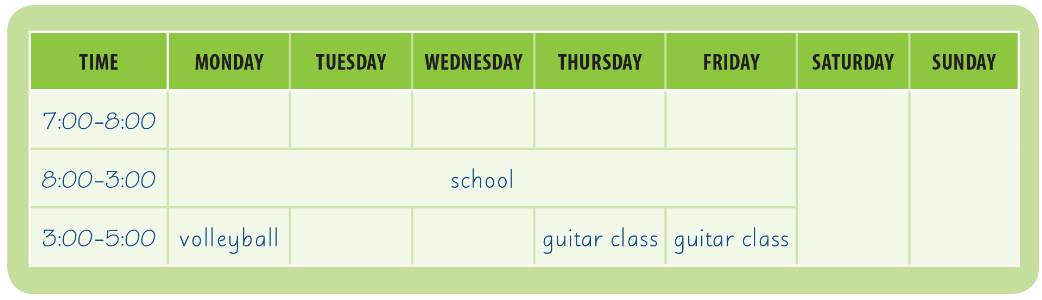
Complete Nadine’s schedule. Use the information in C.
Complete each of the following sentences using the cues given. You can use other words in addition to the cues to complete the sentences.
Temple of Literature/ be/ first/ destination/ schedule.
Đáp án là: Temple of Literature is the first destination in my schedule.
V. Use the words in the box to complete the sentences. There are 2 extra words you don’t need.
adventure; cartoon; character; fact; local; schedule; reasons; viewers |
1. Clint Eastwood’s _________________ is the most sympathetic in the movie.
2. Filming began on _____________________.
3. The program attracted millions of __________________.
4. We had a little ___________________ yesterday.
5. It was difficult to understand the _________________ dialect.
6. He saw many ______________________ to be hopeful.
VI. Read the following text and decide which answer best fits each numbered blank.
Modern cinema audiences expect to see plenty of thrilling scenes in action films. These scenes, which are (38) ________ as stunts, are usually (39) ___________ by the stuntmen who are specially trained to do dangerous things safely. (40) _________ can crash a car, but if you’re shooting a film, you have to be extremely (41) _________ sometimes stopping (42) _____________ in front of the camera and film crew. At an early (43) __________ in the production an expert stuntman is (44) _______________ to work out the action scenes and form a team. He is the only person who can go (45) __________ the wishes of the director, (46) ____________ he will usually only do this in the (47) __________ of safety.
7. a. remarked b. known c. referred d. named
8. a. performed b. given c. fulfilled d. displayed
9. a. Everyone b. Someone c. Anyone d. None
10. a. detailed b. exact c. direct d. strict
11. a. right b. left c. up d. down
12. a. period b. minute c. part d. stage
13. a. let b. taken c. drawn d. called
14. a. over b. against c. through d. across
15. a. despite b. so c. although d. otherwise
16. a. interests b. needs c. purposes d. regards
VII. Read the following text and choose the best answer A, B, C or D.
The television set is an indispensable house item today. It now takes up its familiar place as the local point of the living room. The television set is one of the best ways to get the latest news and to watch films.
The television set was not fully electronic when it was invented. Its screen actually has a small motor and a small lamp. The picture was blurry and it was only about the size of a business card.
It was in 1953 in Europe when many people first started owing a television set. They bought a television set for the sole purpose of watching coronation of Queen Elizabeth II in London. Only a few thousand people were allowed into Westminster Abbey.
Another significant event was the moon landing in 1969. Again, millions of people around the world watched as Neil Armstrong walked on the moon and planted an American flag. This time event was broadcast in color. The program was much more realistic than the previous ones.
