2.
Gọi \(H\left(x;y\right)\) là toạ độ chân đường cao ứng với BC \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\overrightarrow{AH}=\left(x-1;y+2\right)\\\overrightarrow{BC}=\left(2;1\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Do AH vuông góc BC \(\Rightarrow\overrightarrow{AH}.\overrightarrow{BC}=0\)
\(\Rightarrow2\left(x-1\right)+y+2=0\Leftrightarrow y=-2x\)
\(\Rightarrow H\left(x;-2x\right)\Rightarrow\overrightarrow{BH}=\left(x+2;-2x-3\right)\)
Do H thuộc BC nên B, C, H thẳng hàng hay các vecto \(\overrightarrow{BC};\overrightarrow{BH}\) cùng phương
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{x+2}{2}=\dfrac{-2x-3}{1}\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{8}{5}\Rightarrow y=-\dfrac{16}{5}\) \(\Rightarrow H\left(-\dfrac{8}{5};\dfrac{16}{5}\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\overrightarrow{AH}=\left(-\dfrac{13}{5};\dfrac{26}{5}\right)\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}AH=\sqrt{\left(-\dfrac{13}{5}\right)^2+\left(-\dfrac{6}{5}\right)^2}=\dfrac{13\sqrt{5}}{5}\\BC=\sqrt{2^2+1^2}=\sqrt{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow S_{ABC}=\dfrac{1}{2}AH.BC=\dfrac{13}{2}\)
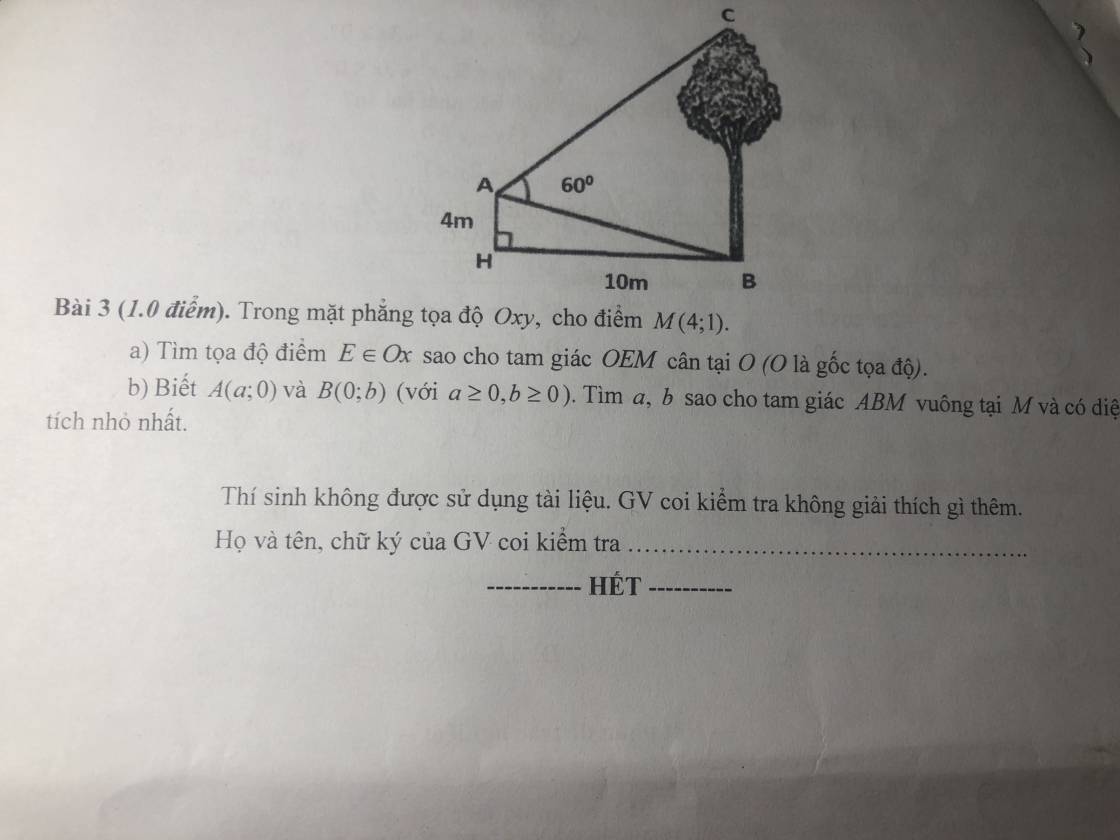
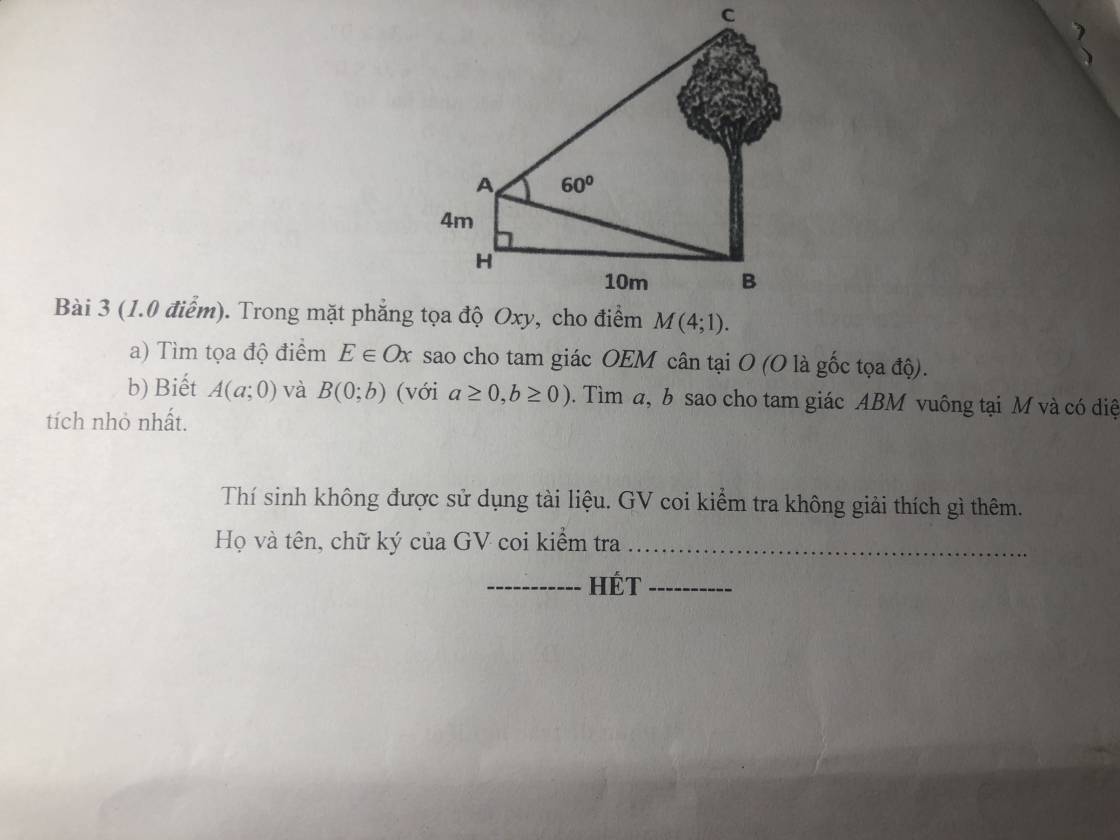
3.
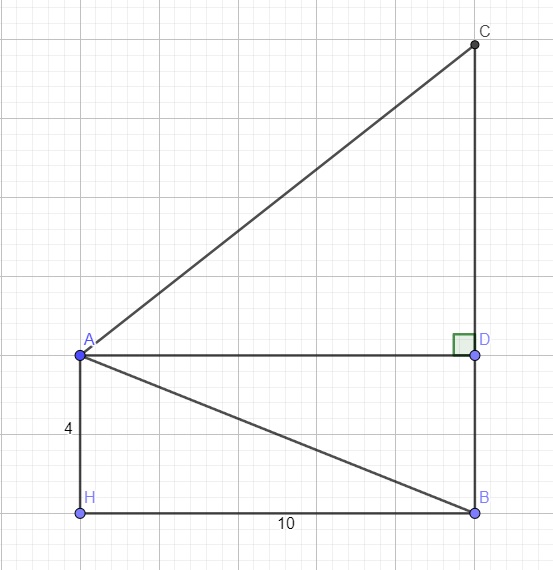
Kẻ AD vuông góc BC tại D
\(\Rightarrow AD=BH=10\) ; \(BD=AH=4\)
\(tan\widehat{BAD}=\dfrac{BD}{AD}=\dfrac{2}{5}\Rightarrow\widehat{BAD}\approx21^048'5''\)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{CAD}=60^0-\widehat{BAD}=38^011'55''\)
\(\Rightarrow CD=AD.tan\widehat{CAD}=7,87\left(m\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow BC=BD+CD=11,87\left(m\right)\)