Đạo hàm cấp 5 của hàm số y =x ln x là
A. ![]()
B. ![]()
C. ![]()
D. ![]()
Tính đạo hàm cấp hai của mỗi hàm số sau:
a) \(y = 2{x^4} - 3{x^3} + 5{x^2}\)
b) \(y = \frac{2}{{3 - x}}\)
c) \(y = \sin 2x\cos x\)
d) \(y = {e^{ - 2x + 3}}\)
e) \(y = \ln (x + 1)\)
f) \(y = \ln ({e^x} + 1)\)
\(a,y'=8x^3-9x^2+10x\\ \Rightarrow y''=24x^2-18x+10\\ b,y'=\dfrac{2}{\left(3-x\right)^2}\\ \Rightarrow y''=\dfrac{4}{\left(3-x\right)^3}\)
\(c,y'=2cos2xcosx-sin2xsinx\\ \Rightarrow y''=-5sin\left(2x\right)cos\left(x\right)-4cos\left(2x\right)sin\left(x\right)\\ d,y'=-2e^{-2x+3}\\ \Rightarrow y''=4e^{-2x+3}\)
e,
\(y = \ln (x + 1) \Rightarrow y' = \frac{1}{{x + 1}} \Rightarrow y'' = - \frac{1}{{{{\left( {x + 1} \right)}^2}}}\)
f,
\(y = \ln ({e^x} + 1) \Rightarrow y' = \frac{{{e^x}}}{{{e^x} + 1}} \Rightarrow y'' = - \frac{{{e^x}.{e^x}}}{{{{\left( {{e^x} + 1} \right)}^2}}} = - \frac{{{e^{2x}}}}{{{{\left( {{e^x} + 1} \right)}^2}}}\)
Tính đạo hàm cấp hai của các hàm số sau:
a) \(y = \ln \left( {x + 1} \right);\)
b) \(y = \tan 2x.\)
a: y=ln(x+1)
=>\(y'=\dfrac{1}{x+1}\)
=>\(y''=\dfrac{1'\left(x+1\right)-1\left(x+1\right)'}{\left(x+1\right)^2}=\dfrac{-1}{\left(x+1\right)^2}\)
b: y=tan 2x
=>\(y'=\dfrac{2}{cos^22x}\)
=>\(y''=\left(\dfrac{2}{cos^22x}\right)'=\dfrac{-2\cdot cos^22x'}{cos^42x}=\dfrac{-2\cdot2\cdot cos2x\left(cos2x\right)'}{cos^42x}\)
\(=\dfrac{4\cdot2\cdot sin2x}{cos^32x}=\dfrac{8\cdot sin2x}{cos^32x}\)
Tính đạo hàm cấp hai của các hàm số sau:
a) \(y = x{e^{2x}};\)
b) \(y = \ln \left( {2x + 3} \right).\)
a: \(y=x\cdot e^{2x}\)
=>\(y'=\left(x\cdot e^{2x}\right)'\)
\(=x\cdot\left(e^{2x}\right)'+x'\cdot\left(e^{2x}\right)\)
\(=e^{2x}+2\cdot x\cdot e^{2x}\)
\(y''=\left(e^{2x}+2\cdot x\cdot e^{2x}\right)'\)
\(=\left(e^{2x}\right)'+\left(2\cdot x\cdot e^{2x}\right)'\)
\(=4\cdot e^{2x}+4\cdot x\cdot e^{2x}\)
b: \(y=ln\left(2x+3\right)\)
=>\(y'=\dfrac{\left(2x+3\right)'}{\left(2x+3\right)}=\dfrac{2}{2x+3}\)
=>\(y''=\left(\dfrac{2}{2x+3}\right)'=\dfrac{2\left(2x+3\right)'-2'\left(2x+3\right)}{\left(2x+3\right)^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{4}{\left(2x+3\right)^2}\)
Đạo hàm của hàmĐạo hàm của hàm số y = (2x+1)ln(1-x) là số y = (2x+1)ln(1-x) là
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Tính đạo hàm của mỗi hàm số sau:
a) \(y = \left( {{x^2} + 2x} \right)\left( {{x^3} - 3x} \right)\)
b) \(y = \frac{1}{{ - 2x + 5}}\)
c) \(y = \sqrt {4x + 5} \)
d) \(y = \sin x\cos x\)
e) \(y = x{e^x}\)
f) \(y = {\ln ^2}x\)
a: \(y'=\left(x^2+2x\right)'\left(x^3-3x\right)+\left(x^2+2x\right)\left(x^3-3x\right)'\)
\(=\left(2x+2\right)\left(x^3-3x\right)+\left(x^2+2x\right)\left(3x^2-3\right)\)
