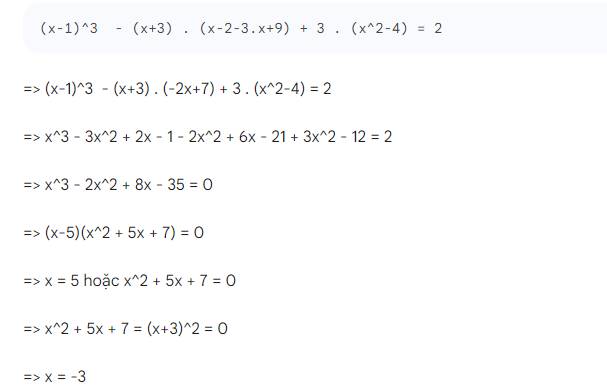Biết \(\left(x;y;z\right)\) là nghiệm nguyên dương của phương trình \(x^2+y^2+z^2=xy+3y+2z-4\).Tìm x,y,z

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Tìm x biết: \(\left(x+1\right)+\left(x+3\right)+\left(x+5\right)+...+\left(x+99\right)=0\)
Ta có: \(\left(x+1\right)+\left(x+3\right)+\left(x+5\right)+...+\left(x+99\right)=0\)
\(\dfrac{\left[\left(x+1\right)+\left(x+99\right)\right].50}{2}=0\)
\(\left(x+50\right).50=0\)
\(x+50=0\)
\(x=-50\)
Đúng 5
Bình luận (0)
\(\left(x+1\right)+\left(x+3\right)+\left(x+5\right)+...+\left(x+99\right)=0\)
Có tất cả số hạng là
\(\left(99-1\right):2+1=50số\)
Ta có: \(\left(x+1\right)+\left(x+3\right)+\left(x+5\right)+...+\left(x+99\right)=0\)
hay: \(\left(x+50\right).50=0\)
\(x+50=0\)
\(=>x=-50\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
tìm x biết a)x+2x+3x+4x+...+2015x2016times2017b)1-3+3^2-3^3+...+left(-3right)^xfrac{9^{1008}-1}{4}c)left|x+1right|+left|x+2right|+...+left|x+100right|605xd)tìm x nguyên biết left|x-1right|+left|x-2right|+...+left|x-100right|2500e) tìm x nguyên biết 2004left|x-4right|+left|x-10right|+left|x+101right|+left|x+99xright|+left|x+1000right|
Đọc tiếp
tìm x biết
a)\(x+2x+3x+4x+...+2015x=2016\times2017\)
b)\(1-3+3^2-3^3+...+\left(-3\right)^x=\frac{9^{1008}-1}{4}\)
c)\(\left|x+1\right|+\left|x+2\right|+...+\left|x+100\right|=605x\)
d)tìm x nguyên biết \(\left|x-1\right|+\left|x-2\right|+...+\left|x-100\right|=2500\)
e) tìm x nguyên biết \(2004=\left|x-4\right|+\left|x-10\right|+\left|x+101\right|+\left|x+99x\right|+\left|x+1000\right|\)
1, Tìm x,y,z biết :
\(\left|x-6\right|+\left|x-10\right|+\left|x-2022\right|+\left|y-2014\right|+\left|z-2015\right|=2016\)
2, Tìm cặp số nguyên x,y biết :
\(\left|x-5\right|+\left|1-x\right|=\frac{12}{\left|y+1\right|+3}\)
\(1)\)
\(VT=\left(\left|x-6\right|+\left|2022-x\right|\right)+\left|x-10\right|+\left|y-2014\right|+\left|z-2015\right|\)
\(\ge\left|x-6+2022-x\right|+\left|0\right|+\left|0\right|+\left|0\right|=2016\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra \(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\hept{\begin{cases}\left(x-6\right)\left(2022-x\right)\ge0\left(1\right)\\x-10=y-2014=z-2015=0\left(2\right)\end{cases}}\)
\(\left(2\right)\)\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\hept{\begin{cases}x=10\\y=2014\\z=2015\end{cases}}\)
\(\left(1\right)\)
TH1 : \(\hept{\begin{cases}x-6\ge0\\2022-x\ge0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ge6\\x\le2022\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow}6\le x\le2022}\) ( nhận )
TH2 : \(\hept{\begin{cases}x-6\le0\\2022-x\le0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\le6\\x\ge2022\end{cases}}}\) ( loại )
Vậy \(x=10\)\(;\)\(y=2014\) và \(z=2015\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
\(2)\)
\(VT=\left|x-5\right|+\left|1-x\right|\ge\left|x-5+1-x\right|=\left|-4\right|=4\)
\(VP=\frac{12}{\left|y+1\right|+3}\le\frac{12}{3}=4\)
\(\Rightarrow\)\(VT\ge VP\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra \(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\hept{\begin{cases}\left(x-5\right)\left(1-x\right)\ge0\left(1\right)\\\left|y+1\right|=0\left(2\right)\end{cases}}\)
\(\left(1\right)\)
TH1 : \(\hept{\begin{cases}x-5\ge0\\1-x\ge0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ge5\\x\le1\end{cases}}}\) ( loại )
