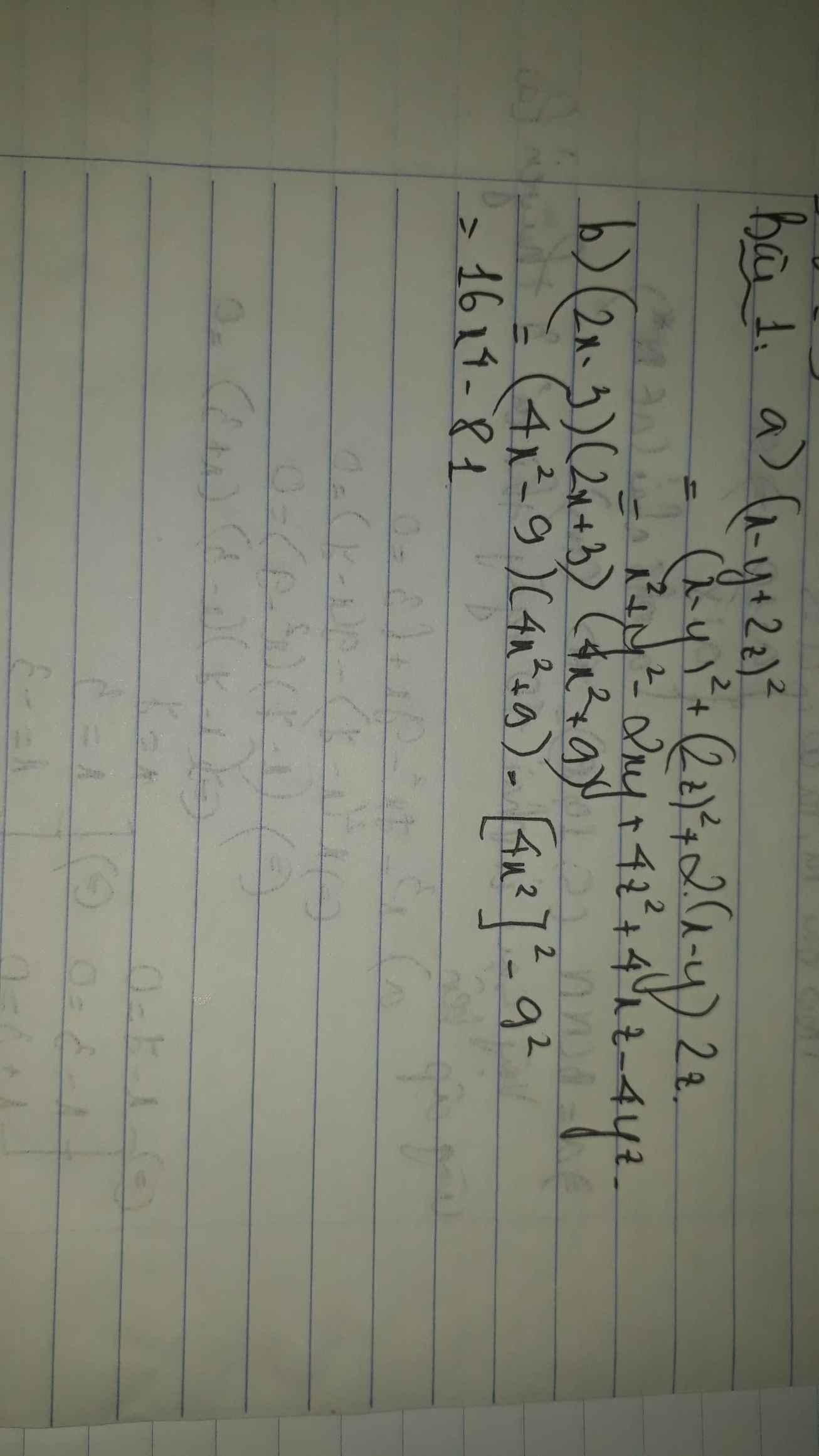Tính:
a)(3x+2)2-(4-2x).(5x+1)
b)(2x-3).(9+6x+4x2)-(2x+3)3

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Bài 5: Tìm nghiệm của các đa thức sau: Dạng 1: a) 4x + 9 b) -5x + 6 c) 7 – 2x d) 2x + 5 Dạng 2: a) ( x+ 5 ) ( x – 3) b) ( 2x – 6) ( x – 3) c) ( x – 2) ( 4x + 10 ) Dạng 3: a) x2 -2x b) x2 – 3x c) 3x2 – 4x d) ( 2x- 1)2 Dạng 4: a) x2 – 1 b) x2 – 9 c)– x 2 + 25 d) x2 - 2 e) 4x2 + 5 f) –x 2 – 16 g) - 4x4 – 25 Dạng 5: a) 2x2 – 5x + 3 b) 4x2 + 6x – 1 c) 2x2 + x – 1 d) 3x2 + 2x – 1
Bài 1: (3 điểm) Thực hiện phép tính:a) 3x2( 2x2 + 5x - 4 )b) (2x -5 )(4x2 - 3x + 1 ) c) ( 49x4y3 - 14x2y2 + 7x2y ) : 7x2yBài 2 : (2 điểm) Phân tích đa thức thành nhân tửa) 5x - 5y b) 9x2 - 4 c) x2 + 2xy - 49 + y2 Bài 3: (1 điểm) Nhân dịp Tết Dương lịch 2021, siêu thị Nguyễn Kim bán hàng khuyến mãi giảm giá 20 % chiếc tivi hiệu SAMSUNG 50 inch. Ông Ba là khách hàng thân th...
