thực hiện phép chia hợp lí
(x^2-2x-y^2+1) : (x-y-1)
1, Thực hiện phép chia sau 1 cách họp lí:
(x2-2x-y2+1):(x-y-1)
2, Phân tích đa thức sau thành nhân tử:
x2+x-y2+y
1, = [(x-1)^2-y^2] : (x-y-1)
= (x+y-1).(x-y-1) : (x-y-1) = x+y-1
2, x^2-x-y^2+y = (x^2-y^2)-(x-y) = (x-y).(x+y) - (x-y) = (x-y).(x+y+1)
k mk nha
Bài 2:Thực hiện phép tính (tình bằng cách hợp lí nếu có thể)
-16-(35-x)=-7
lx-2l=9
(4-2x).(x-3)=0
(x-2)^2-64=0
Bài 3: Tìm số nguyên x,y
(x-1).y=11
2x+5 là bội của x+1
bài 2
1,35-x=-16-(-7)
35-x=-9
x=35-(-9)=44
2,/x-2/=9 suy ra x-2=9 hoặc =-9 rồi tự tính
3, suy ra 4-2x=0 hoặc x-3 =0 tụ tính x
4, (x-2)^2=64 = 8^2 suy ra x-2 =8 hoặc -8
Bài 2: Thực hiện phép tính (tính bằng cách hợp lí nếu có thể)
-16 - (35 - x) = -7
-16 - 35 + x = -7
-51 + x = -7
x = -7 - (-51)
x = 44
lx - 2l = 9
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x-2=9\\x-2=-9\end{cases}}\)
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=9+2\\x=-9+2\end{cases}}\)
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=11\\x=-7\end{cases}}\)
(4 - 2x) . (x - 3) = 0
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}4-2x=0\\x-3=0\end{cases}}\)
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}2x=4-0\\x=0+3\end{cases}}\)
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}2x=4\\x=3\end{cases}}\)
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=4\div2\\x=3\end{cases}}\)
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=2\\x=3\end{cases}}\)
(x - 2)2 - 64 = 0
=> (x - 2)2 = 0 + 64
=> (x - 2)2 = 64
=> (x - 2)2 = 82
=> x - 2 = 8
=> x = 8 + 2
=> x = 10
Thực hiện phép tính :
Thực hiện phép tính :
5.x^2(x-y+1)+(x^2-1)(x+y)
Bài 2:
1: \(A=\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x+4\right)+2\left(x+1\right)\left(1-x\right)\)
\(=\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-x\cdot2+2^2\right)-2\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)\)
\(=x^3+2^3-2\left(x^2-1\right)\)
\(=x^3+8-2x^2+2=x^3-2x^2+10\)
\(B=\left(2x-y\right)^2-2\left(4x^2-y^2\right)+\left(2x+y\right)^2+4\left(y+2\right)\)
\(=\left(2x-y\right)^2-2\cdot\left(2x-y\right)\left(2x+y\right)+\left(2x+y\right)^2+4\left(y+2\right)\)
\(=\left(2x-y-2x-y\right)^2+4\left(y+2\right)\)
\(=\left(-2y\right)^2+4\left(y+2\right)\)
\(=4y^2+4y+8\)
2: Khi x=2 thì \(A=2^3-2\cdot2^2+10=8-8+10=10\)
3: \(B=4y^2+4y+8\)
\(=4y^2+4y+1+7\)
