Tìm TXĐ của hàm số y=cot(x+pi/3)/sinx-cosx

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Tìm TXĐ của các hàm số saua,dfrac{1-cosx}{2sinx+1}b,ysqrt{dfrac{1+cosx}{2-cosx}}c,sqrt{tanx}d,dfrac{2}{2cosleft(x-dfrac{Pi}{4}right)-1}e,tanleft(x-dfrac{Pi}{3}right)+cotleft(x+dfrac{Pi}{4}right)f,ydfrac{sinx}{cos^2x-sin^2x}g,ydfrac{2}{cosx+cos2x}h,ydfrac{1+cos2x}{1-cos4x}
Đọc tiếp
Tìm TXĐ của các hàm số sau
\(a,\dfrac{1-cosx}{2sinx+1}\)
\(b,y=\sqrt{\dfrac{1+cosx}{2-cosx}}\)
\(c,\sqrt{tanx}\)
\(d,\dfrac{2}{2cos\left(x-\dfrac{\Pi}{4}\right)-1}\)
\(e,tan\left(x-\dfrac{\Pi}{3}\right)+cot\left(x+\dfrac{\Pi}{4}\right)\)
\(f,y=\dfrac{sinx}{cos^2x-sin^2x}\)
\(g,y=\dfrac{2}{cosx+cos2x}\)
\(h,y=\dfrac{1+cos2x}{1-cos4x}\)
a: ĐKXĐ: 2*sin x+1<>0
=>sin x<>-1/2
=>x<>-pi/6+k2pi và x<>7/6pi+k2pi
b: ĐKXĐ: \(\dfrac{1+cosx}{2-cosx}>=0\)
mà 1+cosx>=0
nên 2-cosx>=0
=>cosx<=2(luôn đúng)
c ĐKXĐ: tan x>0
=>kpi<x<pi/2+kpi
d: ĐKXĐ: \(2\cdot cos\left(x-\dfrac{pi}{4}\right)-1< >0\)
=>cos(x-pi/4)<>1/2
=>x-pi/4<>pi/3+k2pi và x-pi/4<>-pi/3+k2pi
=>x<>7/12pi+k2pi và x<>-pi/12+k2pi
e: ĐKXĐ: x-pi/3<>pi/2+kpi và x+pi/4<>kpi
=>x<>5/6pi+kpi và x<>kpi-pi/4
f: ĐKXĐ: cos^2x-sin^2x<>0
=>cos2x<>0
=>2x<>pi/2+kpi
=>x<>pi/4+kpi/2
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tìm TXĐ của hàm số \(y=\dfrac{sinx}{\sqrt{3}sinx+cosx}\)
\(\sqrt{3}sinx+cosx\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}sinx+\dfrac{1}{2}cosx\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sin\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{6}\right)\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+\dfrac{\pi}{6}\ne k\pi\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\ne-\dfrac{\pi}{6}+k\pi\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
c1 tập xác định của hàm số \(y=\dfrac{sin2x+cosx}{tanx-sinx}\)
c2 tập xác định của hàm số \(y=\sqrt{1+cot^22x}\)
c3 tập xác định của hàm số \(y=cot\left(x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)+tan\left(x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)\)
1.
ĐKXĐ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}cosx\ne0\\tanx-sinx\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}cosx\ne0\\\dfrac{sinx}{cosx}-sinx\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}cosx\ne0\\sinx\ne0\\cosx\ne1\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow sin2x\ne0\Leftrightarrow x\ne\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\)
2.
ĐKXĐ: \(sin2x\ne0\Leftrightarrow x\ne\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\)
3.
ĐKXĐ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}sin\left(x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)\ne0\\cos\left(x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sin\left(2x-\dfrac{\pi}{2}\right)\ne0\Leftrightarrow cos2x\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{4}+\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (5)
câu 2 ..... \(\dfrac{cos^22x}{sin^22x}=cot^22x\) nên suy ra sin2x khác 0 đúng hơm
còn câu 3, tui ko hiểu chỗ sin(2x-pi/4).. sao ở đây rớt xuống dợ
Đúng 1
Bình luận (2)
Tìm tập xác định của các hàm số sau:1,ysindfrac{3x+2}{2x-1}2,ytanleft(3x+dfrac{2pi}{5}right)3,ycotleft(2x-dfrac{1}{3}right)4,ydfrac{sinx+cosx}{sinx-cosx}5,ydfrac{1}{sinx}+dfrac{1}{cosx}6,ydfrac{sqrt{1-sinx}}{cosx}7,ydfrac{3}{sin^2x-cos^2x}8,ydfrac{1+tanx}{1+sinx}9,ysqrt{dfrac{1+sinx}{1-cosx}}
Đọc tiếp
Tìm tập xác định của các hàm số sau:
1,\(y=sin\dfrac{3x+2}{2x-1}\)
2,\(y=tan\left(3x+\dfrac{2\pi}{5}\right)\)
3,\(y=cot\left(2x-\dfrac{1}{3}\right)\)
4,\(y=\dfrac{sinx+cosx}{sinx-cosx}\)
5,\(y=\dfrac{1}{sinx}+\dfrac{1}{cosx}\)
6,\(y=\dfrac{\sqrt{1-sinx}}{cosx}\)
7,\(y=\dfrac{3}{sin^2x-cos^2x}\)
8,\(y=\dfrac{1+tanx}{1+sinx}\)
9,\(y=\sqrt{\dfrac{1+sinx}{1-cosx}}\)
Tìm txđ của hàm số sau:
1, \(y=sin\sqrt{\dfrac{1+x}{1-x}}\)
2,\(y=\sqrt{\dfrac{sinx+2}{cosx+1}}\)
3,\(y=\dfrac{2}{cosx-cos3x}\)
1.