Đọc tiếp
Bài 1: (3 điểm) Thực hiện phép tính:
a) 3x2( 2x2 + 5x - 4 )
b) (2x -5 )(4x2 - 3x + 1 )
c) ( 49x4y3 - 14x2y2 + 7x2y ) : 7x2y
Bài 2 : (2 điểm) Phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử
a) 5x - 5y
b) 9x2 - 4
c) x2 + 2xy - 49 + y2
Bài 3: (1 điểm) Nhân dịp Tết Dương lịch 2021, siêu thị Nguyễn Kim bán hàng khuyến mãi giảm giá 20 % chiếc tivi hiệu SAMSUNG 50 inch. Ông Ba là khách hàng thân thiết nên được giảm thêm 5% trên giá đã giảm. Hỏi sau 2 lần giảm giá thì Ông Ba phải trả tiền một tivi là bao nhiêu, biết rằng giá ban đầu là 30 000 000 đồng ?
Bài 4: (1 điểm) Bạn Nam dùng thang nhôm dài 8 m đặt cách chân tường 1 m
, biết chân tường và sàn nhà vuông góc với nhau. Hỏi khoảng cách từ chân tường đến đầu thang bao nhiêu mét ? (Kết quả làm tròn hai chữ số thập phân).
Bài 5: (3 điểm)
Cho tam giác ABC cân tại A, có BC = 10 cm. Gọi E, F lần lượt là trung điểm AB, AC .
a) Tính EF.
b) Chứng minh: Tứ giác EFCB là hình thang cân.
c) Vẽ đường cao AH, gọi D là điểm đối xứng với H qua F.
Chứng minh: Tứ giác AHCD là hình chữ nhật.
Bài 2:
a: =5(x-y)
b: \(=\left(3x-2\right)\left(3x+2\right)\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
1.(x2+3).(x4-3x2+9)
2.(2x+1).(4x2-2x+1)
3.(x2+2).(x4-2x2+4)
4.(3x+2).(9x2-6x+4)
\(1,=x^6+27\\ 2,=8x^3+1\\ 3,=x^6+8\\ 4,=27x^3+8\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
1. (x2 + 3)(x4 - 3x2 + 9)
= x6 + 27
2. (2x + 1)(4x2 - 2x + 1)
= 8x3 + 1
3. (x2 + 2)(x4 - 2x2 + 4)
= x6 + 8
4. (3x + 2)(9x2 - 6x + 4)
= 27x3 + 8
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
1: \(\left(x^2+3\right)\left(x^4-3x^2+9\right)=x^6+27\)
2: \(\left(2x+1\right)\left(4x^2-2x+1\right)=8x^3+1\)
3: \(\left(x^2+2\right)\left(x^4-2x^2+4\right)=x^6+8\)
4: \(\left(3x+2\right)\left(9x^2-6x+4\right)=27x^3+8\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Mọi người làm nhanh hộ e với ạ, T7 e nộp rBài 1.Tính:a. x2(x–2x3) b. (x2+ 1)(5–x) c. (x–2)(x2+ 3x–4) d. (x–2)(x–x2+ 4)e. (x2–1)(x2+ 2x) f. (2x–1)(3x + 2)(3–x) g. (x + 3)(x2+ 3x–5)h (xy–2).(x3–2x–6) i. (5x3–x2+ 2x–3).(4x2–x + 2)Bài 2.Tính:a. (x–2y)2 b. (2x2+3)2 c. (x–2)(x2+ 2x + 4) d. (2x–1)2Bài 3: Rút gọn biểu thứca.(6x + 1)2+ (6x–1)2–2(1 + 6x)(6x–1)b. x(2x2–3)–x2(5x + 1) + x2.c. 3x(x–2)–5x(1–x)–8(x2–3)Bài 4: Tìm x, biếta. (x–2)2–(x–3)(x + 3) 6.b. 4(x–3)2–(2x–1)(2x + 1) 10c. (x–4...
