Cho hàm số \(y=f\left(x\right)=\sqrt{x-1}\)
a) Tính f(5); f(1); f(0); f(x-1)
b) Với những giá trị nào của x thì hàm số được xác định?
c) Chứng tỏ rằng với các giá trị \(x\ge1\) thì hàm số đồng biến.
Cho hàm số \(f\left( x \right) = 2x - \sin x,g\left( x \right) = \sqrt {x - 1} \).
Xét tính liên tục hàm số \(y = f\left( x \right).g\left( x \right)\) và \(y = \frac{{f\left( x \right)}}{{g\left( x \right)}}\).
• Xét hàm số \(f\left( x \right) = 2x - \sin x\) có tập xác định \(D = \mathbb{R}\).
Vậy hàm số \(f\left( x \right)\) liên tục trên \(\mathbb{R}\).
• Xét hàm số \(g\left( x \right) = \sqrt {x - 1} \)
ĐKXĐ: \(x - 1 \ge 0 \Leftrightarrow x \ge 1\)
Hàm số \(g\left( x \right) = \sqrt {x - 1} \) có tập xác định \(D = \left[ {1; + \infty } \right)\).
Hàm số \(g\left( x \right) = \sqrt {x - 1} \) là hàm căn thức nên liên tục trên khoảng \(\left( {1; + \infty } \right)\).
Ta có: \(\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {1^ + }} g\left( x \right) = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {1^ + }} \sqrt {x - 1} = \sqrt {1 - 1} = 0 = g\left( 1 \right)\)
Do đó hàm số \(g\left( x \right) = \sqrt {x - 1} \) liên tục tại điểm \({x_0} = 1\).
Vậy hàm số \(g\left( x \right) = \sqrt {x - 1} \) liên tục trên nửa khoảng \(\left[ {1; + \infty } \right)\).
• Xét hàm số \(y = f\left( x \right).g\left( x \right) = \left( {2x - \sin x} \right)\sqrt {x - 1} \)
Do hàm số \(y = f\left( x \right)\) và \(y = g\left( x \right)\) đều liên tục tại mọi điểm \({x_0} \in \left[ {1; + \infty } \right)\) nên hàm số \(y = f\left( x \right).g\left( x \right)\) liên tục trên nửa khoảng \(\left[ {1; + \infty } \right)\).
• Xét hàm số \(y = \frac{{f\left( x \right)}}{{g\left( x \right)}} = \frac{{2x - \sin x}}{{\sqrt {x - 1} }}\)
Do hàm số \(y = f\left( x \right)\) và \(y = g\left( x \right)\) đều liên tục tại mọi điểm \({x_0} \in \left[ {1; + \infty } \right)\) nên hàm số \(y = \frac{{f\left( x \right)}}{{g\left( x \right)}}\) liên tục trên khoảng \(\left( {1; + \infty } \right)\).
Cho hàm số \(y=f\left(x\right)\) có đạo hàm và liên tục trên \(\left[0;\dfrac{\pi}{2}\right]\)thoả mãn \(f\left(x\right)=f'\left(x\right)-2cosx\). Biết \(f\left(\dfrac{\pi}{2}\right)=1\), tính giá trị \(f\left(\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)\)
A. \(\dfrac{\sqrt{3}+1}{2}\) B. \(\dfrac{\sqrt{3}-1}{2}\) C. \(\dfrac{1-\sqrt{3}}{2}\) D. 0
Cho hàm số y=f(x)y=f(x) có đạo hàm và liên tục trên [0;π2][0;π2]thoả mãn f(x)=f′(x)−2cosxf(x)=f′(x)−2cosx. Biết f(π2)=1f(π2)=1, tính giá trị f(π3)f(π3)
A. √3+1/2 B. √3−1/2 C. 1−√3/2 D. 0
\(f'\left(x\right)-f\left(x\right)=2cosx\)
\(\Leftrightarrow e^{-x}.f'\left(x\right)-e^{-x}.f\left(x\right)=2e^{-x}cosx\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[e^{-x}.f\left(x\right)\right]'=2e^{-x}.cosx\)
