Giari phương trình
30x^4+19x^3-15x^2-3x+1
Giải phương trình:
\(15x^4+30x^3+13x^2-2x-1=0\)0
\(15x^4+30x^3+13x^2-2x-1=0\)
<=> \(15x^4+15x^3+15x^3+15x^2-2x^2-2x-1=0\)
<=> \(15x^2\left(x^2+x\right)+15x\left(x^2+x\right)-2\left(x^2+x\right)-1\)
<=> \(15\left(x^2+x\right)^2-2\left(x^2+x\right)-1=0\)
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x^2+x=\frac{1}{3}\\x^2+x=\frac{1}{5}\end{cases}}\)
Em tự giải tiếp nhé!
Giải các bất phương trình bậc hai sau:
a) \(2{x^2} - 15x + 28 \ge 0\)
b) \( - 2{x^2} + 19x + 255 > 0\)
c) \(12{x^2} < 12x - 8\)
d) \({x^2} + x - 1 \ge 5{x^2} - 3x\)
a) Tam thức bậc hai \(f\left( x \right) = 2{x^2} - 15x + 28\) có hai nghiệm phân biệt là \({x_1} = \frac{7}{2};{x_2} = 4\)
và có \(a = 2 > 0\) nên \(f\left( x \right) \ge 0\) khi x thuộc hai nửa khoảng \(\left( { - \infty ;\frac{7}{2}} \right];\left[ {4; + \infty } \right)\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình \(2{x^2} - 15x + 28 \ge 0\) là \(\left( { - \infty ;\frac{7}{2}} \right] \cup \left[ {4; + \infty } \right)\)
b) Tam thức bậc hai \(f\left( x \right) = - 2{x^2} + 19x + 255\) có hai nghiệm phân biệt là \({x_1} = - \frac{{15}}{2};{x_2} = 17\)
và có \(a = - 2 < 0\) nên \(f\left( x \right) > 0\) khi x thuộc khoảng \(\left( { - \frac{{15}}{2};17} \right)\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình \( - 2{x^2} + 19x + 255 > 0\) là \(\left( { - \frac{{15}}{2};17} \right)\)
c) \(12{x^2} < 12x - 8 \Leftrightarrow 12{x^2} - 12x + 8 < 0\)
Tam thức bậc hai \(f\left( x \right) = 12{x^2} - 12x + 8\) có \(\Delta = - 240 < 0\) và \(a = 12 > 0\)
nên \(f\left( x \right) = 12{x^2} - 12x + 8\) dương với mọi x
Vậy bất phương trình \(12{x^2} < 12x - 8\) vô nghiệm
d) \({x^2} + x - 1 \ge 5{x^2} - 3x \Leftrightarrow -4{x^2} + 4x - 1 \ge 0\)
Tam thức bậc hai \(f\left( x \right) = -4{x^2} + 4x - 1\) có \(\Delta = 4^2 - 4.(-4).(-1)\)
Do đó tam thức bậc hai có nghiệm kép \({x_1} = {x_2}= \frac{1}{2}\) và a = - 4 < 0
Vậy bất phương trình \({x^2} + x - 1 \ge 5{x^2} - 3x\) có tập nghiệm S = {\(\frac{1}{2}\)}
Giải hệ phương trình sau :\(\hept{\begin{cases}15x^3-30x^2y-10y^3=4\\10x^3+30xy^2+15y^3=7\end{cases}}\)
3x^4+15x^3-30x-10/x-5
giải phương trình: \(\sqrt{3x+1}\)+2\(\sqrt[3]{19x+8}\)=2x2+x+5
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ge-\dfrac{1}{3}\)
\(2x^2-2x+\left(x+1-\sqrt{3x+1}\right)+2\left(x+2-\sqrt[3]{19x+8}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-2x+\dfrac{x^2-x}{x+1+\sqrt[]{3x+1}}+\dfrac{\left(x+7\right)\left(x^2-x\right)}{\left(x+2\right)^2+\left(x+2\right)\sqrt[3]{19x+8}+\sqrt[3]{\left(19x+8\right)^2}}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-x\right)\left(2+\dfrac{1}{x+1+\sqrt[]{3x+1}}+\dfrac{x+7}{\left(x+2\right)^2+\left(x+2\right)\sqrt[3]{19x+8}+\sqrt[3]{\left(19x+8\right)^2}}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-x=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Giải phương trình sau \(\frac{15x}{x^2+3x-4}-1=12.\left(\frac{1}{x+4}+\frac{1}{3x-3}\right)\)
tìm x
a)x^2-x-12=0
b)x^2+3x-18=0
c)8x^2+30x+7=0
d)x^3-11x^2+30x=0
e)x^3-7x^2+15x-25=0
giúp mk vs ah!!!!!