Đọc tiếp
Mọi người làm nhanh hộ e với ạ, T7 e nộp r![]()
Bài 1.
Tính:
a. x2(x–2x3) b. (x2+ 1)(5–x) c. (x–2)(x2+ 3x–4) d. (x–2)(x–x2+ 4)
e. (x2–1)(x2+ 2x) f. (2x–1)(3x + 2)(3–x) g. (x + 3)(x2+ 3x–5)
h (xy–2).(x3–2x–6) i. (5x3–x2+ 2x–3).(4x2–x + 2)
Bài 2.
Tính:
a. (x–2y)2 b. (2x2+3)2 c. (x–2)(x2+ 2x + 4) d. (2x–1)2
Bài 3: Rút gọn biểu thức
a.(6x + 1)2+ (6x–1)2–2(1 + 6x)(6x–1)
b. x(2x2–3)–x2(5x + 1) + x2.
c. 3x(x–2)–5x(1–x)–8(x2–3)
Bài 4: Tìm x, biết
a. (x–2)2–(x–3)(x + 3) = 6.
b. 4(x–3)2–(2x–1)(2x + 1) = 10
c. (x–4)2–(x–2)(x + 2) = 6.
d. 9 (x + 1)2–(3x–2)(3x + 2) = 10
Bài 5:Phân tích các đa thức sau thành nhân tử
a. 1–2y + y2
b. (x + 1)2–25
c. 1–4x2
d. 8–27x3
e. 27 + 27x + 9x2+ x3
f. 8x3–12x2y +6xy2–y3
g. x3+ 8y3
Bài 6:Phân tích các đa thức sau thành nhân tử
a. 3x2–6x + 9x2
b. 10x(x–y)–6y(y–x)
c. 3x2+ 5y–3xy–5x
d. 3y2–3z2+ 3x2+ 6xy
e. 16x3+ 54y3
f. x2–25–2xy + y2
g. x5–3x4+ 3x3–x2
.
Bài 7: Phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử
a. 5x2–10xy + 5y2–20z2
b. 16x–5x2–3
c. x2–5x + 5y–y2
d. 3x2–6xy + 3y2–12z2
e. x2+ 4x + 3
f. (x2+ 1)2–4x2
g. x2–4x–5
Bài 5:
a. 1 - 2y + y2
= (1 - y)2
b. (x + 1)2 - 25
= (x + 1)2 - 52
= (x + 1 - 5)(x + 1 + 5)
= (x - 4)(x + 6)
c. 1 - 4x2
= 12 - (2x)2
= (1 - 2x)(1 + 2x)
d. 8 - 27x3
= 23 - (3x)3
= (2 - 3x)(4 + 6x + 9x2)
e. (đề hơi khó hiểu ''x3'' !?)