\(=2x^4-6x^2+2x^3-6x+3x^4-3x^2+6x^3-6x\)
\(=5x^4+8x^3-9x^2-12x\)
b: y=1/-2x+5
=>\(y'=\dfrac{2}{\left(2x+5\right)^2}\)
c: \(y'=\dfrac{\left(4x+5\right)'}{2\sqrt{4x+5}}=\dfrac{4}{2\sqrt{4x+5}}=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{4x+5}}\)
d: \(y'=\left(sinx\right)'\cdot cosx+\left(sinx\right)\cdot\left(cosx\right)'\)
\(=cos^2x-sin^2x=cos2x\)
e: \(y=x\cdot e^x\)
=>\(y'=e^x+x\cdot e^x\)
f: \(y=ln^2x\)
=>\(y'=\dfrac{\left(-1\right)}{x^2}=-\dfrac{1}{x^2}\)
4. Tính đạo hàm của các hàm số sau:
a) \(y = (3x^2-4x+1)^{-4}\)
b) \(y = 3^{x^2-1} + e^{-x+1}\)
c) \(y = \ln (x^2-4x) + \log_{3} (2x-1)\)
d) \(y =x . \ln x + 2^{\frac{x-1}{x+1}}\)
e) \(y = x^{-7} - \ln (x^2-1)\)
`a)TXĐ:R\\{1;1/3}`
`y'=[-4(6x-4)]/[(3x^2-4x+1)^5]`
`b)TXĐ:R`
`y'=2x. 3^[x^2-1] ln 3-e^[-x+1]`
`c)TXĐ: (4;+oo)`
`y'=[2x-4]/[x^2-4x]+2/[(2x-1).ln 3]`
`d)TXĐ:(0;+oo)`
`y'=ln x+2/[(x+1)^2].2^[[x-1]/[x+1]].ln 2`
`e)TXĐ:(-oo;-1)uu(1;+oo)`
`y'=-7x^[-8]-[2x]/[x^2-1]`
Lời giải:
a.
$y'=-4(3x^2-4x+1)^{-5}(3x^2-4x+1)'$
$=-4(3x^2-4x+1)^{-5}(6x-4)$
$=-8(3x-2)(3x^2-4x+1)^{-5}$
b.
$y'=(3^{x^2-1})'+(e^{-x+1})'$
$=(x^2-1)'3^{x^2-1}\ln 3 + (-x+1)'e^{-x+1}$
$=2x.3^{x^2-1}.\ln 3 -e^{-x+1}$
c.
$y'=\frac{(x^2-4x)'}{x^2-4x}+\frac{(2x-1)'}{(2x-1)\ln 3}$
$=\frac{2x-4}{x^2-4x}+\frac{2}{(2x-1)\ln 3}$
d.
\(y'=(x\ln x)'+(2^{\frac{x-1}{x+1}})'=x(\ln x)'+x'\ln x+(\frac{x-1}{x+1})'.2^{\frac{x-1}{x+1}}\ln 2\)
\(=x.\frac{1}{x}+\ln x+\frac{2}{(x+1)^2}.2^{\frac{x-1}{x+1}}\ln 2\\ =1+\ln x+\frac{2^{\frac{2x}{x+1}}\ln 2}{(x+1)^2}\)
e.
\(y'=-7x^{-8}-\frac{(x^2-1)'}{x^2-1}=-7x^{-8}-\frac{2x}{x^2-1}\)
Đạo hàm của hàm số y = x + 2 x - 1 ln ( x + 2 ) là
A. y ' = 2 x log ( 2 x - 1 ) - 2 x 2 ( 2 x - 1 ) ln 10 log 2 ( 2 x - 1 )
B. y ' = x log ( 2 x - 1 ) - 2 x 2 ( 2 x - 1 ) ln 10 log 2 ( 2 x - 1 )
C. y ' = 2 x log ( 2 x - 1 ) + 2 x 2 ( 2 x - 1 ) ln 10 log 2 ( 2 x - 1 )
D. y ' = - 2 x log ( 2 x - 1 ) - 2 x 2 ( 2 x - 1 ) ln 10 log 2 ( 2 x - 1 )
Đạo hàm của hàm số y=(2x+1)ln(1-x) là

![]()
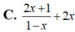
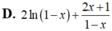
Tính đạo hàm của các hàm số sau:
g) \(y = \ln (x^2+x+1)\)
l) \(y = \dfrac{\ln x}{x+1}\)
g: \(y=ln\left(x^2+x+1\right)\)
=>\(y'=\dfrac{\left(x^2+x+1\right)'}{x^2+x+1}=\dfrac{2x+1}{x^2+x+1}\)
l: \(y=\dfrac{lnx}{x+1}\)
=>\(y'=\dfrac{\left(lnx\right)'\cdot\left(x+1\right)-\left(x+1\right)'\left(lnx\right)}{\left(x+1\right)^2}\)
=>\(y'=\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{x}\left(x+1\right)-lnx}{\left(x+1\right)^2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow y'=\dfrac{\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)}{x}-lnx}{\left(x+1\right)^2}\)