Lấy nguyên hàm 2 vế:
\(\Rightarrow e^{-x}.f\left(x\right)=\int2e^{-x}cosxdx=e^{-x}\left(sinx-cosx\right)+C\)
Thay \(x=\dfrac{\pi}{2}\Rightarrow e^{-\dfrac{\pi}{2}}.1=e^{-\dfrac{\pi}{2}}+C\Rightarrow C=0\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)=sinx-cosx\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}-1}{2}\)
cho hàm số y=f(x)=\(\sqrt{x^2-6x+9}\)
a)tính f(-1), f(5)
b)tìm x để f(x)=10
c) rút gọn A=\(\dfrac{f\left(x\right)}{x^2-9}\) (x≠ -3 và x≠3)
a: \(f\left(x\right)=\sqrt{x^2-6x+9}=\sqrt{\left(x-3\right)^2}=\left|x-3\right|\)
\(f\left(-1\right)=\left|-1-3\right|=4\)
\(f\left(5\right)=\left|5-3\right|=\left|2\right|=2\)
b: f(x)=10
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3=10\\x-3=-10\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=13\\x=-7\end{matrix}\right.\)
c: \(A=\dfrac{f\left(x\right)}{x^2-9}=\dfrac{\left|x-3\right|}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}\)
TH1: x<3 và x<>-3
=>\(A=\dfrac{-\left(x-3\right)}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}=\dfrac{-1}{x+3}\)
TH2: x>3
\(A=\dfrac{\left(x-3\right)}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}=\dfrac{1}{x+3}\)
cho hàm số bậc nhất y=F(x)=\(\left(\sqrt{3}-1\right)\) X+1
a) hàm số trên là đồng biến hay nghịch biến trên R
b)tính các giá trị F(0);F\(\left(\sqrt{3}+1\right)\)
Lời giải:
a. Vì $\sqrt{3}-1>0$ nên hàm trên là hàm đồng biến trên $\mathbb{R}$
b.
$F(0)=(\sqrt{3}-1).0+1=1$
$F(\sqrt{3}+1)=(\sqrt{3}-1)(\sqrt{3}+1)+1=(3-1)+1=3$
Cho hàm số \(f\left(x\right)=2x-1\)
Không tính hãy so sánh \(f\left(\sqrt{3}-2\right)\) và \(f\left(\sqrt{5}-3\right)\)
Lời giải:
Vì $2>0$ nên $f(x)=2x-1$ là hàm đồng biến trên $R$
$\sqrt{3}-2-(\sqrt{5}-3)=1+\sqrt{3}-\sqrt{5}=1-\frac{2}{\sqrt{3}+\sqrt{5}}> 1-\frac{2}{1+1}=0$
$\Rightarrow \sqrt{3}-2> \sqrt{5}-3$
Vì hàm đồng biến nên $f(\sqrt{3}-2)> f(\sqrt{5}-3)$
Cho hàm số bậc nhất \(y=f\left(x\right)=\left(1-\sqrt{5}\right)x+\sqrt{2}\)
Không tính hãy so sánh \(f\left(1\right)\) và \(f\left(\sqrt{5}\right)\)
1, Cho hàm số y=f(x) và f'(0)=3. Hỏi giới hạn \(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0}\dfrac{\sqrt{x+1}-1}{f\left(0\right)-f\left(x\right)}\)=?
2, Cho hàm số f(x) có đạo hàm trên R và f'(x)=0 có các nghiệm là 1 và -2. Đặt \(g\left(x\right)=f\left(\sqrt{x^2+4}\right)\), hỏi g'(x)=0 có bao nhiêu nghiệm?
Mọi người giúp mình với ạ, mình cần gấp!! Cảm ơn mọi người rất nhiều!!!
1. Áp dụng quy tắc L'Hopital
\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0}\dfrac{\sqrt{x+1}-1}{f\left(0\right)-f\left(x\right)}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0}\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2\sqrt{x+1}}}{-f'\left(0\right)}=-\dfrac{1}{6}\)
2.