g. x3 + 8y3
= (x + 2y)(x2 - 2xy + y2)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình1) 2x ( x – 3 ) + 5 ( x – 3 ) 02) ( x2 – 4 ) – ( x – 2 ) ( 3 – 2x ) 03) ( 2x – 1 )2 – ( 2x + 5 )2 114) ( 2x + 1 )2 ( 3x – 5 ) 4x2 – 15) 3x2 – 5x – 8 06) ( 2x + 1 )2 ( 3x – 5 ) 4x2 – 17) 3x2 – 5x – 8 08) left|x-5right|39) left|2x-5right|3-x10) left|2x+1right|left|x-1right|11) dfrac{5x+2}{6}-dfrac{8x-1}{3}dfrac{4x+2}{5}-512) dfrac{3x+2}{2}-dfrac{3x+1}{6}2x+dfrac{5}{3}
Đọc tiếp
Giải phương trình
1) 2x ( x – 3 ) + 5 ( x – 3 ) = 0
2) ( x2 – 4 ) – ( x – 2 ) ( 3 – 2x ) = 0
3) ( 2x – 1 )2 – ( 2x + 5 )2 = 11
4) ( 2x + 1 )2 ( 3x – 5 ) = 4x2 – 1
5) 3x2 – 5x – 8 = 0
6) ( 2x + 1 )2 ( 3x – 5 ) = 4x2 – 1
7) 3x2 – 5x – 8 = 0
8) \(\left|x-5\right|=3\)
9) \(\left|2x-5\right|=3-x\)
10) \(\left|2x+1\right|=\left|x-1\right|\)
11) \(\dfrac{5x+2}{6}-\dfrac{8x-1}{3}=\dfrac{4x+2}{5}-5\)
12) \(\dfrac{3x+2}{2}-\dfrac{3x+1}{6}=2x+\dfrac{5}{3}\)
1) Ta có: \(2x\left(x-3\right)+5\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(2x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-\dfrac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
2) Ta có: \(\left(x^2-4\right)-\left(x-2\right)\left(3-2x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)+\left(x-2\right)\left(2x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(3x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
3) Ta có: \(\left(2x-1\right)^2-\left(2x+5\right)^2=11\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-4x-1-4x^2-20x-25=11\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-24x=11+1+25=37\)
hay \(x=-\dfrac{37}{24}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
5) Ta có: \(3x^2-5x-8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2+3x-8x-8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x\left(x+1\right)-8\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(3x-8\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=\dfrac{8}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
8) Ta có: \(\left|x-5\right|=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-5=3\\x-5=-3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=8\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
10) Ta có: \(\left|2x+1\right|=\left|x-1\right|\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x+1=x-1\\2x+1=1-x\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-x=-1-1\\2x+x=1-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-2\\x=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Thực hiện phép tính:
a) \(\dfrac{x}{2x-y}-\dfrac{2x-y}{4x-2y}\)
b)\(\dfrac{3x+1}{x^2-1}-\dfrac{x}{2x-2}\)
c) \(\dfrac{x-2}{x^2-4}-\dfrac{-8-x}{3x^2+6x}\)
d) \(\dfrac{2}{2x-3}-\dfrac{x}{2x+3}-\dfrac{2x+1}{9-4x^2}\)
a: \(=\dfrac{2x-2x+y}{2\left(2x-y\right)}=\dfrac{y}{2\left(2x-y\right)}\)
b: \(=\dfrac{3x+1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}-\dfrac{x}{2\left(x-1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{6x+2-x^2-x}{2\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{-x^2+5x+2}{2\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
c: \(=\dfrac{1}{x+2}+\dfrac{x+8}{3x\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{3x+x+8}{3x\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{4x+8}{3x\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{4}{3x}\)
d: \(=\dfrac{4x+6-2x^2+3x+2x+1}{\left(2x-3\right)\left(2x+3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{-2x^2+9x+7}{\left(2x-3\right)\left(2x+3\right)}\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Tìm x:
1) -3.(1-2x) - 4.(1+3x) = -5x + 5
2) 3.(2x - 5) - 6.(1 - 4x) = -3x + 7
3) (1 - 3x) - 2.(3x - 6) = -4x - 5
4) x.(4x - 3) - 2x.(2x - 1) = 5x - 7
5) 3x.(2x - 1) - 6x.(x + 2) = -3x + 4
6) (1 - 2x).3 - 4.(6x - 1) = 7x - 5
7) 6x - 3.(1 - 4x) - 5.(x + 1) = 2x + 7
8) 6.(1 - 3x) - 3.(2x + 5) = -10x + 7
9) 3x.(1 - 2x) + 6x^2 - 7x = 8.(1 - 2x) - 9
10) 2x.(1 + 3x) - 3x.(4 + 2x) = 3x - 4
* Trả lời:
\(\left(1\right)\) \(-3\left(1-2x\right)-4\left(1+3x\right)=-5x+5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-3+6x-4-12x=-5x+5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x-12x+5x=3+4+5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=12\)
\(\left(2\right)\) \(3\left(2x-5\right)-6\left(1-4x\right)=-3x+7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x-15-6+24x=-3x+7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x+24x+3x=15+6+7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow33x=28\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{28}{33}\)
\(\left(3\right)\) \(\left(1-3x\right)-2\left(3x-6\right)=-4x-5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow1-3x-6x+12=-4x-5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-3x-6x+4x=-1-12-5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-5x=-18\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{18}{5}\)