Hàm số xác định khi \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1+x}{1-x}\ge0\\1-x\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-1\le x< 1\\x\ne1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow-1\le x< 1\)
2.
Hàm số xác định khi \(cosx+1\ne0\Leftrightarrow cosx\ne-1\Leftrightarrow x\ne-\pi+k2\pi\)
3.
Hàm số xác định khi \(cosx-cos3x\ne0\Leftrightarrow sin2x.sinx\ne0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\ne k\pi\\x\ne\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tìm txđ của hàm số sau:
1.\(y=\sqrt{\dfrac{1+cosx}{1-cosx}}\)
2.\(y=\dfrac{3}{sin^2x-cos^2x}\)
3.\(y=cos\left(x-\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)+tan2x\)
1. Hàm số xác định `<=> 1-cosx \ne 0<=>cosx \ne 1<=>x \ne k2π`
Vì: `1+cosx >=0 forallx ; 1-cosx >=0 forall x`
2. Hàm số xác định `<=> sin^2x \ne cos^2x <=> (1-cos2x)/2 \ne (1+cos2x)/2`
`<=>cos2x \ne 0<=> 2x \ne π/2+kπ <=> x \ne π/4+kπ/2`
3. Hàm số xác định `<=> cos2x \ne 0<=> x \ne π/4+kπ/2 (k \in ZZ)`.
Đúng 3
Bình luận (2)
Tìm txđ của hàm số sau
a, \(y=3tan\left(2x+3\right)\)
b, \(y=cot\left(\dfrac{x}{3}+\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)\)
a, y xác định `<=> 3cos(2x+3) \ne 0`
`<=>cos(2x+3) \ne 0`
`<=>2x+3 \ne π/2+kπ`
`<=>x \ne π/4 -3/2 +k π/2 (k \in ZZ)`
b, y xác định `<=> sin(x/3+π/4) \ne0`
`<=> x/3+π/4 \ne kπ`
`<=> x \ne (-3π)/4+ k3π`
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
ĐKXĐ:
a.
\(cos\left(2x+3\right)\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+3\ne\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k\pi\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{3}{2}+\dfrac{\pi}{4}+\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\)
b.
\(sin\left(\dfrac{x}{3}+\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x}{3}+\dfrac{\pi}{4}\ne k\pi\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\ne-\dfrac{3\pi}{4}+k3\pi\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Hàm số nào sau đây không là hàm số tuần hoàn? Giải thích?
tan2x; cosx+x; \(cot\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)\); sinx+1
Các hàm không tuần hoàn là cosx+x vì \(cosx+x\ne cos\left(x+k2\Omega\right)+x+k2\Omega\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Dùng đồ thị hàm số, tìm giá trị của x trên đoạn \(\left[ { - 2\pi ;2\pi } \right]\) để:
a) Hàm số y = sinx nhận giá trị bằng 1
b) Hàm số y = sinx nhận giá trị bằng 0
c) Hàm số y = cosx nhận giá trị bằng – 1
d) Hàm số y = cosx nhận giá trị bằng 0
a) Hàm số y = sinx nhận giá trị bằng 1
- Vẽ hàm số y = sinx trên đoạn \(\left[ { - 2\pi ;2\pi } \right]\)
- Vẽ hàm số y = 1
- Lấy giao điểm của hai hàm số y = sinx và y = 1 là A, B,...
