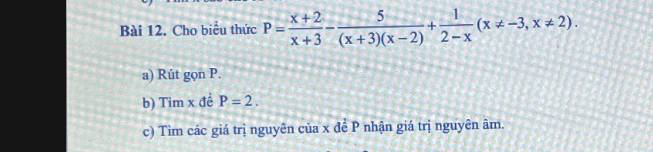a) \(P=\dfrac{x+2}{x+3}-\dfrac{5}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)}+\dfrac{1}{2-x}\left(x\ne-3;x\ne2\right)\)
\(P=\dfrac{x+2}{x+3}-\dfrac{5}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)}-\dfrac{1}{x-2}\)
\(P=\dfrac{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)}-\dfrac{5}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)}-\dfrac{x+3}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)}\)
\(P=\dfrac{x^2-4-5-x-3}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)}\)
\(P=\dfrac{x^2-x-12}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)}\)
\(P=\dfrac{x^2+3x-4x-12}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)}\)
\(P=\dfrac{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-4\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)}\)
\(P=\dfrac{x-4}{x-2}\)
b) \(P=2\) khi:
\(\dfrac{x-4}{x-2}=2\Leftrightarrow x-4=2\left(x-2\right)\Leftrightarrow x-4=2x-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-x=-4+4\Leftrightarrow x=0\left(tm\right)\)
c) Ta có: \(P=\dfrac{x-4}{x-2}=\dfrac{x-2-2}{x-2}=1-\dfrac{2}{x-2}\)
Do P nguyên âm \(\Rightarrow P< 0\Rightarrow\dfrac{2}{x-2}>1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4-x}{x-2}>0\)
TH1: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4-x>0\\x-2>0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< 4\\x>2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow2< x< 4\)
TH2: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4-x< 0\\x-2< 0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>4\\x< 2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x\in\varnothing\)
Mà P lại là 1 số nguyên nên các số nguyên x thỏa mãn là \(x\in\left\{4;0;3;1\right\}\)
Vậy để P là số nguyên âm và x là số nguyên thì \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2< x< 4\\x\in\left\{4;0;3;1\right\}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x=1\)