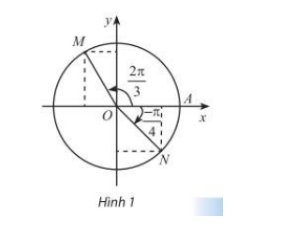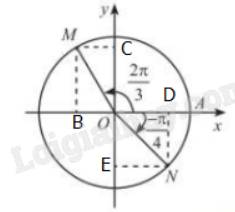
Gọi B, C lần lượt là hình chiếu của M lên Ox, Oy; D, E lần lượt là hình chiếu của N lên Ox, Oy
Ta có: OM = ON = 1
\(\widehat{MOC}=\dfrac{2\pi}{3}-\dfrac{\pi}{2}=\dfrac{\pi}{6}\\ \Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}sin\widehat{MOC}=\dfrac{1}{2}\Rightarrow MC=\dfrac{1}{2}\\cos\widehat{MOC}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\Rightarrow MB=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Do điểm M có hoành độ nằm bên trái trục Ox nên tọa độ của điểm M là \(M\left(-\dfrac{1}{2};\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\right)\)
\(\widehat{NOD}=-\dfrac{\pi}{4}\\ \Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}sin\widehat{NOD}=-\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\Rightarrow ND=-\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\\cos\widehat{NOD}=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\Rightarrow NE=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy tọa độ điểm N là \(N\left(\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2};-\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\right)\)