TH2 : \(\hept{\begin{cases}x-5\le0\\1-x\le0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\le5\\x\ge1\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow}1\le x\le5}\) ( nhận )
\(\left(2\right)\)\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(y=-1\)
Vậy \(1\le x\le5\) và \(y=-1\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
tìm x biết :
\(\left|x-1\right|+2.\left|x-2\right|+3.\left|x-3\right|+4.\left|x-4\right|+5.\left|x-5\right|+20x=0\)
\(\left|x-1\right|+2\left|x-2\right|+3\left|x-3\right|+4\left|x-4\right|+5\left|x-5\right|+20x=0\left(1\right)\)
TH1: x<1
(1) trở thành 1-x+2(2-x)+3(3-x)+4(4-x)+5(5-x)+20x=0
=>\(1-x+4-2x+9-3x+16-4x+25-5x+20x=0\)
=>\(5x+55=0\)
=>x=-11(nhận)
TH2: 1<=x<2
Phương trình (1) sẽ trở thành:
\(x-1+2\left(2-x\right)+3\left(3-x\right)+4\left(4-x\right)+5\left(5-x\right)+20x=0\)
=>\(x-1+4-2x+9-3x+16-4x+25-5x+20x=0\)
=>\(7x+53=0\)
=>\(x=-\dfrac{53}{7}\left(loại\right)\)
TH3: 2<=x<3
Phương trình (1) sẽ trở thành:
\(x-1+2\left(x-2\right)+3\left(3-x\right)+4\left(4-x\right)+5\left(5-x\right)+20x=0\)
=>\(x-1+2x-4+9-3x+16-4x+25-5x+20x=0\)
=>\(11x+45=0\)
=>\(x=-\dfrac{45}{11}\left(loại\right)\)
TH4: 3<=x<4
Phương trình (1) sẽ trở thành:
\(x-1+2\left(x-2\right)+3\left(x-3\right)+4\left(4-x\right)+5\left(5-x\right)+20x=0\)
=>\(x-1+2x-4+3x-9+16-4x+25-5x+20x=0\)
=>\(-3x+27=0\)
=>x=9(loại)
TH5: 4<=x<5
Phương trình (1) sẽ trở thành:
\(\left(x-1\right)+2\left(x-2\right)+3\left(x-3\right)+4\left(x-4\right)+5\left(5-x\right)+20x=0\)
=>\(x-1+2x-4+3x-9+4x-16+25-5x+20x=0\)
=>\(25x-5=0\)
=>x=1/5(loại)
TH6: x>=5
Phương trình (1) sẽ trở thành:
\(\left(x-1\right)+2\left(x-2\right)+3\left(x-3\right)+4\left(x-4\right)+5\left(x-5\right)+20x=0\)
=>\(x-1+2x-4+3x-9+4x-16+5x-25+20x=0\)
=>35x-55=0
=>x=55/35(loại)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
1.Tìm x y thuộc Z biết:
\(\left(x-1\right)^2+2\left(y-3\right)^2=3\)
2. Tìm x biết:
\(\left|x+1\right|+\left|x+2\right|+\left|x+3\right|+....+\left|x+2019\right|=2018x\)
Bài 1:
Vì \((x-1)^2\geq 0, \forall x\in\mathbb{Z}\Rightarrow 2(y-3)^2=3-(x-1)^2\leq 3\)
\(\Rightarrow (y-3)^2\leq \frac{3}{2}\)
Mà \((y-3)^2\geq 0; (y-3)^2\in\mathbb{Z}\) nên \(\left[\begin{matrix} (y-3)^2=0\\ (y-3)^2=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Nếu \((y-3)^2=0\):
\((x-1)^2=3-2(y-3)^2=3\) (vô lý với $x$ nguyên)
Nếu \((y-3)^2=1\Rightarrow y-3=\pm 1\Rightarrow \left[\begin{matrix} y=4\\ y=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\((x-1)^2=3-2(y-3)^2=3-2=1\Rightarrow x-1=\pm 1\Rightarrow \left[\begin{matrix} x=0\\ x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \((x,y)=(0,4); (0,2); (2,4); (2,2)\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Bài 2:
Dễ thấy vế trái của đẳng thức đã cho không âm (tính chất trị tuyệt đối)
\(\Rightarrow 2018x=\text{VT}\geq 0\Rightarrow x\geq 0\)
\(\Rightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} |x+1|=x+1\\ |x+2|=x+2\\ |x+3|=x+3\\ ....\\ |x+2019|=x+2019\end{matrix}\right.\)
Phương trình trở thành:
\((x+1)+(x+2)+(x+3)+....+(x+2019)=2018x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow 2019x+2029095=2018x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-2029095< 0\) (vô lý- loại)
Vậy không tồn tại $x$ thỏa mãn.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tìm số nguyên x , biết
\(10\) ⋮ \(\left(x-1\right)\)
\(b.\left(x+5\right)\) ⋮ \(\left(x-2\right)\)
c. \(\left(3x+8\right)\) ⋮ \(\left(x-1\right)\)
a.
