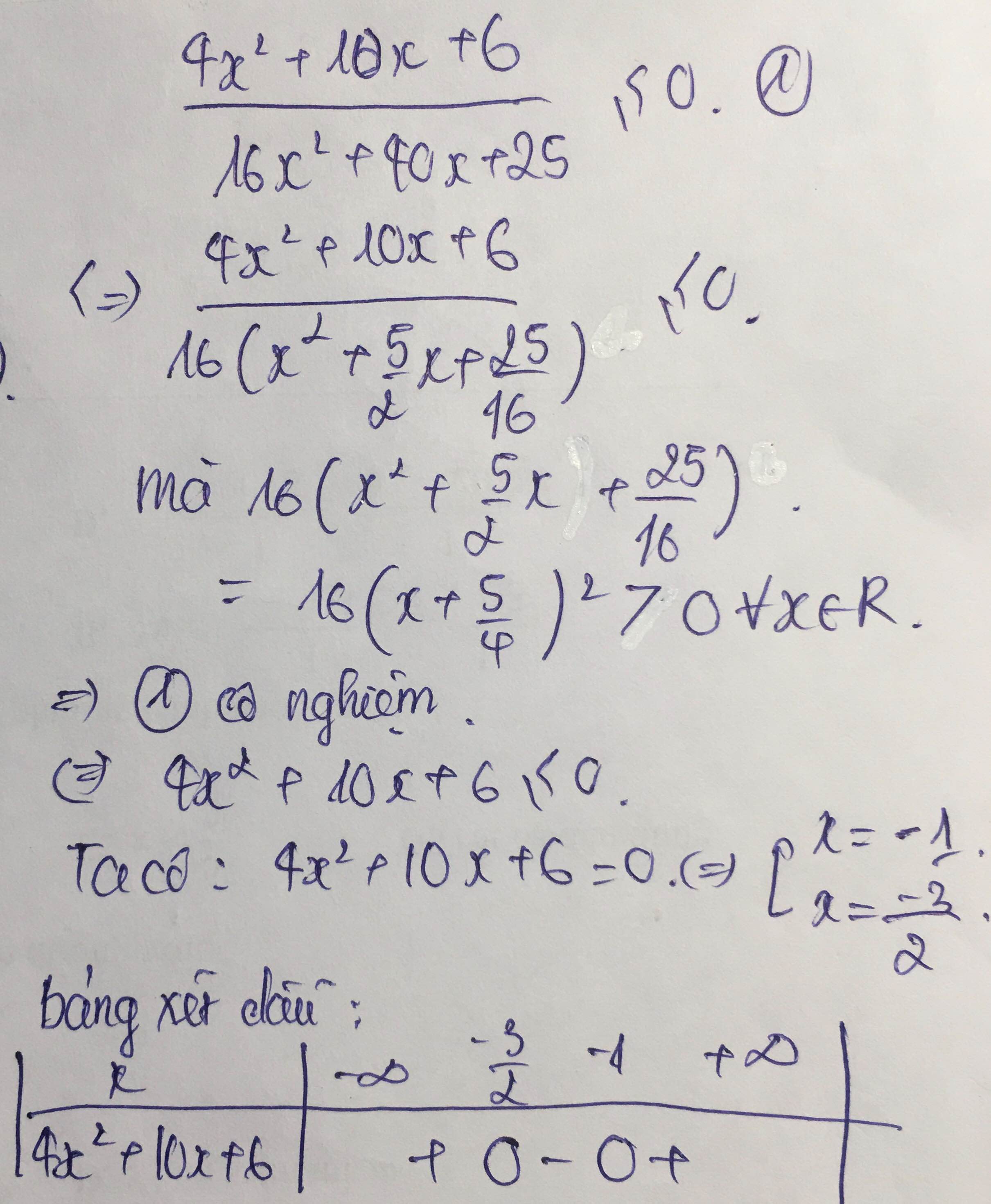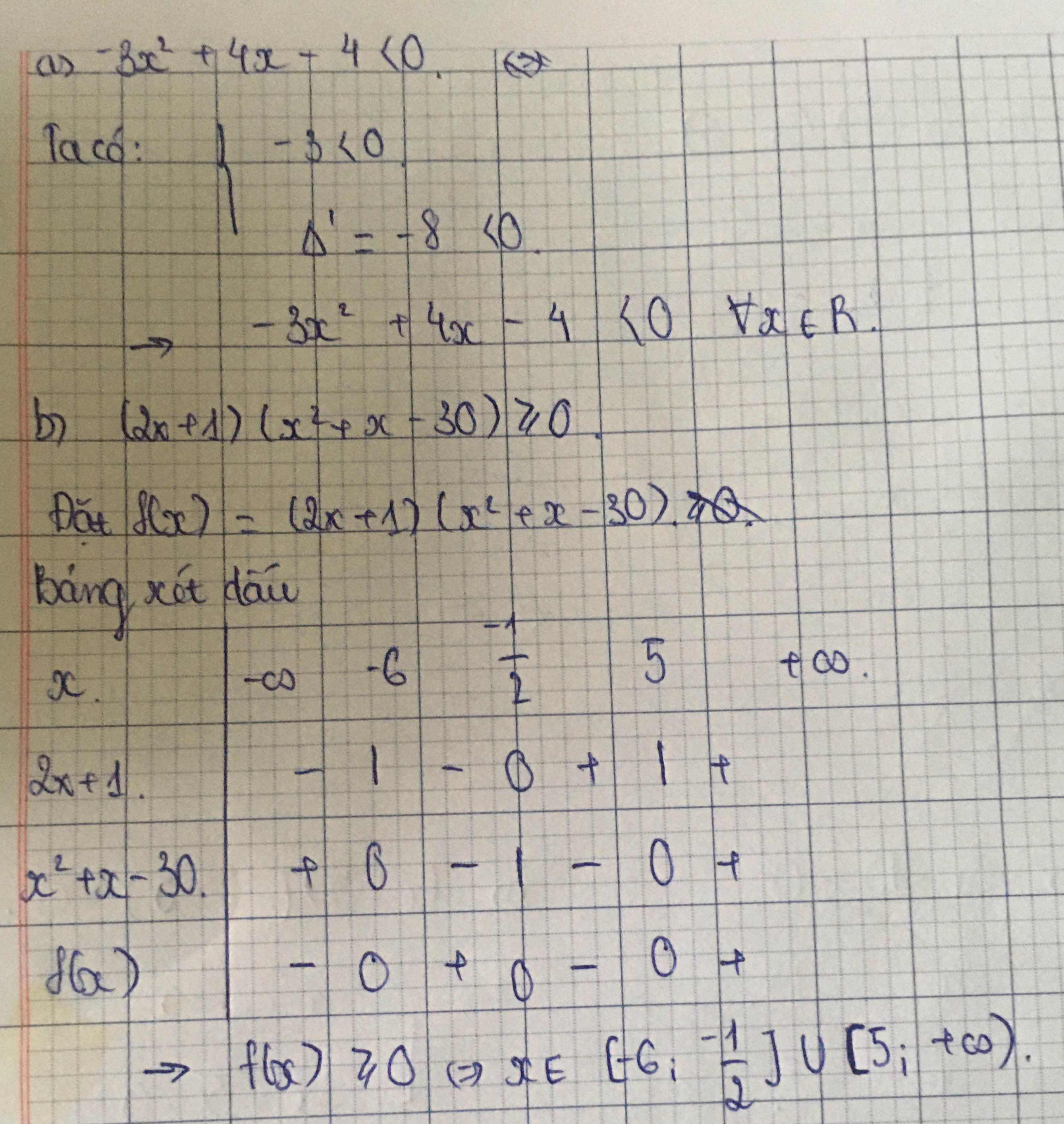(x- 2)(3x2- 10x+ 3) =0

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Tính giá trị của phân thức:a)
x
2
−
1
2
x
2
−
3
x
+
1
với
x
≠
1
và
x
≠
1
2
tại
2...
Đọc tiếp
Tính giá trị của phân thức:
a) x 2 − 1 2 x 2 − 3 x + 1 với x ≠ 1 và x ≠ 1 2 tại 2 x + 1 = 3 ;
b) 3 x 2 − 10 x + 3 x 2 − 4 x + 3 với x ≠ 2 ; x ≠ 3 tại x 2 − 8 x + 15 = 0 .
Tìm cặp số (x;y) thỏa:
a) x2 + 3y2 - 4x + 6y + 7 = 0.
b) 3x2 y2 + 10x - 2xy + 26 = 0.
c) 3x2 + 6y2 - 12x - 20y + 40 = 0.
