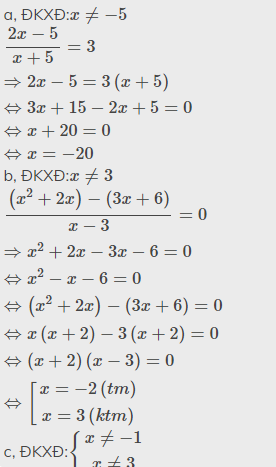Giải các phương trình sau: | 2x | = x - 6

Những câu hỏi liên quan
3.15 giải các phương trình sau :
a) ( x - 6 ) ( 2x - 5 ) ( 3x + 9 ) = 0
b) 2x( x - 3 ) + 5( x - 3 ) = 0
c) ( x^2 - 4 ) - ( x - 2 ) ( 3 - 2x ) =0
3.16 tìm m để phương trình sau có nghiệm :
x=-7 ( 2m - 5 )x - 2m^2 + 8
3.17 giải các phương trình sau :
a) ( 2x - 1 )^2 - ( 2x + 1 ) = 0
\(a,\left(x-6\right)\left(2x-5\right)\left(3x+9\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-6=0\Leftrightarrow x=6\\2x-5=0\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{2}\\3x+9=0\Leftrightarrow x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(b,2x\left(x-3\right)+5\left(x-3\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+5\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3=0\Leftrightarrow x=3\\2x+5=0\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(c,x^2-4-\left(x-2\right)\left(3-2x\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)-\left(x-2\right)\left(3-2x\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2-3+2x\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x=-7\left(2m-5\right)x-2m^2+8\Leftrightarrow x+7\left(2m-5\right)=8-2m^2\Leftrightarrow x\left(14m-34\right)=8-2m^2\)
\(ycđb\Leftrightarrow14m-34\ne0\Leftrightarrow m\ne\dfrac{34}{14}\)\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{8-2m^2}{14m-34}\)
\(3.17\Leftrightarrow4x^2-4x+1-2x-1=0\Leftrightarrow4x^2-6x=0\Leftrightarrow x\left(4x-6\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=\dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
3.15:
a, \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-6=0\\2x-5=0\\3x+9=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=6\\x=\dfrac{5}{2}\\x=-\dfrac{9}{3}=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
b, \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(2x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-3=0\\2x+5=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-\dfrac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
c, \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)-\left(x-2\right)\left(3-2x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2-3+2x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\3x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
3.16
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2m-5\right).-7-2m^2+8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-14m+35-2m^2+8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-14m-2m^2+43=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2\left(7m+m^2\right)=-43\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\left(7-m\right)=\dfrac{43}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{m\left(7-m\right)}{1}-\dfrac{43}{2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{14m-2m^2}{2}-\dfrac{43}{2}=0\)
pt vô nghiệm
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình sau: | 2x | = x - 6
Ta có: | 2x | = x - 6
+ Với x ≥ 0, phương trình tương đương: 2x = x - 6 ⇔ x = - 6.
Không thỏa mãn điều kiện x ≥ 0.
+ Với x < 0, phương trình tương đương: - 2x = x - 6 ⇔ - 3x = - 6 ⇔ x = 2.
Không thỏa mãn điều kiện x < 0.
Vậy phương trình đã cho vô nghiệm.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình sau 5 – (6 – x) = 4(3 – 2x)
5 – (6 – x) = 4(3 – 2x)
⇔ 5 – 6 + x = 12 – 8x
⇔ x + 8x = 12 – 5 + 6
⇔ 9x = 13
⇔ x = 13/9
Vậy phương trình có một nghiệm x = 13/9.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải các bất phương trình sau:
4
x
2
+
3
.
3
x
+
x
.
3
x
2
x
2
.
3
x...
Đọc tiếp
Giải các bất phương trình sau: 4 x 2 + 3 . 3 x + x . 3 x < 2 x 2 . 3 x + 2 x + 6
Ta có bất phương trình đã cho tương đương với
4 x 2 + 3 . 3 x + x . 3 x - 2 x 2 . 3 x - 2 x - 6 < 0
⇔ 3 + x - 2 x 2 3 x − 2(x − 2 x 2 + 3) < 0
⇔(−2 x 2 + x + 3)( 3 x − 2) < 0
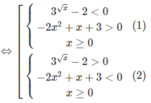
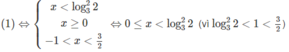
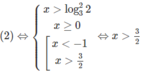
Vậy nghiệm của bất phương trình là x > 3/2 hoặc
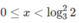
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
giải các phương trình sau : \(\dfrac{2x-3}{4}+2=\dfrac{1-x}{6}\)
\(\dfrac{2x-3}{4}+2=\dfrac{1-x}{6}\)
\(\dfrac{\left(2x-3\right).6}{4.6}+\dfrac{2.16}{16.1}=\dfrac{\left(1-x\right).4}{6.4}\)
khử mẫu:
=>(2x-3).6+32=(1-x).4
=>12x-18+32=4x-1
=>12x-18+32-4x+1=0
=>8x+13=0
=>x=-13:8
=>x=\(-\dfrac{13}{8}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
\(6x-9+24=2-2x\Leftrightarrow8x=-13\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{13}{8}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (1)
Giải các phương trình sau 2x+6=0 3x-9=0 4x+20=0 4x+1=6-x
\(\text{ 2x+6=0 }\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=-6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-3\)
\(S=\left\{-3\right\}\)
\(\text{3x-9=0 }\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=3\)
\(S=\left\{3\right\}\)
\(\text{4x+20=0}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=-20\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-5\)
\(S=\left\{-5\right\}\)
\(\text{4x+1=6-x}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x+1-6-x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{3}\)
\(S=\left\{\dfrac{5}{3}\right\}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
a: 2x+6=0
=>2x=-6
=>x=-3
b: 3x-9=0
=>3x=9
=>x=3
c: 4x+20=0
=>x+5=0
=>x=-5
d: 4x+1=6-x
=>5x=5
=>x=1
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
\(4x+1=6-x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x+1-6+x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x-5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=1\)
\(S=\left\{1\right\}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Bài 1:giải các phương trình sau:
a) (x-3).(x+7)=0 b) (x-2)^2+(x-2).(x-3)=0 c)x^2-5x+6=0
Bài 2:giải các phương trình chứa ẩn ở mẫu sau:
a)x/x+1-1=3/2x b)4x/x-2-7/x=4
Bài 3:giải phương trình sau
a)2x^2-5x-7=0 b)1/x^2-4+2x/x-2=2x/x+2
giúp mình với,mình đang cần gấp
Mình khuyên bạn thế này :
Bạn nên tách những câu hỏi ra
Như vậy các bạn sẽ dễ giúp
Và cũng có nhiều bạn giúp hơn !
