giải phương trình sau
x.(x+3)^2 -3x=(x+2)^3 +1
1) Giải các phương trình sau : a) x-3/x=2-x-3/x+3 b) 3x^2-2x-16=0 2) Giải bất phương trình sau: 4x-3/4>3x-5/3-2x-7/12
\(a,\dfrac{x-3}{x}=\dfrac{x-3}{x+3}\)\(\left(đk:x\ne0,-3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-3}{x}-\dfrac{x-3}{x+3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)-x\left(x-3\right)}{x\left(x+3\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-9-x^2+3x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=3\left(n\right)\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{3\right\}\)
\(b,\dfrac{4x-3}{4}>\dfrac{3x-5}{3}-\dfrac{2x-7}{12}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4x-3}{4}-\dfrac{3x-5}{3}+\dfrac{2x-7}{12}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3\left(4x-3\right)-4\left(3x-5\right)+2x-7}{12}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x-9-12x+20+2x-7>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+4>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x>-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>-2\)
Giải phương trình sau:
(3x / x^2 - x + 3) - (2x / x^2 - 3x + 3) = -1
=>\(\dfrac{3x^3-9x^2+9x-2x^3+2x^2-6x}{\left(x^2-3x+3\right)\left(x^2-x+3\right)}=-1\)
=>x^3-7x^2+3x=-[(x^2+3)^2-4x(x^2+3)+3x^2]
=>x^3-7x^2+3x+(x^2+3)^2-4x(x^2+3)+3x^2=0
=>x^3-4x^2+3x+x^4+6x^2+9-4x^3-12x=0
=>x^4-3x^3+2x^2-9x+9=0
=>(x-3)(x-1)(x^2+x+3)=0
=>x=3;x=1
giải phương trình sau
1/ ( x-3) ^2 =16
2/ (3x-1)^3 =8
3/ (x-11)^3 =-27
4/ x^3 -3x^2 +3x-1'
1/ ( x-3) 2=16
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3=4\\x-3=-4\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=7\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
2/ (3x-1)3=8
\(\Rightarrow3x-1=2\\ \Rightarrow3x=3\\ \Rightarrow x=1\)
3/ (x-11)3=-27
\(\Rightarrow x-11=-3\\ \Rightarrow x=8\)
phần 4 mình ko rõ đề
4) \(x^3-3x^2+3x-1=-64\)
\(\Rightarrow x^3-3x^2+3x+63=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x^3+3x^2\right)-\left(6x^2+18x\right)+\left(21x+63\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow x^2\left(x+3\right)+6x\left(x+3\right)+21\left(x+3\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x+3\right)\left(x^2+6x+21\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+3=0\\x^2+6x+21=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x+3=0\\ \Rightarrow x=-3\)
\(x^2+6x+21=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x^2+6x+9\right)+12=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x+3\right)^2+12=0\)
Vì \(\left(x+3\right)^2\ge0;12>0\Rightarrow\left(x+3\right)^2+12>0\Rightarrow x^2+6x+21vônghiệm\)
Vậy \(x=-3\)
Bài 2: giải phương trình sau
a) \(X^4\)-\(x^2\)-2=0
b) (x+1)\(^4\)-x\(^2\)+2)\(^2\)=0
c)3x\(^2\)-2x-8=0
Bài 3: giải phương trình sau
a) x\(^3\)-0,25=0
b) x\(^4\)+2x\(^3\)+x\(^2\)=0
c) x\(^3\)-1=0
d) 6x\(^2\)-7x+2=0
Mong có người giải giùm xin kẻm ơn :>
Bài 3:
b: \(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x+1\right)^2=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{0;-1\right\}\)
c: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)=0\)
=>x-1=0
hay x=1
d: \(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-3x-4x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-1\right)\left(3x-2\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{\dfrac{1}{2};\dfrac{2}{3}\right\}\)
Bài 1: Giải phương trình và bất phương trình sau: 1. 5.(2-3x). (x-2) = 3.( 1-3x) 2. 4x^2 + 4x + 1= 0 3. 4x^2 - 9= 0 4. 5x^2 - 10=0 5. x^2 - 3x= -2 6. |x-5| - 3= 0
Giải phương trình sau : \(\dfrac{x^2+3x+2}{x-3}\left(\dfrac{x+1}{x-2}+1\right)=\dfrac{x^2+3x+2}{x-3}.\dfrac{x^2}{2-x}\)
\(ĐK:x\ne3;x\ne2\\ PT\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2+3x+2}{x-3}\left(\dfrac{x+1}{x-2}+1+\dfrac{x^2}{x-2}\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)}{x-3}=0\\\dfrac{x^2+x+2}{x-2}=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=-2\\x^2+x+2=0\left(vô.n_0\right)\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Giải phương trình và bất phương trình sau:
a ) | 3 x | = x + 6 b ) x + 2 x - 2 - 1 x = 2 x x - 2 c ) ( x + 1 ) ( 2 x – 2 ) – 3 > – 5 x – ( 2 x + 1 ) ( 3 – x )
a) |3x| = x + 6 (1)
Ta có 3x = 3x khi x ≥ 0 và 3x = -3x khi x < 0
Vậy để giải phương trình (1) ta quy về giải hai phương trình sau:
+ ) Phương trình 3x = x + 6 với điều kiện x ≥ 0
Ta có: 3x = x + 6 ⇔ 2x = 6 ⇔ x = 3 (TMĐK)
Do đó x = 3 là nghiệm của phương trình (1).