17. Many people need the television set today as it ____.
A. allows them to watch the coronation of Queen Elizabeth II.
B. enables them to find out what is happening around the world.
C. is an electronic item.
D. let them see things in color.
18. Television sets in the past ________.
A. were not so clear. B. were very bulky.
C. ran on electricity. D. showed pictures that were full colored.
19. Why do you think the sale of television set rocketed in Europe in 1953?
A. Television sets became more affordable.
B. People wanted to watch the moon landing.
C. People wanted to watch the crowning of the Queen.
D. People wanted to watch live coverage of events around the world.
20. People around the world watched Neil Armstrong ______ in 1969.
A. travel to the moon.
B. sit on the moon.
C. put a flag on the moon.
D. take the American flag away from the moon.
21. From the passage, as television sets improved, _______.
A. the colors on the screen became lighter than before.
B. more realistic programs were showed.
C. people could watch events earlier than before.
D. an event watched on TV looked more like the actual event than that was happening.
VIII. Combine the two sentences using because, so, and, but and although.
53. She doesn’t eat pork. She doesn’t like it.
54. The girl helped me a lot. She didn’t know me well.
55. They worked very hard. They all passed the final test.
56. My teacher didn’t come to my class today. He was ill.
57. Tim plays the guitar. He also sings in the band.
58. Many students in his class love him. He is very helpful.
59. We got up early this morning. We stayed up late last night to do the homework.
60. My sister is very intelligent. She gets a lot of gifts from her teachers.
IX. Use the given words to write the complete sentences.
61. Game show/ this month/ test/ your knowledge/ world heritage.
62. Many people/ work/ hard/ today/ produce/ good/ program/ television.
63. My brother/ I/ dream/ become/ pilot.
64. Many young people/ prefer/ watching TV/ reading books.
65. There/ be/ many/ exciting/ program/ VTV3.
66. We/ often/ read/ book/ watch/ favorite/ program/ free/ time.
Read the sentences in exercise 1. Then choose the correct options to complete rules 1-5.
RULES
We use question tags to check information. In the question tag, we use:
1. a positive / negative verb for negative sentences.
2. a positive / negative verb for affirmative sentences.
3. the same / different auxiliary verb as in the sentence.
4. a form of do / will when there is no auxiliary verb in the sentence.
5. modal verbs when there is / isn't a modal in the statement.
1. positive
2. negative
3. same
4. do
5. is
195,Because people don’t give enough information about their schedule, the disease has spread widely.
A.If people give enough information about their schedule, the disease will not spread widely.
B.If people gave enough information about their schedule, the disease would not spread widely.
C.If people give enough information about their schedule, the disease will spread widely.
D.If people gave enough information about their schedule, the disease would spread widely.
EXERCISE 1: Complete the sentences. Use the information in the box and the modal verb in parentheses.
quit it at once
be very happy
leave the building in order
go out for a walk
find another one
be very worried
come to visit me more
understand the lectures well
buy a smaller one
1. If you have toothache, you mustseethedentisL ............................ (must)
2. If it rains, we ................... (should not)
3. If the class is full, I......................... (will)
4. If it costs too much, we.................. (must) 
5. If you don’t come home early, your parents........................... (may)
6. If that job is boring, Susan ....................... (may)
7. If you listen carefully, you.............................. (can)
8. If a fire breaks out, everyone................................. (have to)
9. If you have more time, you....................................... (ought to)
10. If you phone your parents more often, they..................................... (must)
EXERCISE 1: Complete the sentences. Use the information in the box and the modal verb in parentheses.
quit it at once
be very happy
leave the building in order
go out for a walk
find another one
be very worried
come to visit me more
understand the lectures well
buy a smaller one
1. If you have toothache, you mustseethedentisL ......................(must)
2. If it rains, we ...........................(should not)
3. If the class is full, I................................ (will)
4. If it costs too much, we....................................... (must)
5. If you don’t come home early, your parents............................... (may)
6. If that job is boring, Susan................................ (may)
7. If you listen carefully, you.................................. (can)
8. If a fire breaks out, everyone.................................... (have to)
9. If you have more time, you.............................. (ought to)
10. If you phone your parents more often, they ..................................(must)
1. If you have toothache, you must see the dentist ......................(must)
2. If it rains, we ...........................(should not go out for a walk)
3. If the class is full, I................................ (will find another one)
4. If it costs too much, we....................................... (must buy a smaller one)
5. If you don’t come home early, your parents............................... (may be very worried)
6. If that job is boring, Susan................................ (may quit it at once)
7. If you listen carefully, you.................................. (can understand the lectures well)
8. If a fire breaks out, everyone.................................... (have to leave the building in order)
9. If you have more time, you.............................. (ought to come to visit me more)
10. If you phone your parents more often, they ..................................(must be very happy)
SPEAKING Work in pairs. Use the third conditional to complete the sentences. Ask and answer about the information in the sentences.
