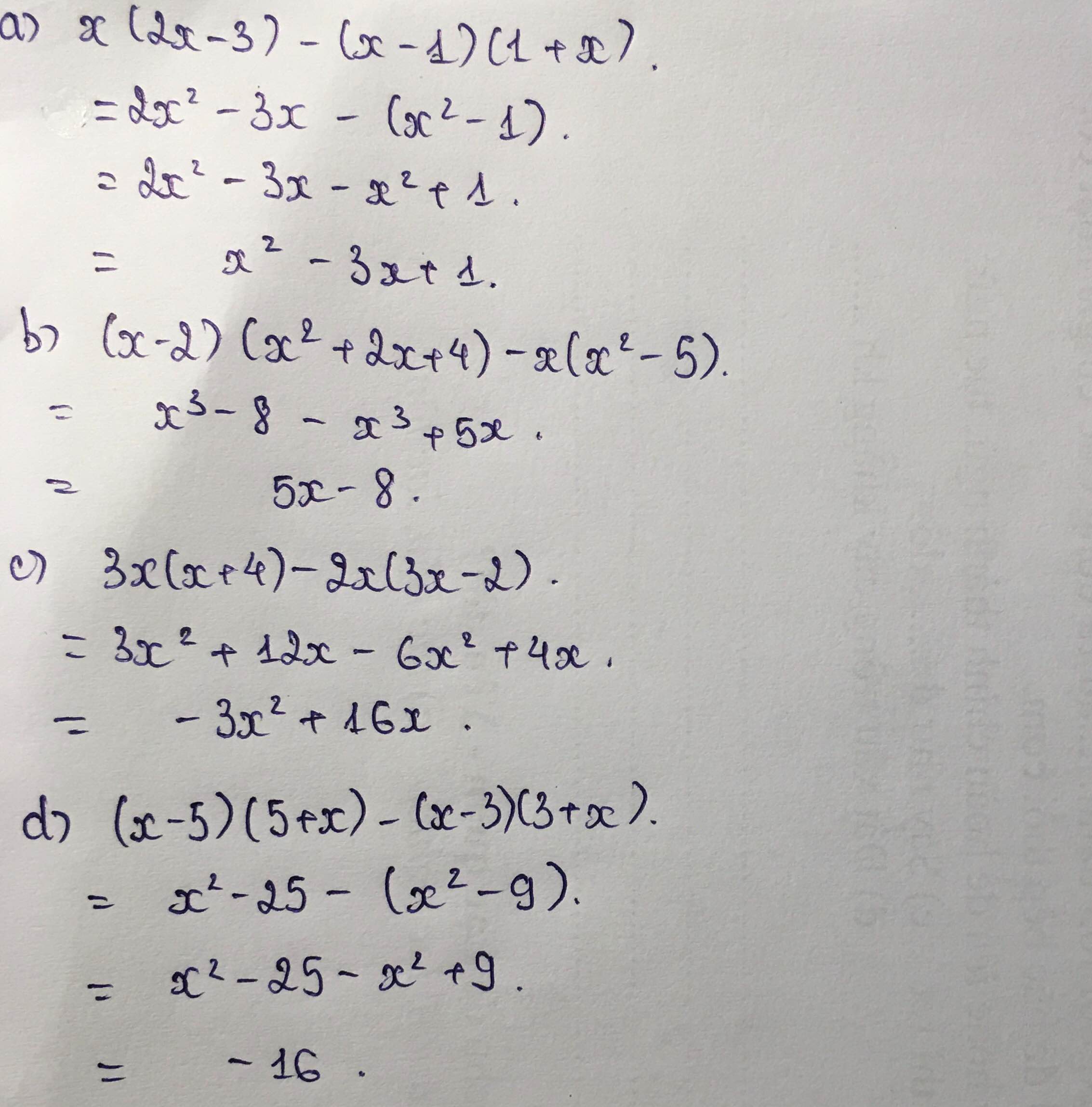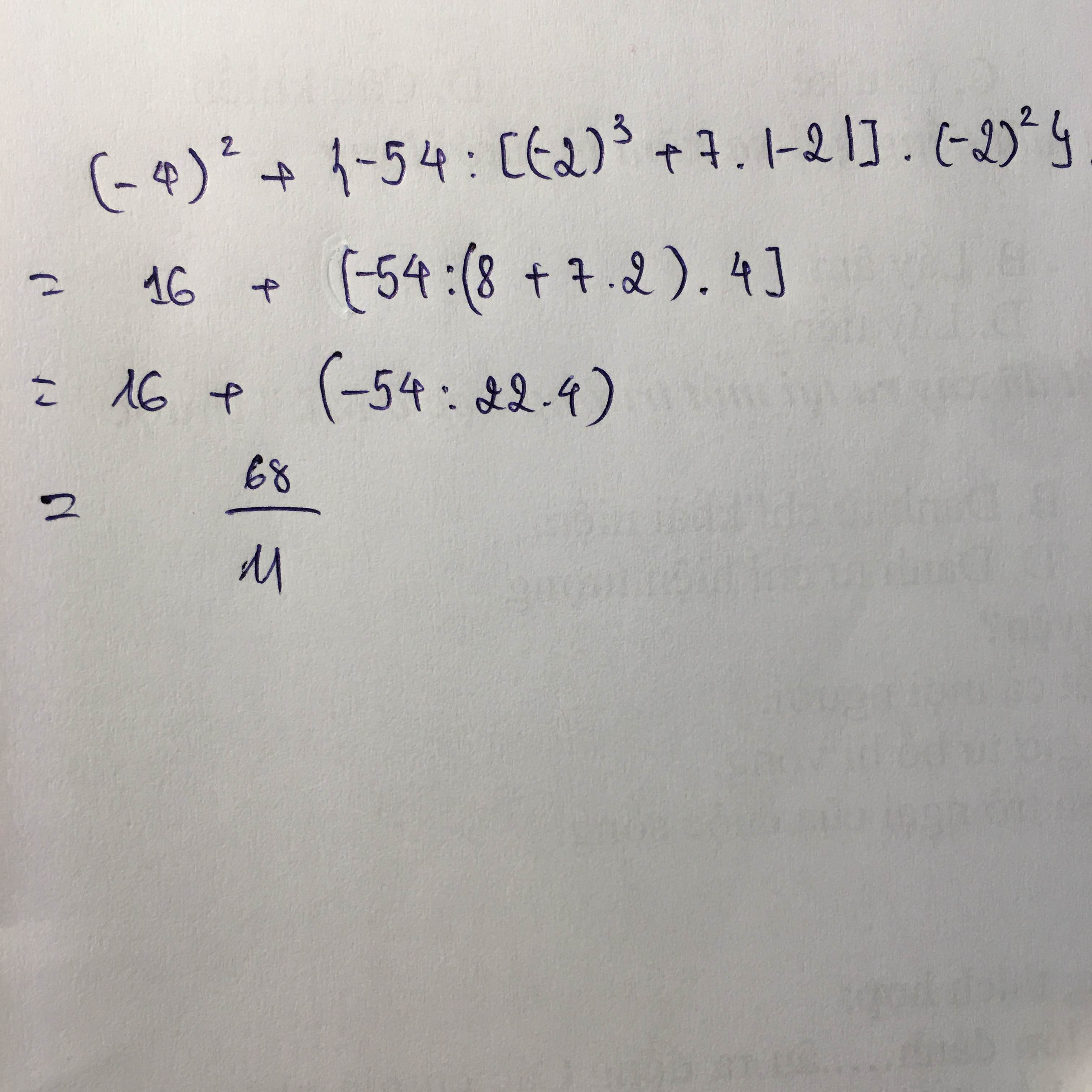Học tại trường
Chưa có thông tin
Đến từ
Chưa có thông tin , Chưa có thông tin
Số lượng câu hỏi
3
Số lượng câu trả lời
2829
Điểm GP
716
Điểm SP
2174