a) Ta có: \(x^2-x-12=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-4\right)\left(x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) Ta có: \(x^2+3x-18=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+6\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-6\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Bài 5: Giải các phương trình sau:
a. (3x - 1)2 - (x + 3)2 = 0
b. x3 = \(\dfrac{x}{49}\)
c. x2 - 7x + 12 = 0
d. 4x2 - 3x -1 = 0
e. x3 - 2x - 4 = 0
f. x3 + 8x2 + 17x +10 = 0
g. x3 + 3x2 + 6x + 4 = 0
h. x3 - 11x2 + 30x = 0
a. (3x - 1)2 - (x + 3)2 = 0
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-1+x+3\right)\left(3x-1-x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4x+2\right)\left(2x-4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x+2=0\) hoặc \(2x-4=0\)
1. \(4x+2=0\Leftrightarrow4x=-2\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
2. \(2x-4=0\Leftrightarrow2x=4\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
S=\(\left\{-\dfrac{1}{2};2\right\}\)
b. \(x^3=\dfrac{x}{49}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow49x^3=x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow49x^3-x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(49x^2-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(7x+1\right)\left(7x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=0\) hoặc \(7x+1=0\) hoặc \(7x-1=0\)
1. x=0
2. \(7x+1=0\Leftrightarrow7x=-1\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{7}\)
3. \(7x-1=0\Leftrightarrow7x=1\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{7}\)
*Cách khác:
a) Ta có: \(\left(3x-1\right)^2-\left(x+3\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-1\right)^2=\left(x+3\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x-1=-x-3\\3x-1=x+3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}4x=-2\\2x=4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{-\dfrac{1}{2};2\right\}\)
Giải phương trình sau đây :
a ) 8 ( 3 x - 2 ) - 14 x = 2 ( 4 – 7 x ) + 15 x b ) ( 3 x – 1 ) ( x – 3 ) – 9 + x 2 = 0 c ) | x - 2 | = 2 x - 3 d ) x + 2 x - 2 - 1 x = 2 x x - 2
a) 8( 3x - 2 ) - 14x = 2( 4 – 7x ) + 15x
⇔ 24x – 16 -14x = 8 – 14x + 15x
⇔ 10x -16 = 8 + x
⇔ 9x = 24
⇔ x = 24/9
b) ( 3x – 1 )( x – 3 ) – 9 + x2 = 0
⇔ (3x -1)( x – 3) + (x - 3)( x + 3) = 0
⇔ (x - 3)(3x - 1 + x - 3) = 0
⇔ (x - 3)(4x - 4) = 0
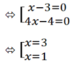
c) |x - 2| = 2x - 3
TH1: x - 2 ≥ 0 ⇔ x ≥ 2
Khi đó: x - 2 = 2x – 3
⇔ 2x – x = -2 + 3
⇔ x = 1 (không TM điều kiện x ≥ 2)
TH2: x – 2 < 0 ⇔ x < 2
Khi đó: x-2 = -(2x – 3)
⇔ x – 2 = -2x + 3
⇔ 3x = 5
⇔ x = 5/3 ( TM điều kiện x < 2)
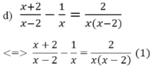
MTC: x(x-2)
ĐKXĐ: x ≠ 0;x ≠ 2

Đối chiếu với ĐKXĐ thì pt có nghiệm x = - 1