1 If I'd felt ill this morning, ___________________________
2 If there hadn't been school last Friday, ___________________________
3 If I'd felt hungry on the way home from school yesterday, _______________________
4 If I'd forgotten to do my homework at the weekend, ___________________________
5 If I hadn't studied English in primary school, ___________________________
6 If I'd been late for school this morning, ___________________________
A: What would you have done if you'd felt ill this morning?
B: I'd have.../ I wouldn't have...
Bài tham khảo
A: If you'd felt ill this morning, what would you have done?
B: If I’d felt ill this morning, I would have stayed at home and rested.
A: If there hadn't been school last Friday, what would you have done?
B: If there hadn't been school last Friday, I would have gone to the beach.
A: If you’d felt hungry on the way home from school yesterday, what would you have eaten?
B: If I'd felt hungry on the way home from school yesterday, I would have bought a sandwich or a snack.
A: If I'd forgotten to do my homework at the weekend, what would have happened?
B: If you'd forgotten to do your homework at the weekend, you would have got a lower grade or failed the assignment.
A: If I hadn't studied English in primary school, what would I be doing now?
B: If you hadn't studied English in primary school, you might not have been able to understand or speak to me in English now.
A: If I'd been late for school this morning, what would I have missed?
B: If you'd been late for school this morning, you would have missed the first lesson or the school assembly.
Tạm dịch
A: Nếu bạn cảm thấy ốm sáng nay, bạn sẽ làm gì?
B: Nếu tôi cảm thấy ốm sáng nay, tôi sẽ ở nhà và nghỉ ngơi.
A: Nếu không có tiết học vào thứ Sáu tuần trước, bạn sẽ làm gì?
B: Nếu thứ sáu tuần trước không đi học thì tôi đã đi biển rồi.
A: Nếu bạn cảm thấy đói trên đường đi học về ngày hôm qua, bạn sẽ ăn gì?
B: Nếu tôi cảm thấy đói trên đường từ trường về nhà ngày hôm qua, tôi sẽ mua một chiếc bánh sandwich hoặc đồ ăn nhẹ.
A: Nếu tôi quên làm bài tập về nhà vào cuối tuần, điều gì sẽ xảy ra?
B: Nếu bạn quên làm bài tập về nhà vào cuối tuần, bạn sẽ bị điểm thấp hoặc trượt bài tập.
A: Nếu tôi không học tiếng Anh ở trường tiểu học, tôi sẽ làm gì bây giờ?
B: Nếu bạn không học tiếng Anh ở trường tiểu học, bạn có thể không hiểu hoặc nói chuyện với tôi bằng tiếng Anh bây giờ.
A: Nếu sáng nay tôi đi học muộn, tôi sẽ bỏ lỡ điều gì?
B: Nếu sáng nay bạn đi học muộn, bạn sẽ bỏ lỡ buổi học đầu tiên hoặc buổi tập trung của trường.
Listen to a radio programme. Complete the information about the Queen's residences. Use the places below in the first column.
Belfast, Northern Ireland
the Highlands, Scotland
near London, England
Edinburgh, Scotland
London, England
Norfolk, England
Royal Residence
| Location
| Private or state-owned?
|
Buckingham Palace
|
|
|
Windsor Castle
|
|
|
Sandringham House
|
|
|
Balmoral Castle
|
|
|
Holyrood Palace
|
|
|
Hillsborough Castle
|
|
|
Royal Residence (Nơi ở hoàng gia) | Location (Vị trí) | Private or state-owned? (Riêng tư hay của nhà nước?) |
Buckingham Palace (cung điện Buckingham) | England (Vương Quốc Anh) | State-owned (của nhà nước) |
Windsor Castle (lâu đài Windsor) | Near London (gần Luân Đôn) | State-owned (của nhà nước) |
Sandringham House (nhà Sandringham) | Nofolk | Private (tư nhân) |
Balmoral Castle (lâu đài Balmoral) | The highlands, Scotland (cao nguyên Scotland) | Private (tư nhân) |
Holyrood Palace (cung điện Holyrood) | Edinburgh, Scotland | State-owned (của nhà nước) |
Hillsborough Castle (lâu đài Hillsborough) | Castle Belfast (cung điện Belfast) | State-owned (của nhà nước) |
Bài nghe:
I = Interviewer
B = Bill
I My guest today is Bill Edwards, who has written a book about the royal residences. Welcome Bill.
