\dfrac{2\pi}{3}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
c.
\(\sqrt{3}sin\dfrac{x}{3}+cos\dfrac{x}{2}=\sqrt{2}\)
Câu này đề đúng không nhỉ? Nhìn thấy có vẻ không đúng lắm
d.
\(cosx-sinx=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2}cos\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+\dfrac{\pi}{4}=\dfrac{\pi}{4}+k2\pi\\x+\dfrac{\pi}{4}=-\dfrac{\pi}{4}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=k2\pi\\x=-\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (1)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Giải phương trình sau: sin x + 1 = 2 3
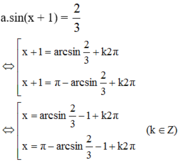
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm
{arcsin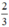 – 1 + k2π; π - arcsin
– 1 + k2π; π - arcsin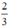 – 1 + k2π} (k ∈ Z)
– 1 + k2π} (k ∈ Z)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
giải phương trình sau:
\(\dfrac{\left(1-2sinx\right)cosx}{\left(1+2sinx\right)\left(1-sinx\right)}=\sqrt{3}\)
ĐKXĐ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\\x\ne-\dfrac{\pi}{6}+k2\pi\\x\ne\dfrac{7\pi}{6}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\dfrac{cosx-2sinx.cosx}{1-2sin^2x+sinx}=\sqrt{3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{cosx-sin2x}{cos2x+sinx}=\sqrt{3}\)
\(\Rightarrow cosx-sin2x=\sqrt{3}cos2x+\sqrt{3}sinx\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cosx-\sqrt{3}sinx=\sqrt{3}cos2x+sin2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}cosx-\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}sinx=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}cos2x+\dfrac{1}{2}sin2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)=cos\left(2x-\dfrac{\pi}{6}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-\dfrac{\pi}{6}=x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k2\pi\\2x-\dfrac{\pi}{6}=-x-\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\left(loại\right)\\x=-\dfrac{\pi}{18}+\dfrac{k2\pi}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
ĐKXĐ : \(sinx\ne1;-\dfrac{1}{2}\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{2}+2k\pi\\x\ne\dfrac{-\pi}{6}+2k\pi;\dfrac{7\pi}{6}+2k\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\ne\dfrac{-\pi}{6}+\dfrac{2}{3}k\pi\)( k thuộc Z )
P/t đã cho \(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{cosx-sin2x}{1-2sin^2x+sinx}=\sqrt{3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cosx-sin2x=\sqrt{3}\left(cos2x+sinx\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cosx-\sqrt{3}sinx=\sqrt{3}cos2x+sin2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}cosx-\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}sinx=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}cos2x+\dfrac{1}{2}sin2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)=cos\left(2x+\dfrac{\pi}{6}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x+\dfrac{\pi}{6}=x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}+2k\pi\\2x+\dfrac{\pi}{6}=-x-\dfrac{\pi}{3}+2k\pi\end{matrix}\right.\) ( k thuộc Z )
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\pi}{6}+2k\pi\\x=\dfrac{-\pi}{6}+\dfrac{2}{3}k\pi\left(L\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy ...
Đúng 0
Bình luận (1)
Giải các phương trình sau cos2x - sinx - 1 = 0
cos 2 x - sin x - 1 = 0 ⇔ 1 - 2 sin 2 x - sin x - 1 = 0 ⇔ sin x ( 2 sin x + 1 ) = 0
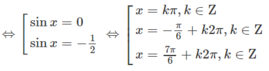
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Trong các phương trình sau
cos
x
5
-
3
(1);
sin
x
1
-
2
(2);
sin
x
+
cos
x
2
(3), phương trình nào vô nghiệm? A. (2). B. (1). C. (3). D. (1) và (2).
Đọc tiếp
Trong các phương trình sau cos x = 5 - 3 (1); sin x = 1 - 2 (2); sin x + cos x = 2 (3), phương trình nào vô nghiệm?
