Giải phương trình x^2-5x-2√3x+12=0

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Giải các phương trình sau:
a. \(5x^2+10x=0\)
b. \(3x^2-12=0\)
c. \(3x^2+7=0\)
d. \(12x^2-3x=0\)
Giải các bất phương trình sau:
a) \(2{x^2} - 3x + 1 > 0\)
b) \({x^2} + 5x + 4 < 0\)
c) \( - 3{x^2} + 12x - 12 \ge 0\)
d) \(2{x^2} + 2x + 1 < 0.\)
a) \(2{x^2} - 3x + 1 > 0\)
Tam thức \(f\left( x \right) = 2{x^2} - 3x + 1\) có \(a + b + c = 2 - 3 + 1 = 0\) nên hai nghiệm phân biệt \({x_1} = 1\) và \({x_2} = \frac{1}{2}.\)
Mặt khác \(a = 2 > 0,\) do đó ta có bảng xét dấu sau:

Tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là: \(S= \left( { - \infty ;\frac{1}{2}} \right) \cup \left( {1; + \infty } \right).\)
b) \({x^2} + 5x + 4 < 0\)
Tam thức \(f\left( x \right) = {x^2} + 5x + 4\) có \(a - b + c = 1 - 5 + 4 = 0\) nên phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt \(x = - 1\) và \(x = - 4.\)
Mặt khác \(a = 1 > 0,\) do đó ta có bảng xét dấu sau:
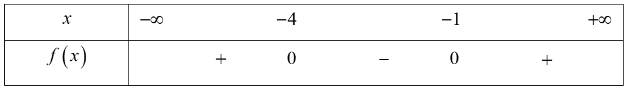
Tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là: \(S = \left( { - 4; - 1} \right).\)
c) \( - 3{x^2} + 12x - 12 \ge 0\)
Tam thức \(f\left( x \right) = - 3{x^2} + 12x - 12 = - 3\left( {{x^2} - 4x + 4} \right) = - 3{\left( {x - 2} \right)^2} \le 0\)
Do đó
\( - 3{x^2} + 12x - 12 \ge 0 \Leftrightarrow - 3{x^2} + 12x - 12 = 0 \Leftrightarrow - 3{\left( {x - 2} \right)^2} = 0 \Leftrightarrow x = 2.\)
Tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là: \(S = \left( { 2} \right).\)
d) \(2{x^2} + 2x + 1 < 0.\)
Tam thức \(f\left( x \right) = 2{x^2} + 2x + 1\) có \(\Delta = - 1 < 0,\) hệ số \(a = 2 > 0\) nên \(f\left( x \right)\) luôn dướng với mọi \(x,\) tức là \(2{x^2} + 2x + 1 > 0\) với mọi \(x \in \mathbb{R}.\)
\( \Rightarrow \) bất phương trình vô nghiệm
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình sau:
\(x^2-5x-2\sqrt{3x}+12=0\)
\(\left(x^2-6x+9\right)+\left(x-2\sqrt{3x}+9\right)=0\) (dk:x>=0)
\(\left(x-3\right)^2+\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)^2=0\)
=>\(\hept{\begin{cases}x-3=0\\\sqrt{x}-3=0\end{cases}}\)
=>x=3 tmdk
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
\(\left(x-3\right)^2+\left(\sqrt{x}-\sqrt{3}\right)^2=0\)
=>x=3
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Giải Phương Trình sau:
\(x^2-5x-2\sqrt{3x}+12=0\)
giải hệ bất phương trình. em cần gấp lắm ạaaaaaa
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x^2+5x-2\text{≥}0\\-x^2+x+12\text{≥}0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(< =>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(3x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)\ge0\\\left(4-x\right)\left(x+3\right)\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(< =>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge\dfrac{1}{3},x\le-2\\-3\le x\le4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(< =>\dfrac{1}{3}\le x\le4,-3\le x\le-2\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
giải phương trình sau
1/ x^2 -3x+2=0
2/ x^2 -6x+5=0
3/ 2x^2 +5x+3 =0
4/ x^2-8x+15=0
5/ x^2 -x-12=0
1/ x2-3x+2=0
⇒ (x2-2x)-(x-2)=0
⇒ x(x-2)-(x-2)=0
⇒ (x-1)(x-2)=0
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\x-2=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
2) x2-6x+5=0
⇒x2-6x+9-4=0
⇒(x2-6x+9)-22=0
⇒(x-3)2-22=0
⇒(x-3-2)(x-3+2)=0
⇒(x-5)(x-1)=0
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\x-5=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
3) 2x2+5x+3=0
⇒ (2x2+2x)+(3x+3)=0
⇒ 2x(x+1)+3(x+1)=0
⇒ (x+1)(2x+3)=0
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+1=0\\2x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=-1,5\end{matrix}\right.\)
4) x2-8x+15=0
⇒ (x2-8x+16)-1=0
⇒ (x-4)2-12=0
⇒ (x-4-1)(x-4+1)=0
⇒ (x-5)(x-3)=0
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3=0\\x-5=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
5) x2-x-12=0
⇒ (x2-4x)+(3x-12)=0
