Giải
\(A^2+B^2=0\)
Câu 1: M=(-∞;5] và N=[-2;6). Tìm M∩N,giải thích Câu 2: Cho A=[-4;7], B=(-∞;-2)∪(3;+∞). Tìm A∩B, giải thích Câu 3: Cho A=(-∞;5], B=(0;+∞). Tìm A∩B, giải thích Câu 4. Cho A=(-∞;0)∪(4;+∞) và B=[-2;5]. Tìm A∩B,giải thích Câu 5: Cho M=[-4;7] và N=(-∞;2)∪(3;+∞). Tìm M∩N, giải thích Câu 6: Cho a,b,c là những số thực dương thỏa a
Giải phương trình:
\(4x^2+8\sqrt{x-1}=14-3x\)
Giải CHI TIẾT phương trình này bằng phương pháp tạo \(A^2+B^2=0\) hoặc \(A^2-B^2=0\) hộ mình cái ạ!
Đk: \(x\ge1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(2\sqrt{x-1}-1\right)+\left(4x-5\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4\left(4x-5\right)}{2\sqrt{x-1}+1}+\left(4x-5\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4x-5\right)\left(\dfrac{4}{2\sqrt{x-1}+1}+x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{4}\)(Dễ thấy ngoặc to lớn hơn 0 với \(x\ge1\))
Muốn giải mấy bài kiểu này thì mình hay đoán nghiệm trước
Việc đoán nghiệm thì có thể dùng kinh nghiệm hoặc bấm máy tính
Ở đây mình đoán được nghiệm là x=5/4 nên ta sẽ cố gắng tạo ra nhân tử dạng
4x-5 hoặc x-(5/4) ở đầy mình chọn nhân tử 4x-5
Trong những phương trình chứa căn thức thì để tạo nhân tử thì cách thường dùng nhất là phép liên hợp
Phép liên hợp là phép kiểu: \(\sqrt{a}-\sqrt{b}=\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{a}-\sqrt{b}\right)\left(\sqrt{a}+\sqrt{b}\right)}{\sqrt{a}+\sqrt{b}}=\dfrac{a-b}{\sqrt{a}+\sqrt{b}}\)
Ok, ta biến đổi pt lại để tạo nhân tử 4x-5:
\(\left(8\sqrt{x-1}-4\right)+\left(4x^2+3x-10\right)=0\) (ở đây ta thay x=5/4 vào 8căn(x-1) thì được 4 nên ta sẽ ghép với 4, còn phần còn lại của pt thì gộp lại chung)
\(\dfrac{4\left(2\sqrt{x-1}-1\right)\left(2\sqrt{x-1}+1\right)}{2\sqrt{x-1}+1}+\left(4x-5\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\)(sử dụng phép liên hợp)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4\left(4x-5\right)}{2\sqrt{x-1}+1}+\left(4x-5\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4x-5\right)\left(\dfrac{4}{2\sqrt{x-1}+1}+x+2\right)=0\)
Ở đây thì với đk x>=1 thì ngoặc to sẽ lớn hơn 0 nên kêt luận x=5/4
Giải bất phương trình sau : a/ 2x ^ 2 + 6x - 8 < 0 x ^ 2 + 5x + 4 >=\ 2) Giải phương trình sau : a/ sqrt(2x ^ 2 - 4x - 2) = sqrt(x ^ 2 - x - 2) c/ sqrt(2x ^ 2 - 4x + 2) = sqrt(x ^ 2 - x - 3) b/ x ^ 2 + 5x + 4 < 0 d/ 2x ^ 2 + 6x - 8 > 0 b/ sqrt(- x ^ 2 - 5x + 2) = sqrt(x ^ 2 - 2x - 3) d/ sqrt(- x ^ 2 + 6x - 4) = sqrt(x ^ 2 - 2x - 7)
2:
a: =>2x^2-4x-2=x^2-x-2
=>x^2-3x=0
=>x=0(loại) hoặc x=3
b: =>(x+1)(x+4)<0
=>-4<x<-1
d: =>x^2-2x-7=-x^2+6x-4
=>2x^2-8x-3=0
=>\(x=\dfrac{4\pm\sqrt{22}}{2}\)
Bài 1:giải các phương trình sau:
a) (x-3).(x+7)=0 b) (x-2)^2+(x-2).(x-3)=0 c)x^2-5x+6=0
Bài 2:giải các phương trình chứa ẩn ở mẫu sau:
a)x/x+1-1=3/2x b)4x/x-2-7/x=4
Bài 3:giải phương trình sau
a)2x^2-5x-7=0 b)1/x^2-4+2x/x-2=2x/x+2
giúp mình với,mình đang cần gấp
Mình khuyên bạn thế này :
Bạn nên tách những câu hỏi ra
Như vậy các bạn sẽ dễ giúp
Và cũng có nhiều bạn giúp hơn !