B Thank you.
I So, first of all, how many residences did the Queen have?
B Well, the Queen herself had six royal homes, though she owned only two of them. She inherited these private residences from her father, King George VI. She used them for holidays. The others are owned by the State.
I And which are they?
B Buckingham Palace, Windsor Castle, Holyrood Palace in Scotland and Hillsborough Castle in Northern Ireland. These are the four official royal residences.
I That’s a lot of homes! Can you tell us a bit about how she used them all?
B TheQueenhadquiteastrictroutine,actually,whenshe wasn’t travelling around the world. Buckingham Palace in
the centre of London was the royal residence from Monday to Friday. And that’s where she entertained all the heads of state and official visitors. She also met with the Prime Minister every Tuesday evening to catch up with the nation’s politics. Apparently, she was very well-informed and asked a lot of questions!
I And what did she do at weekends?
B She usually went to Windsor Castle. That was her official country residence, and owned by the state. It’s near London. It’s the largest and oldest inhabited castle in the world. It’s been the family home of British kings and queens since the tenth century. The Queen spent most weekends there with her family, when she had time. The family always stayed there for a month over Easter, too, and for a week in June. That’s when the horse-racing at Ascot takes place. She loved Ascot and owned some nice racehorses.
I Where did she spend her other holidays?
B Well, Christmas and January were spent at Sandringham House in Norfolk. Prince Albert, Queen Victoria’s eldest son, bought it in 1862 when he got married, so it’s owned by the family privately. The family have loved the place ever since and have made many improvements over the years. The house was hit by bombs in the First World War and there were huge holes in the ground that filled with water. King George VI turned the holes into duck ponds!
I Really? And the Queen also went to Scotland every year, didn’t she?
B She did – every summer. The family stayed at Balmoral Castle in the Highlands of Scotland. Queen Victoria fell in love with the Scottish landscape and bought a private house so that the family could holiday there. That tradition has continued. The Castle is also a working estate and provides jobs for many people.
I The Queen had another residence in Scotland, though?
B Yes, her official residence was Holyrood Palace in Edinburgh, the capital city of Scotland. She stayed there when she had official business. And she was there every July for a week. It was called ‘Holyrood Week’, appropriately.
I And was that the same for her official residence in Northern Ireland?
B Exactly. Hillsborough Castle is near the capital city of Belfast. She stayed there and entertained guests when she was on official business in Northern Ireland.
I OK. So that’s a lot of homes. How did the Queen look after them?
B Well, some were open to the public when the Queen
was not in residence. Buckingham Palace is the latest one
to open its doors. It’s open for two months in the summer and it’s extremely popular with visitors, both from home and abroad, as you can imagine.
I Indeed. It would be well worth a visit. Many thanks, Bill, for giving us the tour of the royal residences. A fascinating insight into royal life!
B Thank you. My pleasure.
Tạm dịch:
I = Người phỏng vấn
B = Bill Edward
I Khách của tôi hôm nay là Bill Edwards, người đã viết một cuốn sách về nơi ở của hoàn thân quốc thích. Xin chào Bill.
B Cảm ơn bạn.
I Vậy trước hết, Nữ hoàng có bao nhiêu nơi ở?
B Bản thân Nữ hoàng có sáu dinh thự hoàng gia, mặc dù bà chỉ sở hữu hai trong số đó. Bà được thừa kế những dinh thự riêng này từ cha mình, Vua George VI. Bà ấy đã sử dụng chúng cho những ngày lễ. Những cái khác thuộc sở hữu của Nhà nước.
I Chúng là những gì?
B Cung điện B Buckingham, Lâu đài Windsor, Cung điện Holyrood ở Scotland và Lâu đài Hillsborough ở Bắc Ireland. Đây là bốn nơi ở chính thức của hoàng gia.
I Thật là nhiều! Bạn có thể cho chúng tôi biết một chút về cách bà ấy sử dụng tất cả chúng không?
B Thực ra, Nữ hoàng có một thói quen khá nghiêm ngặt khi bà không đi du lịch vòng quanh thế giới. Cung điện Buckingham ở trung tâm London là nơi ở của hoàng gia từ thứ Hai đến thứ Sáu. Và đó là nơi bà chiêu đãi tất cả các nguyên thủ quốc gia và các vị khách chính thức. Bà cũng gặp Thủ tướng vào mỗi tối thứ Ba để cập nhật tình hình chính trị của quốc gia. Rõ ràng, bà ấy rất hiểu biết và hỏi rất nhiều câu hỏi!
