Giải pt
X4+2x3-6x2-2x+1=0
Giải phương trình
a) 2x3+6x2=x2+3x
b) (2+x)2-(2x-5)2=0
`2x^3 +6x^2 =x^2 +3x`
`<=> 2x^3 +6x^2 -x^2 -3x=0`
`<=> 2x^3 +5x^2 -3x=0`
`<=> x(2x^2 +5x-3)=0`
`<=> x(2x^2 +6x-x-3)=0`
`<=> x[2x(x+3)-(x+3)]=0`
`<=> x(2x-1)(x+3)=0`
\(< =>\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\2x-1=0\\x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ < =>\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=\dfrac{1}{2}\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
b)
`(2+x)^2 -(2x-5)^2=0`
`<=> (2+x-2x+5)(2+x+2x-5)=0`
`<=> (-x+7)(3x-3)=0`
\(< =>\left[{}\begin{matrix}-x+7=0\\3x-3=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ < =>\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=7\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
`a) 2x^3 + 6x^2 = x^2 + 3x`
`=> 2x^3 + 6x^2 - x^2 - 3x = 0`
`=> 2x^3 + 5x^2 - 3x = 0`
`=> x(2x^2 + 5x - 3) = 0`
`=> x (2x^2 + 6x - x - 3) = 0`
`=> x [(2x^2 + 6x) - (x+3)] = 0`
`=> x [2x(x+3) - (x+3)] = 0`
`=> x (2x - 1)(x+3) = 0`
`=> x = 0` hoặc `2x - 1 = 0` hoặc `x + 3 = 0`
`=> x = 0` hoặc `x = 1/2` hoặc `x = -3`
`b) (2+x)^2 - (2x-5)^2 = 0`
`=> (2+x+2x-5)(2+x-2x+5) = 0`
`=> (3x - 3)(7-x) = 0`
`=> 3x - 3 = 0` hoặc `7 - x = 0`
`=> x = 1` hoặc `x = 7`
giải phương trình:
a, x4-x2-2=0
b, x4+2x3+x2=0
c,x3-1= 0
d, 6x2-7x+2=0
a, \(x^4-x^2-2=0\Leftrightarrow x^4-2x^2+x^2-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x^2-2\right)+\left(x^2-2\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+1>0\right)\left(x^2-2\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x=\pm\sqrt{2}\)
b, \(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x^2+2x+1\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x+1\right)^2=0\Leftrightarrow x=0;x=-1\)
c, \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1>0\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x=1\)
d, \(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-3x-4x+2=0\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-2\right)\left(2x-1\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{2}{3};x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
a)
/ \(x^4+x^2-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2\right)^2-x^2+2x^2-2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x^2-1\right)+2\left(x^2-1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+2\right)\left(x^2-1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+2\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2+2=0\\x+1=0\\x-1-0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Câu 6:Thực hiện phép nhân -2x(x2 + 3x - 4) ta được:
A.-2x3 - 6x2 – 8x B. 2x3 -6x2 – 8x C. -2x3 - 6x2 + 8x D. -2x3 + 3x2 -4
Câu 7 : Phân tích đa thức x2 + 2xy + y2 – 9z2 thành nhân tử ta được:
A. (x+y+3z)(x+y–3z)
B. (x-y+3z)(x+y–3z)
C.(x - y +3z)(x - y – 3z)
D. (x + y +3z)(x -y – 3z)
Câu 8: Phân tích đa thức 27x3 – ![]() thành nhân tử ta được:
thành nhân tử ta được:
A.(3x+![]() )(9x2-x+
)(9x2-x+![]() )
)
B.(3x–![]() )(9x2+x+
)(9x2+x+![]() )
)
C.(27x–![]() )(9x2+x+
)(9x2+x+![]() )
)
D.(27x+![]() )(9x2+x+
)(9x2+x+![]() )
)
Câu 9: Phân tích đa thức x2 + 7x + 12 thành nhân tử ta được:
A. (x - 3)( x + 4 ) B. (x + 3)( x + 4 ) C.(x + 5)( x + 2 ) D. (x -5)( x + 2 )
Câu 10: Giá trị của biểu thức (x2 + 4x + 4) tại x = - 2 là:
A. 4 B. -2 C. 0 D. -8
Câu 6:Thực hiện phép nhân -2x(x2 + 3x - 4) ta được:
A.-2x3 - 6x2 – 8x B. 2x3 -6x2 – 8x C. -2x3 - 6x2 + 8x D. -2x3 + 3x2 -4
Câu 7 : Phân tích đa thức x2 + 2xy + y2 – 9z2 thành nhân tử ta được:
A. (x+y+3z)(x+y–3z)
B. (x-y+3z)(x+y–3z)
C.(x - y +3z)(x - y – 3z)
D. (x + y +3z)(x -y – 3z)
Câu 9: Phân tích đa thức x2 + 7x + 12 thành nhân tử ta được:
A. (x - 3)( x + 4 ) B. (x + 3)( x + 4 ) C.(x + 5)( x + 2 ) D. (x -5)( x + 2 )
Câu 10: Giá trị của biểu thức (x2 + 4x + 4) tại x = - 2 là:
A. 4 B. -2 C. 0 D. -8
Mấy câu còn lại bị lỗi r nhé
giúp mình bài này với
giải phương trình :
a) 2x3=6x2=x2+3x;2x3+6x2=x2+3x;
b) (3x-1)(x2+2)= (3x-1)(7x-10)(3x-1)(x2+2)=((3x-1)(7x-10)
Giải phương trình: 2x3 + 6x2 = x2 + 3x
2x3 + 6x2 = x2 + 3x
⇔ (2x3 + 6x2) – (x2 + 3x) = 0
⇔ 2x2(x + 3) – x(x + 3) = 0
⇔ x(x + 3)(2x – 1) = 0
(Nhân tử chung là x(x + 3))
⇔ x = 0 hoặc x + 3 = 0 hoặc 2x – 1 = 0
+ x + 3 = 0 ⇔ x = -3.