Bài 1.
a) ( x - 3 )( x + 7 ) = 0
<=> x - 3 = 0 hoặc x + 7 = 0
<=> x = 3 hoặc x = -7
Vậy S = { 3 ; -7 }
b) ( x - 2 )2 + ( x - 2 )( x - 3 ) = 0
<=> ( x - 2 )( x - 2 + x - 3 ) = 0
<=> ( x - 2 )( 2x - 5 ) = 0
<=> x - 2 = 0 hoặc 2x - 5 = 0
<=> x = 2 hoặc x = 5/2
Vậy S = { 2 ; 5/2 }
c) x2 - 5x + 6 = 0
<=> x2 - 2x - 3x + 6 = 0
<=> x( x - 2 ) - 3( x - 2 ) = 0
<=> ( x - 2 )( x - 3 ) = 0
<=> x - 2 = 0 hoặc x - 3 = 0
<=> x = 2 hoặc x = 3
Bài 2.
a) \(\frac{x}{x+1}-1=\frac{3}{2}x\)
ĐKXĐ : x khác -1
<=> \(\frac{x}{x+1}-\frac{x+1}{x+1}=\frac{3}{2}x\)
<=> \(\frac{-1}{x+1}=\frac{3x}{2}\)
=> 3x( x + 1 ) = -2
<=> 3x2 + 3x + 2 = 0
Vi 3x2 + 3x + 2 = 3( x2 + x + 1/4 ) + 5/4 = 3( x + 1/2 )2 + 5/4 ≥ 5/4 > 0 ∀ x
=> phương trình vô nghiệm
b) \(\frac{4x}{x-2}-\frac{7}{x}=4\)
ĐKXĐ : x khác 0 ; x khác 2
<=> \(\frac{4x^2}{x\left(x-2\right)}-\frac{7x-14}{x\left(x-2\right)}=\frac{4x^2-8x}{x\left(x-2\right)}\)
=> 4x2 - 7x + 14 = 4x2 - 8x
<=> 4x2 - 7x - 4x2 + 8x = -14
<=> x = -14 ( tm )
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm x = -14
Với a ≥ 0, b ≥ 0, chứng minh
√( (a+b)^2) ≥ (√a+√b)/ 2
giải chi tiết ra giúp. phần giải trên mạng mình k hiểu nên đừng chép
thanks
Chứng minh rằng với a+b>c và |a-b|<c với a,b,c >0 thì phương trình bậc hai a^2x^2 +(a^2+b^2-c^2)x +b^2=0 vô nghiệm
ĐOẠN MK BÔI ĐỎ GIẢI THÍCH HỘ
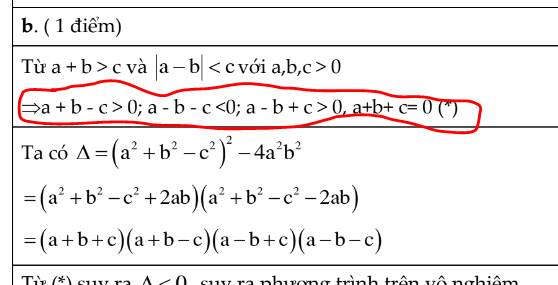
Lời giải:
Từ $a+b> c\Rightarrow a+b-c>0$ (cái này hiển nhiên)
Từ $|a-b|< c\Leftrightarrow |a-b|^2< c^2$
$\Leftrightarrow (a-b)^2< c^2$
$\Leftrightarrow (a-b-c)(a-b+c)<0$
Với $c>0$ thì $a-b-c< a-b+c$ nên để tích âm thì $a-b-c<0< a-b+c$
Hay $a-b-c<0$ và $a-b+c>0$
giải pt
a) -3x\(^2\)+15x=0 b)2x\(^2\)-32=0 c)2x\(^2\)-5x+1=0
❤ s ❤
\(a.-3x^2+15x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x\left(-x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x=0\\-x+5=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(b.2x^2-32=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2=32\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2=16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|x\right|=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(c.2x^2-5x+1=0\)
\(a=2;b=-5;c=1\)
\(\Delta=\left(-5\right)^2-4.2.1=17>0\)
Do \(\Delta>0\) nên phương trình có 2 nghiệm phân biệt:
\(x_1=\dfrac{5+\sqrt{17}}{4}\)
\(x_2=\dfrac{5-\sqrt{17}}{4}\)
\(a,-3x^2+15x=0\\ -3x\left(x-5\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x-5=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(b,\\ 2\left(x^2-16\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-16=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-4\right)\left(x+4\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(c,\\ \Delta=5^2-4.2=17\\ \Rightarrow x_1,x_2=\dfrac{\Delta\pm b}{2ac}\\ =\dfrac{5\pm\sqrt{17}}{4}\)
Cho ba tập hợp : A = { -3; -2; -1; 0; 1} , B = { -1; 0; 1; 2; 3 } , C = { -3; -2; -1; 0; 1; 2 ;3 }.
