Phương trình 2 sin 2 x + 3 cos 2 x = 4 . 3 sin 2 x có bao nhiêu nghiệm thuộc - 2017 , 2017
A. 1284.
B. 4034
C. 1285.
D. 4035
Trong các phương trình sau: cos x = 5 - 3 (1); sin x = 1 - 2 (2); sin x + cos x = 2 (3), phương trình nào vô nghiệm?
A. (2)
B. (1)
C. (3)
D. (1) và (2)
Trong các phương trình sau: cos x = 5 - 3 (1); sin x = 1 - 2 (2); sin x + cos x = 2 (3), phương trình nào vô nghiệm?
A. (2).
B. (1).
C. (3).
D. (1) và (2).
Chọn C
Ta có: ![]() nên (1) và (2) có nghiệm.
nên (1) và (2) có nghiệm.
Cách 1:
Xét: ![]()
![]() nên (3) vô nghiệm.
nên (3) vô nghiệm.
Cách 2:
Điều kiện có nghiệm của phương trình: sin x + cos x = 2 là: 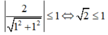
(vô lý) nên (3) vô nghiệm.
Cách 3:
Vì 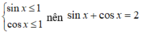
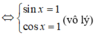
nên (3) vô nghiệm.
giải phương trình sin^2 x − 4√3 sin x · cos x + cos^2 x = −2.
Với \(cosx=0\) ko phải nghiệm
Với \(cosx\ne0\) chia 2 vế cho \(cos^2x\)
\(\Rightarrow tan^2x-4\sqrt{3}tanx+1=-2\left(1+tan^2x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3tan^2x-4\sqrt{3}tanx+3=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}tanx=\sqrt{3}\\tanx=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k\pi\\x=\dfrac{\pi}{6}+k\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
Nghiệm của phương trình sin x - 3 . cos x = 2 . sin 3 x là
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
giải phương trình: sin(2x+pi/2)=sin(x-pi/3)
\(sin\left(2x+\dfrac{\Omega}{2}\right)=sin\left(x-\dfrac{\Omega}{3}\right)\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x+\dfrac{\Omega}{2}=x-\dfrac{\Omega}{3}+k2\Omega\\2x+\dfrac{\Omega}{2}=\Omega-x+\dfrac{\Omega}{3}+k2\Omega\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{5}{6}\Omega+k2\Omega\\3x=\dfrac{4}{3}\Omega-\dfrac{1}{2}\Omega+k2\Omega\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{5}{6}\Omega+k2\Omega\\x=\dfrac{5}{18}\Omega+\dfrac{k2\Omega}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
giải phương trình: sin(2x+pi/2)=sin(x-pi/3)
Lời giải:
$\sin (2x+\frac{\pi}{2})=\sin (x-\frac{\pi}{3})$
\(\Rightarrow \left[\begin{matrix}\ 2x+\frac{\pi}{2}=x-\frac{\pi}{3}+2k\pi\\ 2x+\frac{\pi}{2}=\pi -(x-\frac{\pi}{3})+2k\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow \left[\begin{matrix}\ x=\pi (2k-\frac{5}{6})\\ x=\frac{1}{3}\pi (\frac{5}{6}+2k)\end{matrix}\right.\) với $k$ nguyên bất kỳ.
Giải phương trình: \(Sin^4\left(\dfrac{x}{2}\right)-Sin^2\dfrac{x}{2}\left(Sinx+3\right)+Sinx+2=0\)
Giải phương trình \(Sin^4\left(\dfrac{x}{2}\right)-Sin^2\dfrac{x}{2}\left(Sinx+3\right)+Sinx+2=0\)
- Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sin^2\dfrac{x}{2}=a\\\sin x+3=b\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(PTTT:a^2-ab+b-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-b\left(a-1\right)+\left(a-1\right)\left(a+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(a-1\right)\left(a+1-b\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}a=1\\a-b=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
- Thay lại vào phương trình ta được :\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sin^2\dfrac{x}{2}=1\\\sin^2\dfrac{x}{2}-\sin x-3=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sin^2\dfrac{x}{2}=1\\\dfrac{1-\cos x}{2}-\sin x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sin^2\dfrac{x}{2}=1\\\cos x+2\sin x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Thấy : \(-\sqrt{5}\le2\sin x+\cos x\le\sqrt{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow2\sin x+\cos x=-3\left(L\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sin\dfrac{x}{2}=1\\\sin\dfrac{x}{2}=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{x}{2}=\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\\\dfrac{x}{2}=-\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\pi+k4\pi\\x=-\pi+k4\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\left(K\in Z\right)\)
Vậy ....
Giải phương trình
\(\left(2\cos x+\sqrt{3}\right)\left(\cos2x+2\sin x-\sqrt{3}\right)=1-4\sin^2x\)
\(\left(2cosx+\sqrt{3}\right)\left(cos2x+2sinx-\sqrt{3}\right)=1-4\left(1-cos^2x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2cosx+\sqrt{3}\right)\left(cos2x+2sinx-\sqrt{3}\right)=4cos^2x-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2cosx+\sqrt{3}\right)\left(cos2x+2sinx-\sqrt{3}\right)=\left(2cosx+\sqrt{3}\right)\left(2cosx-\sqrt{3}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}cosx=-\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\Rightarrow x=...\\cos2x+2sinx-\sqrt{3}=2cosx-\sqrt{3}\left(1\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow cos^2x-sin^2x-2\left(cosx-sinx\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(cosx-sinx\right)\left(cosx+sinx\right)-2\left(cosx-sinx\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(cosx-sinx\right)\left(cosx+sinx-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow...\)
Có bao nhiêu số nguyên m để phương trình ln m + 2 sin x + ln m + 3 sin x = sin x có nghiệm thực ?
A. 4.
B. 3.
C. 5.
D. 6.