\(10⋮\left(x-1\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow x-1=Ư\left(10\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow x-1=\left\{-10;-5;-2;-1;1;2;5;10\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\left\{-9;-4;-1;0;2;3;6;11\right\}\)
b.
\(\left(x+5\right)⋮\left(x-2\right)\Rightarrow\left(x-2\right)+7⋮x-2\)
\(\Rightarrow7⋮x-2\)
\(\Rightarrow x-2=Ư\left(7\right)=\left\{-7;-1;1;7\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\left\{-5;1;3;9\right\}\)
c.
\(\left(3x+8\right)⋮\left(x-1\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(3x-3+11\right)⋮\left(x-1\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow3\left(x-1\right)+11⋮x-1\)
\(\Rightarrow11⋮\left(x-1\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow x-1=Ư\left(11\right)=\left\{-11;-1;1;11\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\left\{-10;0;2;12\right\}\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Tìm x biết :
\(\left(x^2-20\right)\left(x^2-15\right)\left(x^2-10\right)\left(x^2-5\right)< 0\)
Để \(\left(x^2-20\right)\left(x^2-15\right)\left(x^2-10\right)\left(x^2-5\right)< 0\)
Thì phải có một sốâm và 3 số dương hoặc 1 số dương và 3 số âm
Mà \(x^2\ge0\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2-20< x^2-15< x^2-10< x^2-5\)
+ Với TH có 1 số âm và 3 số dương:
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2-20< 0\\x^2-15>0\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow15< x^2< 20\Leftrightarrow x^2=16\Leftrightarrow x=\pm4\)
+ Với TH có 1 số dương và 3 số âm:
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2-10< 0\\x^2-5>0\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow5< x^2< 10\Leftrightarrow x^2=9\Leftrightarrow x=\pm3\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{\pm3;\pm4\right\}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Tìm x biết:
\(\left(x-1\right)^3-\left(x+3\right)\left(x^2-3x+9\right)+3\left(x^2-4\right)=2\)
(x-1)^3-(x+3)(x^2-3x+9)+3(x^2-4)=2
=>x^3-3x^2+3x-1-x^3-27+3x^2-12=2
=>3x-40=2
=>x=42/3=14
Đúng 3
Bình luận (0)
a) Tìm tập hợp các số nguyên x, biết rằng4dfrac{5}{9}:2dfrac{5}{18}-7 x left(3dfrac{1}{5}:3,2+4,5.1dfrac{31}{45}right):left(-21dfrac{1}{2}right)b) tìm x, biết left|x+dfrac{1}{2}right|+left|x+dfrac{1}{6}right|+left|x+dfrac{1}{12}right|+left|x+dfrac{1}{20}right|+....+left|x+dfrac{1}{110}right|-11xc)Tính gt biểu thức C2x^3-5y^3+2015 tại x,y thỏa mãn left|x-1right|+left(y+2right)^{20}0
Đọc tiếp
a) Tìm tập hợp các số nguyên x, biết rằng\(4\dfrac{5}{9}:2\dfrac{5}{18}-7< x< \left(3\dfrac{1}{5}:3,2+4,5.1\dfrac{31}{45}\right):\left(-21\dfrac{1}{2}\right)\)
b) tìm x, biết \(\left|x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right|+\left|x+\dfrac{1}{6}\right|+\left|x+\dfrac{1}{12}\right|+\left|x+\dfrac{1}{20}\right|+....+\left|x+\dfrac{1}{110}\right|-11x\)
c)Tính gt biểu thức \(C=2x^3-5y^3+2015\) tại x,y thỏa mãn \(\left|x-1\right|+\left(y+2\right)^{20}=0\)
giải phương trình: \(\left(x+1\right)^2\left(x+2\right)+\left(x-1\right)^2\left(x-2\right)=12\) biết kết quả x=1 mà mình k biết cách làm
\(\left(x^2+2x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)+\left(x^2-2x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)=12\)
\(x^3+2x^2+x+2x^2+4x+2+x^3-2x^2+x-2x^2+4x-2=12\)
\(2x^3+10x-12=0\)
\(2x^3-2x^2+2x^2-2x+12x-12=0\)
\(2x^2\left(x-1\right)+2x\left(x-1\right)+12\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\left(x-1\right)\left(2x^2+2x+12\right)=0\)
\(\left(x-1\right)\times2\left(x^2+x+6\right)=0\)
\(\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+2\times x\times\frac{1}{2}+\frac{1}{4}-\frac{1}{4}+6\right)=0\)
\(\left(x-1\right)\left(\left(x+\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{23}{4}\right)=9\)
Vế 2 >0
=> Nghiệm là x=1
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)