Bài 1.
a) ( x - 3 )( x + 7 ) = 0
<=> x - 3 = 0 hoặc x + 7 = 0
<=> x = 3 hoặc x = -7
Vậy S = { 3 ; -7 }
b) ( x - 2 )2 + ( x - 2 )( x - 3 ) = 0
<=> ( x - 2 )( x - 2 + x - 3 ) = 0
<=> ( x - 2 )( 2x - 5 ) = 0
<=> x - 2 = 0 hoặc 2x - 5 = 0
<=> x = 2 hoặc x = 5/2
Vậy S = { 2 ; 5/2 }
c) x2 - 5x + 6 = 0
<=> x2 - 2x - 3x + 6 = 0
<=> x( x - 2 ) - 3( x - 2 ) = 0
<=> ( x - 2 )( x - 3 ) = 0
<=> x - 2 = 0 hoặc x - 3 = 0
<=> x = 2 hoặc x = 3
Bài 2.
a) \(\frac{x}{x+1}-1=\frac{3}{2}x\)
ĐKXĐ : x khác -1
<=> \(\frac{x}{x+1}-\frac{x+1}{x+1}=\frac{3}{2}x\)
<=> \(\frac{-1}{x+1}=\frac{3x}{2}\)
=> 3x( x + 1 ) = -2
<=> 3x2 + 3x + 2 = 0
Vi 3x2 + 3x + 2 = 3( x2 + x + 1/4 ) + 5/4 = 3( x + 1/2 )2 + 5/4 ≥ 5/4 > 0 ∀ x
=> phương trình vô nghiệm
b) \(\frac{4x}{x-2}-\frac{7}{x}=4\)
ĐKXĐ : x khác 0 ; x khác 2
<=> \(\frac{4x^2}{x\left(x-2\right)}-\frac{7x-14}{x\left(x-2\right)}=\frac{4x^2-8x}{x\left(x-2\right)}\)
=> 4x2 - 7x + 14 = 4x2 - 8x
<=> 4x2 - 7x - 4x2 + 8x = -14
<=> x = -14 ( tm )
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm x = -14
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Giải các phương trình sau. 2x-1=2-x ; x-5x-1/6=8-3x/4. ; x/3 - 2x+1/2=x/6 - x ; (2x-5)(x+3)=0. ; (1-7)(2+x)=0
Bạn cần viết đề bằng công thức toán (biểu tượng $\sum$ góc trái khung soạn thảo) đẻ được hỗ trợ tốt hơn. Viết như thế kia rất khó đọc => khả năng bị bỏ qua bài cao.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
a: =>3x=3
=>x=1
b: =>12x-2(5x-1)=3(8-3x)
=>12x-10x+2=24-9x
=>2x+2=24-9x
=>11x=22
=>x=2
c: =>2x-3(2x+1)=x-6x
=>-5x=2x-6x-3=-4x-3
=>-x=-3
=>x=3
d: =>2x-5=0 hoặc x+3=0
=>x=5/2 hoặc x=-3
e: =>x+2=0
=>x=-2
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình sau: a. 2x-5/x+5=3
b. (x^2+2x)-(3x+6)/x-3=0
c. x/2(x-3)+x/2x+2=2x/(x+1)(x-3)
a, ĐKXĐ:\(x\ne-5\)
\(\dfrac{2x-5}{x+5}=3\\ \Rightarrow2x-5=3\left(x+5\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow3x+15-2x+5=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x+20=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x=-20\)
b, ĐKXĐ:\(x\ne3\)
\(\dfrac{\left(x^2+2x\right)-\left(3x+6\right)}{x-3}=0\\ \Rightarrow x^2+2x-3x-6=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-x-6=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+2x\right)-\left(3x+6\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x\left(x+2\right)-3\left(x+2\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-2\left(tm\right)\\x=3\left(ktm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
c, ĐKXĐ:\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne-1\\x\ne3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\dfrac{x}{2\left(x-3\right)}+\dfrac{x}{2x+2}=\dfrac{2x}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)}\\ \Leftrightarrow x\left(\dfrac{1}{2\left(x-3\right)}+\dfrac{1}{2\left(x+1\right)}-\dfrac{2}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)}\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x\left(\dfrac{x+1}{2\left(x-3\right)\left(x+1\right)}+\dfrac{x-3}{2\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)}-\dfrac{4}{2\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)}\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x.\dfrac{x+1+x-3-4}{2\left(x-3\right)\left(x+1\right)}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x\left(2x-6\right)}{2\left(x-3\right)\left(x+1\right)}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x\left(x-3\right)}{2\left(x-3\right)\left(x+1\right)}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x}{x+1}=0\\ \Rightarrow x=0\left(tm\right)\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)