A. (2).
B. (1).
C. (3).
D. (1) và (2).
Trong các phương trình sau:
cos
x
5
-
3
(1);
sin
x
1
-
2
(2);
sin
x
+
cos
x
2
(3), phương trình nào vô nghiệm? A. (2) B. (1) C. (3) D. (1) và (2)
Đọc tiếp
Trong các phương trình sau: cos x = 5 - 3 (1); sin x = 1 - 2 (2); sin x + cos x = 2 (3), phương trình nào vô nghiệm?
A. (2)
B. (1)
C. (3)
D. (1) và (2)
giải phương trình lượng giác
\(\dfrac{cosx-\sqrt{3}sinx}{sinx-\dfrac{1}{2}}=0\)
ĐK: \(x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{6}+k2\pi;x\ne\dfrac{5\pi}{6}+k2\pi\)
\(\dfrac{cosx-\sqrt{3}sinx}{sinx-\dfrac{1}{2}}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cosx-\sqrt{3}sinx=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}cosx-\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}sinx=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}=\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k\pi\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{\pi}{6}+k\pi\)
Đối chiếu điều kiện ta được \(x=-\dfrac{5\pi}{6}+k2\pi\).
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình sau: 1 + sin x - cos x - sin 2 x + 2 cos 2 x = 0
1 + sin x - cos x - sin 2 x + 2 cos 2 x = 0 ( 1 ) T a c ó : 1 - sin 2 x = sin x - cos x 2 ⇔ 2 cos 2 x = 2 ( cos 2 x - sin 2 x ) = - 2 ( sin x - cos x ) ( sin x + cos x ) V ậ y ( 1 ) ⇔ ( sin x - cos x ) ( 1 + sin x - cos x - 2 sin x - 2 cos x ) = 0 ⇔ ( sin x - cos x ) ( 1 - sin x - 3 cos x ) = 0
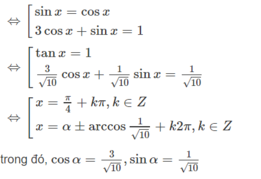
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình lượng giác sau:
\(\dfrac{cos2x}{1-sinx}=0\)
Để giải phương trình cos(2x) - sin(x) = 0, ta có thể sử dụng các công thức lượng giác để đưa phương trình về dạng phù hợp.
Bước 1: Sử dụng công thức cos(2x) = 2cos^2(x) - 1, phương trình trở thành 2cos^2(x) - 1 - sin(x) = 0.
Bước 2: Sử dụng công thức sin^2(x) + cos^2(x) = 1, ta có thể thay thế cos^2(x) bằng 1 - sin^2(x), phương trình trở thành 2(1 - sin^2(x)) - 1 - sin(x) = 0.
Bước 3: Giải phương trình 2 - 2sin^2(x) - 1 - sin(x) = 0.
Bước 4: Đặt sin(x) = t, phương trình trở thành 2 - 2t^2 - 1 - t = 0.
Bước 5: Rút gọn phương trình, ta có -2t^2 - t + 1 = 0.
Bước 6: Giải phương trình bậc hai trên, ta có thể sử dụng công thức hoặc phân tích thành nhân tử để tìm giá trị của t.
Bước 7: Giải phương trình -2t^2 - t + 1 = 0, ta tìm được hai giá trị t = -1 và t = 1/2.
Bước 8: Đặt sin(x) = -1 và sin(x) = 1/2, ta tìm được hai giá trị x = -π/2 và x = π/6.
Vậy, phương trình cos(2x) - sin(x) = 0 có hai nghiệm là x = -π/2 và x = π/6.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
ĐKXĐ: 1-sin x<>0
=>sin x<>1
=>x<>pi/2+k2pi
cos2x/1-sinx=0
=>cos2x=0
=>2x=pi/2+kpi
=>x=pi/2+kpi/2
Kết hợp ĐKXĐ, ta được: \(x\in\left\{pi+k2pi;\dfrac{3}{2}pi+k2pi;2pi+k2pi\right\}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)