+ 2x – 1 = 0 ⇔ 2x = 1 ⇔ x = 1/2.
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là 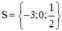
Tìm nghiệm:
a)2x4-3x3-6x2-x+2=0
b)x4-2x3+4x2-3x-1=0
a) x3 + x2 + x + 1 = 0
b) x3 - 6x2 + 11x - 6 = 0
c) x3 - x2 - 21x + 45 = 0
d) x4 + 2x3 - 4x2 - 5x - 6 = 0
a) Ta có: \(x^3+x^2+x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x+1\right)+\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2+1\right)=0\)
mà \(x^2+1>0\forall x\)
nên x+1=0
hay x=-1
Vậy: S={-1}
b) Ta có: \(x^3-6x^2+11x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-x^2-5x^2+5x+6x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x-1\right)-5x\left(x-1\right)+6\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2-5x+6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\x-2=0\\x-3=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=2\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: S={1;2;3}
c) Ta có: \(x^3-x^2-21x+45=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-3x^2+2x^2-6x-15x+45=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x-3\right)+2x\left(x-3\right)-15\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x^2+2x-15\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x^2+5x-3x-15\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)^2\cdot\left(x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3=0\\x+5=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: S={3;-5}
d) Ta có: \(x^4+2x^3-4x^2-5x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^4-2x^3+4x^3-8x^2+4x^2-8x+3x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3\left(x-2\right)+4x^2\cdot\left(x-2\right)+4x\left(x-2\right)+3\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x^3+4x^2+4x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x^3+3x^2+x^2+4x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left[x^2\left(x+3\right)+\left(x+1\right)\left(x+3\right)\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+3\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)=0\)
mà \(x^2+x+1>0\forall x\)
nên (x-2)(x+3)=0
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: S={2;-3}
Cho hàm số f ( x ) = 2 x 3 - 6 x 2 + 3 Số nghiệm của phương trình f(f(x))=0 là
A. 6
B. 9
C. 3
D. 8
Bài 1 . cho hai đa thức: P(x) = 4x4 - 2x3 - 7x2 + 2x + 1/3 và Q(x) = x4 + 3x3 - 6x2 - x - 1/4
a. Tính P(x) + Q(x);
b. Tính P(x) - Q(x).
Bài 2. cho đa thức: M(x) = x2 - 2x3 + x + 5 và N(x) = 2x3 - x - 6
a. Tính M(2)
b. Tìm đa thức A(x) sao cho A(x) = M(x) + N(x); A(x), tính B(x) = M(x) - N(x)
c. Tìm nghiệm của đa thức A(x)
Bài 3. Tìm nghiệm của các đa thức sau:
a. 2x - 8 b. 2x + 7 c. 4 - x2 d. 4x2 - 9
e. 2x2 - 6 f. x(x - 1) g. x + 2x h. x( x + 2 )
Bài 4. cho hai đa thức: f(x) = 2x4 + 3x2 - x + 1 - x2 - x4 - 6x3
g(x) = 10x3 + 3 - x4 - 4x3 + 4x - 2x2
a. Thu gọn đa thức: f(x), g(x) và sắp xếp các hạng tử của mỗi đa thức theo lũy thừa giảm dần của biến.
b. Tính h(x) = f(x) + g(x); K(x) = f(x) - g(x)
c. Tìm nghiệm của đa thức h(x)
Bài 5. Tìm nghiệm của các đa thức:
a. 9 - 3x b. -3x + 4 c. x2 - 9 d. 9x2 - 4
e. x2 - 2 f. x( x - 2 ) g. x2 - 2x h. x(x2 + 1 )
Tách ra, dài quá mn đọc là mất hứng làm đó.