\(=\left(2y+1\right)^2+7>=7>0\forall y\)
=>B luôn dương với mọi y
Bài 1:
5: \(x^2\left(x-y+1\right)+\left(x^2-1\right)\left(x+y\right)\)
\(=x^3-x^2y+x^2+x^3+x^2y-x-y\)
\(=2x^3-x+x^2-y\)
6: \(\left(3x-5\right)\left(2x+11\right)-6\left(x+7\right)^2\)
\(=6x^2+33x-10x-55-6\left(x^2+14x+49\right)\)
\(=6x^2+23x-55-6x^2-84x-294\)
=-61x-349
thực hiện phép chia hợp lí
(x^2-2x-y^2+1) : (x-y-1)
\(\dfrac{x^2-2x-y^2+1}{x-y-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x^2-2x+1\right)^2-y^2}{x-y-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x-y-1\right)\left(x-y+1\right)}{x-y-1}\)
\(=x-y+1\)
Bài 3:
3: \(6x\left(x-y\right)-9y^2+9xy\)
\(=6x\left(x-y\right)+9xy-9y^2\)
\(=6x\left(x-y\right)+9y\left(x-y\right)\)
\(=\left(x-y\right)\left(6x+9y\right)\)
\(=3\left(2x+3y\right)\left(x-y\right)\)
Bài 4:
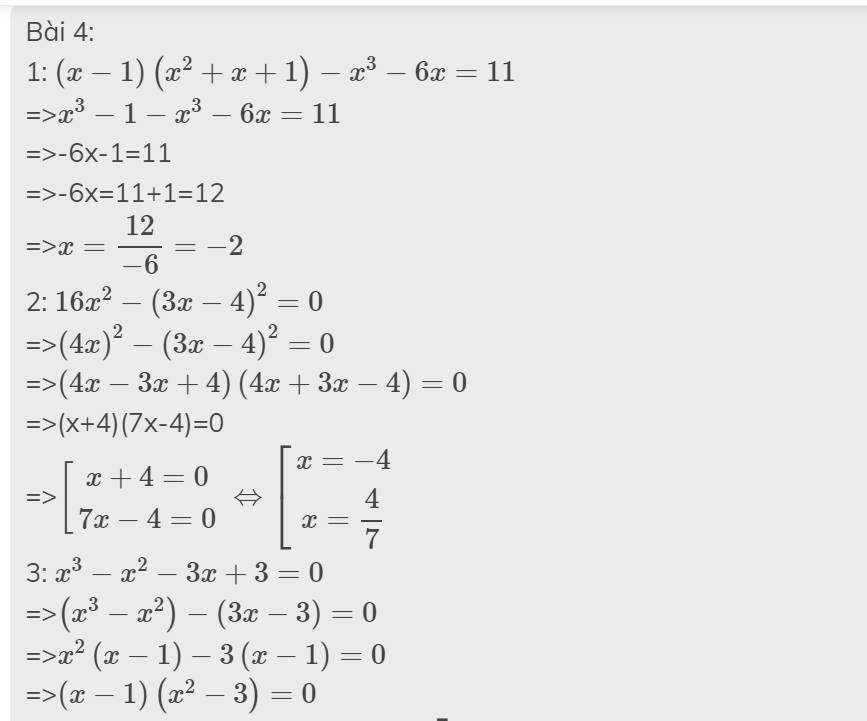

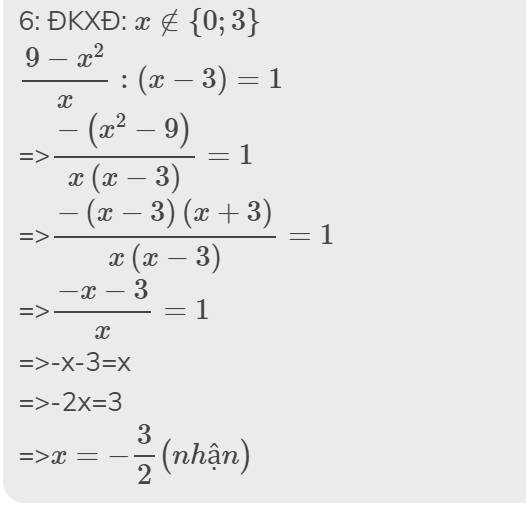
Thực hiện phép tính sau
A.(2x^2y-3xy+4xy^2)÷(2xy)
B.1/xy-x^2-1/y^2-xy
C.[x/xy-y^2- 2x-y/x^2-xy]:(1/x-1/y)
a: \(=x-\dfrac{3}{2}+2y\)
b: \(=\dfrac{1}{x\left(y-x\right)}-\dfrac{1}{y\left(y-x\right)}=\dfrac{y-x}{xy\left(y-x\right)}=\dfrac{1}{xy}\)
Thực hiện các phép tính sau: b)(xy/2x- y)-( 2x² / y-2x) c) (3x² - x/ x-1) +( x + 2/1-x) + (3 -2x²/ x-1 )
b: \(\dfrac{xy}{2x-y}-\dfrac{2x^2}{y-2x}=\dfrac{xy}{2x-y}+\dfrac{2x^2}{2x-y}=\dfrac{xy+2x^2}{2x-y}\)
b: \(\dfrac{3x^2-x}{x-1}+\dfrac{x+2}{1-x}+\dfrac{3-2x^2}{x-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{3x^2-x-x-2+3-2x^2}{x-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2-2x+1}{x-1}=x-1\)
thực hiện phép chia
a (4x^5-8x^3):(-2x^3)
b(9x^3-12x^2 + 3x ) : (-3x)
c (xy^2 + 4x^2y^3 -3x^2y^4):(-1/2x^2y^3)
d[2(x-y)^3-7(y-x)^2 - (y-x)] : (x-y)
e[(x^3 - y) ^5 -2(x-y)^4 + 3(x-y)^2] :[5(x-y)^2]
Thực hiện phép tính
a) \(\dfrac{3-x}{x-5}+\dfrac{2x-8}{x-5}\)
b) \(\dfrac{1}{x-y}+\dfrac{1}{x+y}+\dfrac{2x}{x^2-y^2}\)
a,\(\dfrac{3-x}{x-5}+\dfrac{2x-8}{x-5}=\dfrac{3-x+2x-8}{x-5}=\dfrac{x-5}{x-5}=1\)
b, \(\dfrac{1}{x-y}+\dfrac{1}{x+y}+\dfrac{2x}{x^2-y^2}=\dfrac{x+y}{\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)}+\dfrac{x-y}{\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)}+\dfrac{2x}{\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)}=\dfrac{x+y+x-y+2x}{\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)}=\dfrac{4x}{\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)}\)