⇒ x(x-4)+3(x-4)=0
⇒ (x-4)(x+3)=0
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+3=0\\x-4=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\x=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
1: Ta có: \(x^2-3x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
2: Ta có: \(x^2-6x+5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
3: Ta có: \(2x^2+5x+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(2x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=-\dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
4: Ta có: \(x^2-8x+15=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x-5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
5: Ta có: \(x^2-x-12=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-4\right)\left(x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
1 giải các phương trình chứa dấu giá trị tuyệt đối saua ( 9+x)2x b ( x+6) 2x+9c ( 2x-3) 2x-3d ( 4+2x) -4xe ( 5 x) 3x-2g ( -2,5x)x-12h ( 5x ) -3x-20i ( -2x) +x-5x-302 giải phương trình ( ẩn x): 4x2-25+k2+4kx0a giải phương trình với k0b giải phương trinh với k--3c tìm các giá trị của k để nhận phương trình nhận x -2 làm nghiệm3 giải bất phương trình trên trục sốa 3x-60b 5x+150c -4x+117 d x+100 goải giúp mình với mình đang cần gấp
Đọc tiếp
1 giải các phương trình chứa dấu giá trị tuyệt đối sau
a ( 9+x)=2x
b ( x+6) = 2x+9
c ( 2x-3)= 2x-3
d ( 4+2x)= -4x
e ( 5 x)= 3x-2
g ( -2,5x)=x-12
h ( 5x ) -3x-2=0
i ( -2x) +x-5x-3=0
2 giải phương trình ( ẩn x): 4x2-25+k2+4kx=0
a giải phương trình với k=0
b giải phương trinh với k=--3
c tìm các giá trị của k để nhận phương trình nhận x =-2 làm nghiệm
3 giải bất phương trình trên trục số
a 3x-6<0
b 5x+15>0
c -4x+1>17
d x+10>0
goải giúp mình với mình đang cần gấp
1
a (9+x)=2 ta có (9+x)= 9+x khi 9+x >_0 hoặc >_ -9
(9+x)= -9-x khi 9+x <0 hoặc x <-9
1)pt 9+x=2 với x >_ -9
<=> x = 2-9
<=> x=-7 thỏa mãn điều kiện (TMDK)
2) pt -9-x=2 với x<-9
<=> -x=2+9
<=> -x=11
x= -11 TMDK
vậy pt có tập nghiệm S={-7;-9}
các cau con lai tu lam riêng nhung cau nhan với số âm thi phan điều kiện đổi chiều nha vd
nhu cau o trên mk lam 9+x>_0 hoặc x>_0
với số âm thi -2x>_0 hoặc x <_ 0 nha
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
3/ dễ làm mk làm một cau nha
a 3x-6<0
3x<6
3x/3<6/3
x<2
c -4x+1>17
-4x>17-1
-4x>16
-4x : (-4) < 16 : (-4)
x < 4 khi nhân , chia với số âm thì đổi chiều
bai 2 mk khong biet lm
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình :
1 ) \(x^3+5x^2-11=0\)
2 ) \(x^3-3x^2+4x+11=0\)
( phương trình bậc ba cardano )
Giải các phương trình sau:
a) \(x^3-3x^2-4x=0\)
b) \(3x^2-5x-2=0\)
a) \(x^3-3x^2-4x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x^2-3x-4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-4\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x-4=0\\x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=4\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{0;4;-1\right\}\).
b) \(3x^2-5x-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2+x-6x-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(3x+1\right)-2\left(3x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x+1=0\\x-2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{3}\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{-\dfrac{1}{3};2\right\}\).
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình:\(\sqrt{5x^2+x+3}-2\sqrt{5x-1}+x^2-3x+3=0\)
ĐKXĐ:
\(\left(2x+2-2\sqrt{5x-1}\right)+\left(\sqrt{5x^2+x+3}-\left(2x+1\right)\right)+x^2-3x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2\left(x^2-3x+2\right)}{x+1+\sqrt{5x-1}}+\dfrac{x^2-3x+2}{\sqrt{5x^2+x+3}+2x+1}+x^2-3x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-3x+2\right)\left(\dfrac{2}{x+1+\sqrt{5x-1}}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5x^2+x+3}+2x+1}+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-3x+2=0\)
Đúng 4
Bình luận (0)