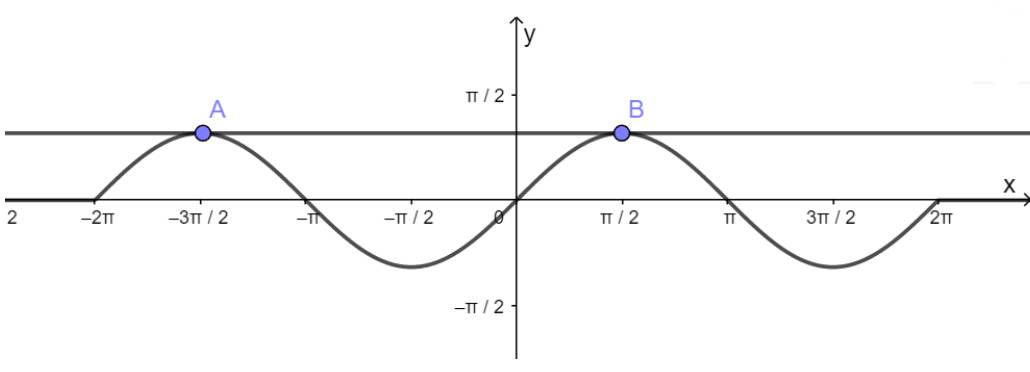
b) Hàm số y = sinx nhận giá trị bằng 0
- Vẽ hàm số y = sinx trên đoạn \(\left[ { - 2\pi ;2\pi } \right]\)
- Vẽ hàm số y = 0
- Lấy giao điểm của hai hàm số y = sinx và y = 0 là A, B, C, D, E,...
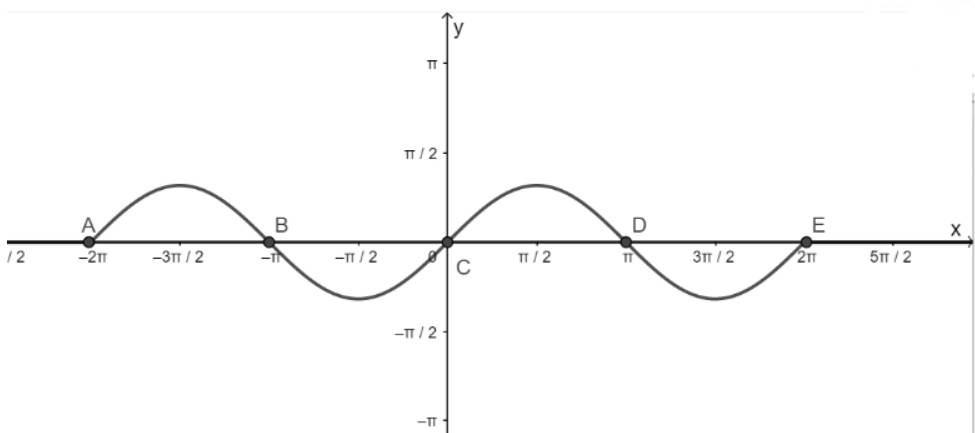
c) Hàm số y = cosx nhận giá trị bằng – 1
- Vẽ hàm số y = cosx trên đoạn \(\left[ { - 2\pi ;2\pi } \right]\)
- Vẽ hàm số y = - 1
- Lấy giao điểm của hai hàm số y = cosx và y = - 1 là A, B,...
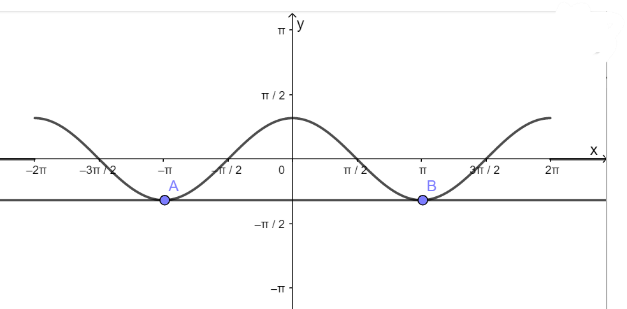
d) Hàm số y = cosx nhận giá trị bằng 0
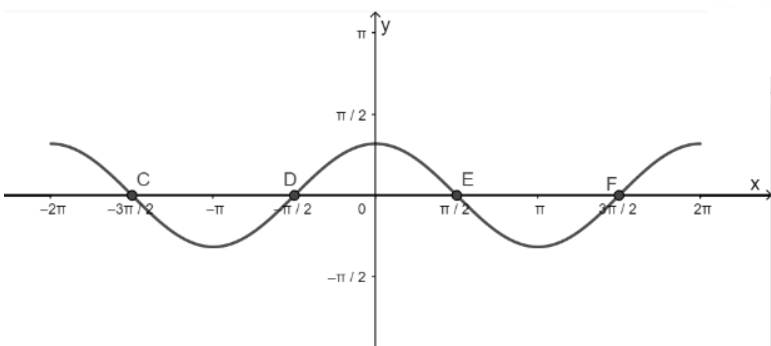
- Vẽ hàm số y = cosx trên đoạn \(\left[ { - 2\pi ;2\pi } \right]\)
- Vẽ hàm số y = 0
- Lấy giao điểm của hai hàm số y = cosx và y = 0 là C, D, E, F,...
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)

