\(\left(4\right)\) \(x\left(4x-3\right)-2x\left(2x-1\right)=5x-7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-3x-4x^2+2x=5x-7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x-5x=-7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-6x=-7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{7}{6}\)
\(\left(5\right)\) \(3x\left(2x-1\right)-6x\left(x+2\right)=-3x+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-3x-6x^2-12x=-3x+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-15x+3x=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-12x=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{3}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Bài 1: Khai triển hằng đẳng thức:
a, ( x - y + 2z )2
b, ( 2x-3 ). ( 2x+3 ) . ( 4x2+9 )
Bài 2: Rút gọn biểu thức:
a, ( 5x+2 ).( 2-5x ) - ( 3x+2 ).( 2x+5 )2
b, ( -2x-3 )2 + 2(2x+1).( 2x+5 ) + ( 2x+5 )2
Bài 1:
a, \(\left(x-y+2z\right)^2=x^2+y^2+4z^2-2xy-4yz+4zx\)
b, \(\left(2x-3\right)\left(2x+3\right)\left(4x^2+9\right)=\left(4x^2-9\right)\left(4x^2+9\right)=16x^4-81\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Bài 1: Giải các phương trình dưới đây1) x2 - 9 (x - 3)(5x +2)2) x3 - 1 (x - 1)(x2 - 2x +16)3) 4x2 (x - 1) - x + 1 04) x3 + 4x2 - 9x - 36 05) (3x + 5)2 (x - 1)26) 9 (2x + 1)2 4 (x - 5)27) x2 + 2x 158) x4 + 5x3 + 4x2 09) (x2 - 4) - (x - 2)(3 - 2x) 010) (3x + 2)(x2 - 1) (9x2 - 4) (x + 1)11) (3x - 1)(x2 + 2) (3x - 1)(7x - 10)12) (2x2 + 1) (4x - 3) (x - 12)(2x2 + 1)
Đọc tiếp
Bài 1: Giải các phương trình dưới đây
1) x2 - 9 = (x - 3)(5x +2)
2) x3 - 1 = (x - 1)(x2 - 2x +16)
3) 4x2 (x - 1) - x + 1 = 0
4) x3 + 4x2 - 9x - 36 = 0
5) (3x + 5)2 = (x - 1)2
6) 9 (2x + 1)2 = 4 (x - 5)2
7) x2 + 2x = 15
8) x4 + 5x3 + 4x2 = 0
9) (x2 - 4) - (x - 2)(3 - 2x) = 0
10) (3x + 2)(x2 - 1) = (9x2 - 4) (x + 1)
11) (3x - 1)(x2 + 2) = (3x - 1)(7x - 10)
12) (2x2 + 1) (4x - 3) = (x - 12)(2x2 + 1)
1: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)-\left(x-3\right)\left(5x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(-4x+1\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{3;\dfrac{1}{4}\right\}\)
2: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)-\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2-2x+16\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1-x^2+2x-16\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(3x-15\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{1;5\right\}\)
3: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(4x^2-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{1;\dfrac{1}{2};-\dfrac{1}{2}\right\}\)
4: \(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x+4\right)-9\left(x+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+4\right)\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{-4;3;-3\right\}\)
5: \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x+5=x-1\\3x+5=1-x\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=-6\\4x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
6: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(6x+3\right)^2-\left(2x-10\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(6x+3-2x+10\right)\left(6x+3+2x-10\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4x+13\right)\left(8x-7\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{-\dfrac{13}{4};\dfrac{7}{8}\right\}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
1.
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)=\left(x-3\right)\left(5x-2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+3=5x-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=5\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{4}\)
2.
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)=\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2-2x+16\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x+1=x^2-2x+16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=15\Leftrightarrow x=5\)
3.
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2\left(x-1\right)-\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(4x^2-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=\dfrac{1}{2};x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (1)
7.
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x-15=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
8.\(\Leftrightarrow x^4+x^3+4x^3+4x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3\left(x+1\right)+4x^2\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x^3+4x^2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=0;x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
9.\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)=\left(x-2\right)\left(3-2x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+2=3-2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=1\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời