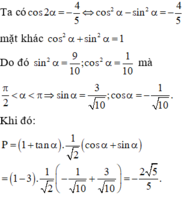Cho biết cos∝ =12/13 giá trị của tan ∝ là:

Những câu hỏi liên quan
bài 1: a)biết sin α=√3/2.tính cos α,tan α,cot α
b)cho tan α=2.tính sin α,cos α,cot α
c)biết sin α=5/13.tính cos,tan,cot α
bài 2
biết sin α x cos α=12/25.tính sin,cos α
1:
a: sin a=căn 3/2
\(cosa=\sqrt{1-sin^2a}=\sqrt{1-\dfrac{3}{4}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{1}{4}}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(tana=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}:\dfrac{1}{2}=\sqrt{3}\)
cot a=1/tan a=1/căn 3
b: \(tana=2\)
=>cot a=1/tan a=1/2
\(1+tan^2a=\dfrac{1}{cos^2a}\)
=>\(\dfrac{1}{cos^2a}=5\)
=>cos^2a=1/5
=>cosa=1/căn 5
\(sina=\sqrt{1-cos^2a}=\sqrt{\dfrac{4}{5}}=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{5}}\)
c: \(cosa=\sqrt{1-\left(\dfrac{5}{13}\right)^2}=\dfrac{12}{13}\)
tan a=5/13:12/13=5/12
cot a=1:5/12=12/5
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Biết sin + cos = \(\sqrt{2}\)
tính giá trị của sin , cot tan cos
Ta dễ có hệ: \(\hept{\begin{cases}\sin\alpha+\cos\alpha=\sqrt{2}\\\sin^2\alpha+\cos^2\alpha=1\end{cases}}\)
Đặt \(\sin\alpha=x;\cos\alpha=y\)thì hệ trở thành \(\hept{\begin{cases}x+y=\sqrt{2}\\x^2+y^2=1\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x+y=\sqrt{2}\\\left(x+y\right)^2-2xy=1\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x+y=\sqrt{2}\\xy=\frac{1}{2}\end{cases}}\)
x, y là nghiệm của phương trình \(t^2-\sqrt{2}t+\frac{1}{2}=0\Leftrightarrow\left(t-\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\right)^2=0\Leftrightarrow t=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=y=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\)hay \(\sin\alpha=\cos\alpha=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\)suy ra \(\tan\alpha=\cot\alpha=1\)
Tính giá trị của biểu thức sau : B= \(\dfrac{tan\left(\dfrac{21\pi}{2}-x\right).cos\left(38\pi-x\right).sin\left(x-7\pi\right)}{sin\left(\dfrac{13\pi}{2}-x\right).cos\left(x-2023\pi\right)}\)
1.Tính giá trị lượng giác của x biết tan x = -3 và pi/2 < x < pi
2. cho sin x - cos x = -4/ căn 10. Tính sin x và cos x
1.
\(\frac{\pi}{2}< x< \pi\\ \Rightarrow cosx< 0,sinx>0,cotx< 0\)
\(cotx=\frac{1}{tanx}=\frac{-1}{3}\)
\(1+tan^2x=\frac{1}{cos^2x}\\ \Rightarrow cosx=\sqrt{\frac{1}{1+tan^2}}=\sqrt{\frac{1}{1+9}}=-\frac{\sqrt{10}}{10}\)
\(sinx=\sqrt{1-cos^2x}=\sqrt{1-\frac{10}{100}}=\frac{3\sqrt{10}}{10}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Cho biết \(\sin {30^o} = \frac{1}{2};\sin {60^o} = \frac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2};\tan {45^o} = 1.\) Sử dụng mối liên hệ giữa các giá trị lượng giác của hai góc bù nhau, phụ nhau để tính giá trị của \(E = 2\cos {30^o} + \sin {150^o} + \tan {135^o}.\)
Ta có:
\(\begin{array}{l}\cos {30^o} = \sin \left( {{{90}^o} - {{30}^o}} \right) = \sin {60^o} = \frac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2};\\\sin {150^o} = \sin \left( {{{180}^o} - {{150}^o}} \right) = \sin {30^o} = \frac{1}{2};\\\tan {135^o} = - \tan \left( {{{180}^o} - {{135}^o}} \right) = - \tan {45^o} = - 1\end{array}\)
\( \Rightarrow E = 2.\frac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} + \frac{1}{2} - 1 = \sqrt 3 - \frac{1}{2}.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho cos x = -3/5 và \(\pi< x< \dfrac{3\pi}{2}\). Giá trị của biểu thức P = tan x + cot x là?
\(\pi< x< \dfrac{3\pi}{2}\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}sinx< 0\\cosx< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow sinx=-\sqrt{1-cos^2x}=-\dfrac{4}{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow tanx=\dfrac{sinx}{cosx}=\dfrac{4}{3}\) ; \(cotx=\dfrac{1}{tanx}=\dfrac{3}{4}\)
\(P=\dfrac{4}{3}+\dfrac{3}{4}=\dfrac{25}{12}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho
cos
2
α
-
4
5
với
π
2
α
π
. Tính giá trị của biểu thức:
P
1
+
tan...
Đọc tiếp
Cho cos 2 α = - 4 5 với π 2 < α < π . Tính giá trị của biểu thức: P = 1 + tan α cos π 4 - α .Đáp án đúng của P là:
A. P = - 2 5 3
B. P = - 2 5 5
C. P = - 5 5
D. P = - 2 3 5
Câu 1 : Cho tan a- cot a =2√3. Tính giá trị của biểu thức P= |tan a + cot a|
Câu 2: Cho sin x +cos x=1/5. Tính giá trị biểu thức P=tan x + cot x
Xem chi tiết
\(tana-cota=2\sqrt{3}\Rightarrow\left(tana-cota\right)^2=12\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(tana+cota\right)^2-4=12\Rightarrow\left(tana+cota\right)^2=16\)
\(\Rightarrow P=4\)
\(sinx+cosx=\dfrac{1}{5}\Rightarrow\left(sinx+cosx\right)^2=\dfrac{1}{25}\)
\(\Rightarrow1+2sinx.cosx=\dfrac{1}{25}\Rightarrow sinx.cosx=-\dfrac{12}{25}\)
\(P=\dfrac{sinx}{cosx}+\dfrac{cosx}{sinx}=\dfrac{sin^2x+cos^2x}{sinx.cosx}=\dfrac{1}{sinx.cosx}=\dfrac{1}{-\dfrac{12}{25}}=-\dfrac{25}{12}\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (1)