Cho hàm số f(x)=\(x-2\sqrt{9-x^2}\)
a) Xét tính chẵn, lẻ
b) Tìm x sao cho f(x)=3
Cho hàm số f(x) = \(\frac{\sqrt{1-x}+\sqrt{x+1}}{\sqrt{x+2}-\sqrt{2-x}}\). Xét tính chẵn, lẻ của hàm số f
Mọi người làm cho mình tham khảo đáp án.
\(DK:\hept{\begin{cases}-1\le x\le1\\x\ne0\end{cases}}\)
Ta co:
\(f\left(-x\right)=\frac{\sqrt{1-\left(-x\right)}+\sqrt{-x+1}}{\sqrt{-x+2}-\sqrt{2-\left(-x\right)}}=-\left(\frac{\sqrt{1-x}+\sqrt{x+1}}{\sqrt{x+2}-\sqrt{2-x}}\right)=-f\left(x\right)\)
Suy ra: f(x) la ham so chan
Tìm tập xác định và xét tính chẵn lẻ của hàm số f(x) = \(\sqrt{4-x}+\sqrt{x+4}\).
TXĐ: D=[-4;4]
\(f\left(-x\right)=\sqrt{4-\left(-x\right)}+\sqrt{-x+4}\)
\(=\sqrt{4-x}+\sqrt{4+x}\)
=f(x)
=>f(x) là hàm số chẵn
Bài 1: Xét tính chẵn lẻ của hàm số :y=|x3-x|
Bài 2: ho hàm số y= f(x)=\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-3,x\ge1\\2x^2-x-3,x< 1\end{matrix}\right.\) có đồ thị (C)
a) Tính f(4),f(-1)
b) Điểm nào sau đấy thuộc (c): A(4:1), b(-1,-4)
Bài 3: Cho tập hợp A= \(\left\{n\in◻\cdot\left|\right|9⋮\right\}\) B = (0;10)
a)Liệt kê các phần tử của A
b) Tính \(A\cap B\), \(A\cup B\)
(mình đag cần rất gấp)
Bài 1:
\(f\left(-x\right)=\left|\left(-x\right)^3+x\right|=\left|-x^3+x\right|=\left|-\left(x^3-x\right)\right|=\left|x^3-x\right|=f\left(x\right)\)
Vậy hàm số chẵn
Bài 2:
\(f\left(4\right)=4-3=1\\ f\left(-1\right)=2.1+1-3=0\\ b,\text{Thay }x=4;y=1\Leftrightarrow4-3=1\left(\text{đúng}\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow A\left(4;1\right)\in\left(C\right)\\ \text{Thay }x=-1;y=-4\Leftrightarrow2\left(-1\right)^2+1-3=-4\left(\text{vô lí}\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow B\left(-1;-4\right)\notin\left(C\right)\)
xét tính chẵn lẻ của hàm số
a)\(y=f\left(x\right)=\sin^22x+cos3x\)
b)\(y=f\left(x\right)=cos\sqrt{x^2-16}\)
a, \(f\left(-x\right)=sin^2\left(-2x\right)+cos\left(-3x\right)=sin^22x+cos3x=f\left(x\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\) Là hàm số chẵn.
b, \(f\left(-x\right)=\sqrt{\left(-x\right)^2-16}=\sqrt{x^2-16}=f\left(x\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\) Là hàm số chẵn.
Xét tính chẵn lẻ của các hàm số sau:
a) f (x) = -2x3+3x
b) f (x) = x2 + x
c) f (x) =\(\sqrt{6-3x}-\sqrt{6+3x}\)
d) f (x)= \(\dfrac{\sqrt{x+5}-\sqrt{5-x}}{4-x^2}\)
Mn giúp e bài này với ạ.E đang cần gấp ạ.
a: \(f\left(-x\right)=-2\cdot\left(-x\right)^3+3\cdot\left(-x\right)\)
\(=2x^3-3x\)
\(=-\left(-2x^3+3x\right)\)
=-f(x)
Vậy: f(x) là hàm số lẻ
c: TXĐ: D=[-2;2]
Nếu \(x\in D\Leftrightarrow-x\in D\)
\(f\left(-x\right)=\sqrt{6-3\cdot\left(-x\right)}-\sqrt{6+3\cdot\left(-x\right)}\)
\(=\sqrt{6+3x}-\sqrt{6-3x}\)
\(=-f\left(x\right)\)
Vậy: f(x) là hàm số lẻ
1/ Xét tính chẵn lẻ của hàm số: y = f(x) = căn (2-sin3x) - căn(2+sin3x) 2/ Tìm GTLN-GTNN của hàm số sau: y = f(x)= cos2x + 3 sin2sin2x - 2
Xét tính chẵn lẻ của các hàm số sau
c) y = \(\sqrt{2x+9}\)
d) y = \(\left(x-1\right)^{2010}+\left(x+1\right)^{2010}\)
e) y = \(\dfrac{x^4+3x^2-1}{x^2-4}\)
f) y = \(\left|x\right|^7.x^3\)
g) y = \(\sqrt[3]{5x-3}+\sqrt[3]{5x+3}\)
h) y = \(\sqrt{3+x}-\sqrt{3-x}\)
GIÚP MÌNH VỚI, MÌNH ĐANG CẦN GẤP
e: \(f\left(-x\right)=\dfrac{\left(-x\right)^4+3\cdot\left(-x\right)^2-1}{\left(-x\right)^2-4}=\dfrac{x^4+3x^2-1}{x^2-4}=f\left(x\right)\)
Vậy: f(x) là hàm số chẵn
\(c,f\left(-x\right)=\sqrt{-2x+9}=-f\left(x\right)\)
Vậy hàm số lẻ
\(d,f\left(-x\right)=\left(-x-1\right)^{2010}+\left(1-x\right)^{2010}\\ =\left[-\left(x+1\right)\right]^{2010}+\left(x-1\right)^{2010}\\ =\left(x+1\right)^{2010}+\left(x-1\right)^{2010}=f\left(x\right)\)
Vậy hàm số chẵn
\(g,f\left(-x\right)=\sqrt[3]{-5x-3}+\sqrt[3]{-5x+3}\\ =-\sqrt[3]{5x+3}-\sqrt[3]{5x-3}=-f\left(x\right)\)
Vậy hàm số lẻ
\(h,f\left(-x\right)=\sqrt{3-x}-\sqrt{3+x}=-f\left(x\right)\)
Vậy hàm số lẻ
Cho hàm số f(x)=\(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}-1}\)
a) Tìm các g/trị của x để hàm số xác định
b) Tính f(\(4-2\sqrt{3}\)) và f(\(a^2\)) với a< -1
c) Tìm x sao cho f(x)=f(\(x^2\))
Xét tính chẵn, lẻ của hai hàm số: f ( x ) = x + 2 - x - 2 , g ( x ) = - x
A. f(x) là hàm số chẵn, g(x)là hàm số chẵn.
B. f(x) là hàm số lẻ,g(x) là hàm số chẵn.
C. f(x) là hàm số lẻ, g(x) là hàm số lẻ.
D. f(x) là hàm số chẵn, g(x) là hàm số lẻ.
Đáp án B
+ Hàm số f(x) và g(x) đều có tập xác định là D= R.
+ Xét hàm số y=f(x) : Với mọi ![]() và
và
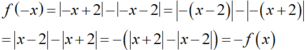
Nên y= f(x) là hàm số lẻ.
+ Xét hàm số y = g(x) :
Với mọi ![]() nên y = g(x) là hàm số chẵn.
nên y = g(x) là hàm số chẵn.
Chọn B.