a) Tìm A ∪ B ; A ∩ B ; A ∪ C ; A ∩ C ; B ∪ C .
b) Tìm A ∩ N ; B ∩ N ; A ∪ N ; B ∪ N ; ( A ∩ B ) ∩ N ; ( A ∩ B ) ∩ Z .
Giải nhanh giúp mình với ạ
giải phương trình a)x-2√x +1=0 b)x-2√x -3=0
a
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)^2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}-1=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}=1\\ \Leftrightarrow x=1^2=1\)
b
ĐK: \(x\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+\sqrt{x}-3\sqrt{x}-3=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x+\sqrt{x}-\left(3\sqrt{x}+3\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)-3\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x}+1=0\\\sqrt{x}-3=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x}=-1\left(loại\right)\\x=9\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
a: =>(căn x-1)^2=0
=>căn x-1=0
=>x=1
b: =>(căn x-3)(căn x+1)=0
=>căn x-3=0
=>căn x=3
=>x=9
Lời giải:
a. ĐK: $x\geq 0$
$x-2\sqrt{x}+1=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (\sqrt{x}-1)^2=0$
$\Leftrightarrow \sqrt{x}-1=0$
$\Leftrightarrow \sqrt{x}=1$
$\Leftrightarrow x=1$ (tm)
b. ĐK: $x\geq 0$
PT $\Leftrightarrow (x+\sqrt{x})-(3\sqrt{x}+3)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow \sqrt{x}(\sqrt{x}+1)-3(\sqrt{x}+1)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (\sqrt{x}+1)(\sqrt{x}-3)=0$
Vì $\sqrt{x}+1\geq 1>0$ với mọi $x\geq 0$ nên $\sqrt{x}-3=0$
$\Leftrightarrow \sqrt{x}=3$
$\Leftrightarrow x=9$ (tm)
1.Giải các phương trình sau :
a) 2sinx+1=0
b) √2 cosx+1=0
c) tanx-√3=0
d) cotx=0
2. Giải các phương trình sau :
a) sin2x+sinx-2=0
b) cot2x-2cotx-3=0
3.Giải các phương trình sau :
sin2x+sin22x+sin23x=3/2
1/ \(sinx=-\frac{1}{2}=sin\left(-\frac{\pi}{6}\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\frac{\pi}{6}+k2\pi\\x=\frac{7\pi}{6}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
b/ \(cos=-\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}=cos\left(\frac{3\pi}{4}\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\pm\frac{3\pi}{4}+k2\pi\)
c/ \(tanx=\sqrt{3}=tan\left(\frac{\pi}{3}\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\frac{\pi}{3}+k\pi\)
d/ \(cotx=0\Rightarrow x=\frac{\pi}{2}+k\pi\)
2/
a/ \(sin^2x+sinx-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(sinx-1\right)\left(sinx+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}sinx=1\\sinx=-2\left(vn\right)\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow x=\frac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\)
b/ \(cot^2x-2cotx-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(cotx+1\right)\left(cotx-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}cotx=-1\\cotx=3\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\frac{\pi}{4}+k\pi\\x=arccot3+k\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
3/ \(\Leftrightarrow1-cos2x+1-cos4x+1-cos6x=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos2x+cos6x+cos4x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2coss4x.cos2x+cos4x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos4x\left(2cos2x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}cos4x=0\\cos2x=-\frac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}4x=\frac{\pi}{2}+k\pi\\2x=\frac{2\pi}{3}+k2\pi\\2x=-\frac{2\pi}{3}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\frac{\pi}{8}+\frac{k\pi}{4}\\x=\frac{\pi}{3}+k\pi\\x=-\frac{\pi}{3}+k\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)