a: \(x^2+3y^2-4x+6y+7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-4x+4+3y^2+6y+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2+3\left(y+1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x,y\right)=\left(-2;1\right)\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tìm x, biết: 5 x 3 – 3 x 2 + 10 x – 6 = 0
b) Ta có: 5x3 – 3x2 + 10x – 6 = (5x3 + 10x )+ ( -3x2– 6)
= 5x(x2 + 2) – 3(x2 + 2) = (x2 + 2)(5x – 3)
Vậy (x2 + 2)(5x – 3) = 0 ⇒ 5x – 3 = 0 (vì x2 + 2 ≥ 0, với mọi x)
⇒x = 3/5
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
1. giải phương trình bậc hai một ẩn
a, 3x2+7x+2=0
b,\(\dfrac{x^2}{3}+\dfrac{4x}{5}-\dfrac{1}{12}\)=0
c\(\left(5-\sqrt{2}\right).x^2-10x+5x+\sqrt{2}=0\)
d,(x-1)(x+2)=70
`a,3x^2+7x+2=0`
`<=>3x^2+6x+x+2=0`
`<=>3x(x+2)+x+2=0`
`<=>(x+2)(3x+1)=0`
`<=>x=-2\or\x=-1/3`
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
d) Ta có: (x-1)(x+2)=70
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x-x-2-70=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x-72=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+9x-8x-72=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x+9\right)-8\left(x+9\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+9\right)\left(x-8\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+9=0\\x-8=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-9\\x=8\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: S={8;-9}
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
`d,(x+1)(x+2)=70`
`<=>x^2+3x+2=70`
`<=>x^2+3x-68=0`
`<=>(x+3/2)^2=281/4`
`<=>x=(+-\sqrt{281}-3)/2`
Đúng 0
Bình luận (1)
giải bất phương trình:
a) -3x2 + 4x - 4 <0 b) (2x + 1) ( x2 +x - 30) ≥ 0
c) \(\dfrac{4x^2+10x+6}{16x^2+40x+25}\le0\) d) I3x+5I < 2 -x
giải bất phương trình:
a) -3x2 + 4x - 4 <0 b) (2x + 1) ( x2 +x - 30) ≥ 0
c) 4x + 10x + 6
Bài 3: Phân tích các đa thức sau thành nhân tử:
a) x2 + 10x + 25. b) 8x - 16 - x2
c) x3 + 3x2 + 3x + 1 d) (x + y)2 - 9x2
e) (x + 5)2 – (2x -1)2
Bài 4: Tìm x biết
a) x2 – 9 0 b) (x – 4)2 – 36 0
c) x2 – 10x -25 d) x2 + 5x + 6 0
Đọc tiếp
Bài 3: Phân tích các đa thức sau thành nhân tử:
a) x2 + 10x + 25. b) 8x - 16 - x2
c) x3 + 3x2 + 3x + 1 d) (x + y)2 - 9x2
e) (x + 5)2 – (2x -1)2
Bài 4: Tìm x biết
a) x2 – 9 = 0 b) (x – 4)2 – 36 = 0
c) x2 – 10x = -25 d) x2 + 5x + 6 = 0
Bài 3
a) x² + 10x + 25
= x² + 2.x.5 + 5²
= (x + 5)²
b) 8x - 16 - x²
= -(x² - 8x + 16)
= -(x² - 2.x.4 + 4²)
= -(x - 4)²
c) x³ + 3x² + 3x + 1
= x³ + 3.x².1 + 3.x.1² + 1³
= (x + 1)³
d) (x + y)² - 9x²
= (x + y)² - (3x)²
= (x + y - 3x)(x + y + 3x)
= (y - 2x)(4x + y)
e) (x + 5)² - (2x - 1)²
= (x + 5 - 2x + 1)(x + 5 + 2x - 1)
= (6 - x)(3x + 4)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Bài 4
a) x² - 9 = 0
x² = 9
x = 3 hoặc x = -3
b) (x - 4)² - 36 = 0
(x - 4 - 6)(x - 4 + 6) = 0
(x - 10)(x + 2) = 0
x - 10 = 0 hoặc x + 2 = 0
*) x - 10 = 0
x = 10
*) x + 2 = 0
x = -2
Vậy x = -2; x = 10
c) x² - 10x = -25
x² - 10x + 25 = 0
(x - 5)² = 0
x - 5 = 0
x = 5
d) x² + 5x + 6 = 0
x² + 2x + 3x + 6 = 0
(x² + 2x) + (3x + 6) = 0
x(x + 2) + 3(x + 2) = 0
(x + 2)(x + 3) = 0
x + 2 = 0 hoặc x + 3 = 0
*) x + 2 = 0
x = -2
*) x + 3 = 0
x = -3
Vậy x = -3; x = -2
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
3) Chứng minh rằng không có các số x; y nào thỏa mãn mỗi đẳng thức sau:
a) 3x2+y2+10x-2xy+26=0
b) 4x2+3y2-4x+30y+78=0
c) 3x2+6y2-12x-20y+40=0
a/
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2xy+y^2+2x^2+10x+26=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-y\right)^2+2\left(x-\frac{5}{2}\right)^2+\frac{27}{2}=0\)
\(VT>0\Rightarrow\) ko tồn tại x; y thỏa mãn
b/
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-4x+1+3\left(y^2+10y+25\right)+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-1\right)^2+3\left(y+5\right)^2+2=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\) Không tồn tại x; y thỏa mãn
c/
\(3\left(x^2-4x+4\right)+6\left(y^2-\frac{10}{3}y+\frac{25}{9}\right)+\frac{34}{3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3\left(x-2\right)+6\left(y-\frac{5}{3}\right)^2+\frac{34}{3}=0\)
Không tồn tại x; y thỏa mãn
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)