+ ) Phương trình -3x = x + 6 với điều kiện x < 0
Ta có -3x = x + 6 ⇔ -4x + 6 ⇔ x = -3/2 (TMĐK)
Do đó x = -3/2 là nghiệm của phương trình (1).
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình đã cho S = {3; -3/2}
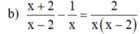
ĐKXĐ: x ≠ 0, x ≠ 2
Quy đồng mẫu hai vễ của phương trình, ta được:
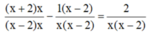
![]()
![]()
![]()
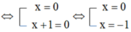
![]()
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là S = {-1}
c) (x + 1)(2x – 2) – 3 > –5x – (2x + 1)(3 – x)
⇔ 2x2 – 2x + 2x – 2 – 3 > –5x – (6x – 2x2 + 3 – x)
⇔ 2x2 – 5 ≥ –5x – 6x + 2x2 – 3 + x
⇔ 10x ≥ 2 ⇔ x ≥ 1/5
Tập nghiệm: S = {x | x ≥ 1/5}
Giải phương trình sau: \(\sqrt{x^2-3x+2}+3=3\sqrt{x-1}+\sqrt{x-2}\)
\(ĐK:x\ge2\\ PT\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)}+3=3\sqrt{x-1}+\sqrt{x-2}\)
Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x-1}=a\\\sqrt{x-2}=b\end{matrix}\right.\left(a,b\ge0\right)\)
\(PT\Leftrightarrow ab+3=3a+b\\ \Leftrightarrow3a-3+b-ab=0\\ \Leftrightarrow3\left(a-1\right)-b\left(a-1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(3-b\right)\left(a-1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}a=1\Rightarrow x-1=1\Rightarrow x=2\left(tm\right)\\b=3\Rightarrow x-2=9\Rightarrow x=11\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{2;11\right\}\)
Giải phương trình sau : \(\dfrac{x^2+3x+2}{x-3}\left(x+1\right)=\dfrac{x^2+3x+2}{x-3}\left(x^2-2x-7\right)\)
\(ĐK:x\ne3\\ PT\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2+3x+2}{x-3}\left(-x-1+x^2-2x-7\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)}{x-3}=0\\x^2-3x-8=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=-2\\x=\dfrac{3+\sqrt{41}}{2}\\x=\dfrac{3-\sqrt{41}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
a) ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{-1;0\right\}\)
Ta có: \(\dfrac{x+3}{x+1}+\dfrac{x-2}{x}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x\left(x+3\right)}{x\left(x+1\right)}+\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)}{x\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{2x\left(x+1\right)}{x\left(x+1\right)}\)
Suy ra: \(x^2+3x+x^2-3x+2=2x^2+2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+2-2x^2-2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x=-2\)
hay x=1(nhận)
Vậy: S={1}
b) ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{-7;\dfrac{3}{2}\right\}\)
Ta có: \(\dfrac{3x-2}{x+7}=\dfrac{6x+1}{2x-3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-2\right)\left(2x-3\right)=\left(6x+1\right)\left(x+7\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-9x-4x+6=6x^2+42x+x+7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-13x+6-6x^2-43x-7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-56x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-56x=1\)
hay \(x=-\dfrac{1}{56}\)(nhận)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{-\dfrac{1}{56}\right\}\)
c) ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne-\dfrac{2}{3}\)
Ta có: \(\dfrac{5}{3x+2}=2x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5=\left(3x+2\right)\left(2x-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-3x+4x-2-5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2+x-7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-6x+7x-7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x\left(x-1\right)+7\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(6x+7\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\6x+7=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\6x=-7\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\left(nhận\right)\\x=-\dfrac{7}{6}\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{1;-\dfrac{7}{6}\right\}\)
d) ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne\dfrac{2}{7}\)
Ta có: \(\left(2x+3\right)\cdot\left(\dfrac{3x+8}{2-7x}+1\right)=\left(x-5\right)\left(\dfrac{3x+8}{2-7x}+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+3\right)\cdot\left(\dfrac{3x+8+2-7x}{2-7x}\right)-\left(x-5\right)\left(\dfrac{3x+8+2-7x}{2-7x}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+3-x+5\right)\cdot\dfrac{-4x+6}{2-7x}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+8\right)\cdot\left(-4x+6\right)=0\)(Vì \(2-7x\ne0\forall x\) thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+8=0\\-4x+6=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-8\\-4x=-6\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-8\left(nhận\right)\\x=\dfrac{3}{2}\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{-8;\dfrac{3}{2}\right\}\)