\(g'\left(x\right)=2x.f'\left(\sqrt{x^2+4}\right)=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\f'\left(\sqrt{x^2+4}\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\\sqrt{x^2+4}=1\\\sqrt{x^2+4}=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
2 pt cuối đều vô nghiệm nên \(g'\left(x\right)=0\) có đúng 1 nghiệm
Cho hàm số \(f\left(x\right)=ax+b\). Biết \(f\left(1\right)=\sqrt{3}\) và \(f'\left(1\right)=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\). Tính a-b>
\(f\left(1\right)=3\Rightarrow a+b=3;f'\left(x\right)=a\Rightarrow f'\left(1\right)=a=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\\a+b=3\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow...\)
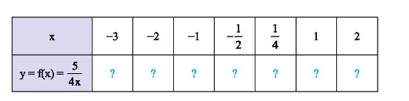
Cho hàm số \(y = f\left( x \right) = \dfrac{5}{{4x}}\).
a) Tính \(f\left( {\dfrac{1}{5}} \right);f\left( { - 5} \right);f\left( {\dfrac{4}{5}} \right)\).
b) Hãy tìm các giá trị tương ứng của hàm số trong bảng sau:
a) Ta có:
\(f\left( {\dfrac{1}{5}} \right) = \dfrac{5}{{4.\dfrac{1}{5}}} = \dfrac{5}{{\dfrac{4}{5}}} = 5:\dfrac{4}{5} = 5.\dfrac{5}{4} = \dfrac{{25}}{4};\)
\(f\left( { - 5} \right) = \dfrac{5}{{4.\left( { - 5} \right)}} = \dfrac{5}{{ - 20}} = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{4};\)
\(f\left( {\dfrac{4}{5}} \right) = \dfrac{5}{{4.\dfrac{4}{5}}} = \dfrac{5}{{\dfrac{{16}}{5}}} = 5:\dfrac{{16}}{5} = 5.\dfrac{5}{{16}} = \dfrac{{25}}{{16}}\)
b) Ta có:
\(f\left( { - 3} \right) = \dfrac{5}{{4.\left( { - 3} \right)}} = \dfrac{5}{{ - 12}} = \dfrac{{ - 5}}{{12}};\)
\(f\left( { - 2} \right) = \dfrac{5}{{4.\left( { - 2} \right)}} = \dfrac{5}{{ - 8}} = \dfrac{{ - 5}}{8};\)
\(f\left( { - 1} \right) = \dfrac{5}{{4.\left( { - 1} \right)}} = \dfrac{5}{{ - 4}} = \dfrac{{ - 5}}{4};\)
\(f\left( { - \dfrac{1}{2}} \right) = \dfrac{5}{{4.\left( { - \dfrac{1}{2}} \right)}} = \dfrac{5}{{\dfrac{{ - 4}}{2}}} = \dfrac{5}{{ - 2}} = \dfrac{{ - 5}}{2}\);
\(f\left( {\dfrac{1}{4}} \right) = \dfrac{5}{{4.\dfrac{1}{4}}} = \dfrac{5}{{\dfrac{4}{4}}} = \dfrac{5}{1} = 5\);
\(f\left( 1 \right) = \dfrac{5}{{4.1}} = \dfrac{5}{4}\);
\(f\left( 2 \right) = \dfrac{5}{{4.2}} = \dfrac{5}{8}\)
Ta có bảng sau:
\(x\) | –3 | –2 | –1 | \( - \dfrac{1}{2}\) | \(\dfrac{1}{4}\) | 1 | 2 |
\(y = f\left( x \right) = \dfrac{5}{{4x}}\) | \(\dfrac{{ - 5}}{{12}}\) | \(\dfrac{{ - 5}}{8}\) | \(\dfrac{{ - 5}}{4}\) | \(\dfrac{{ - 5}}{2}\) | 5 | \(\dfrac{5}{4}\) | \(\dfrac{5}{8}\) |
Cho hàm số y=f(x)=\(6x-1-\sqrt{5}\left(2x-1\right)\)
tìm x khi f(x)=0
\(f\left(x\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x\left(6-2\sqrt{5}\right)+\sqrt{5}-1=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x\left(1-\sqrt{5}\right)^2=1-\sqrt{5}\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1-\sqrt{5}}{\left(1-\sqrt{5}\right)^2}=\dfrac{1}{1-\sqrt{5}}=-\dfrac{\sqrt{5}+1}{4}\)