I Bà ấy đã làm gì vào cuối tuần?
B Cô ấy thường đến Lâu đài Windsor. Đó là nơi ở chính thức của bà ấy ở đất nước và thuộc sở hữu của nhà nước. Nó gần Luân Đôn. Đây là lâu đài có người ở lớn nhất và lâu đời nhất trên thế giới. Đó là ngôi nhà gia đình của các vị vua và hoàng hậu Anh từ thế kỷ thứ mười. Nữ hoàng đã dành hầu hết các ngày cuối tuần ở đó với gia đình khi bà có thời gian. Gia đình cũng luôn ở đó một tháng trong lễ Phục sinh và một tuần vào tháng Sáu. Đó là khi cuộc đua ngựa ở Ascot diễn ra. Cô ấy yêu Ascot và sở hữu một số con ngựa đua đẹp.
I Bà ấy đã dành những ngày nghỉ khác của mình ở đâu?
B Chà, Giáng sinh và tháng Giêng đã được dành tại Sandringham House ở Norfolk. Hoàng tử Albert, con trai cả của Nữ hoàng Victoria, đã mua nó vào năm 1862 khi ông kết hôn, vì vậy nó thuộc sở hữu tư nhân của gia đình. Gia đình đã yêu thích nơi này kể từ đó và đã có nhiều cải tiến trong những năm qua. Ngôi nhà bị trúng bom trong Chiến tranh thế giới thứ nhất và có những cái hố lớn trên mặt đất chứa đầy nước. Vua George VI đã biến những cái hố thành ao vịt!
I Vậy sao? Và Nữ hoàng cũng đến Scotland hàng năm phải không?
B Đúng thế – mỗi mùa hè. Gia đình ở tại Lâu đài Balmoral ở Cao nguyên Scotland. Nữ hoàng Victoria yêu phong cảnh Scotland và mua một ngôi nhà riêng để gia đình có thể đi nghỉ ở đó. Truyền thống đó đã tiếp tục. Lâu đài cũng là một khu đất làm việc và cung cấp việc làm cho nhiều người.
I Nữ hoàng có một nơi ở khác ở Scotland, phải không?
B Đúng thế, nơi ở chính thức của bà là Cung điện Holyrood ở Edinburgh, thủ đô của Scotland. Bà ấy ở đó khi có công việc chính thức. Và bà ấy đã ở đó vào trong vòng một tuần mỗi tháng Bảy. Nó được gọi là 'Tuần lễ Holyrood'.
I Và nó có giống với nơi ở chính thức của bà ấy ở Bắc Ireland không?
B Chính xác là vậy. Lâu đài Hillsborough nằm gần thủ đô Belfast. Bà ấy ở đó và tiếp đãi khách khi bà đi công tác chính thức ở Bắc Ireland.
I Được. Vậy thì với nhiều chỗ ở như vậy, Nữ hoàng đã trông coi chúng như thế nào?
B À, một số đã được mở cửa cho công chúng khi Nữ hoàng không ở đó. Cung điện Buckingham là nơi mở cửa muộn nhất. Nó mở cửa trong hai tháng vào mùa hè và cực kỳ nổi tiếng với du khách, cả trong và ngoài nước, như bạn có thể tưởng tượng.
I Thật vậy. Nó rất đáng để ghé thăm. Rất cám ơn Bill đã dẫn chúng tôi tham quan các dinh thự hoàng gia. Đó là một góc nhìn sâu sắc hấp dẫn về cuộc sống hoàng gia!
B Cảm ơn bạn. Rất hân hạnh.
Read the text and complete the table below with information from the text. Use no more than TWO words or a number in each gap.
UK EDUCATION AFTER SECONDARY SCHOOL
In the UK, students can choose to end their formal education at 16, but in England they must stay in full-time education or do a training course until the age of 18.
Many 16-year-old students go on to study at different vocational colleges. Vocational education usually lasts up to three years. During this time, students learn job-specific skills. That is why vocational education is often referred to as career education or technical education. Many students still go on to higher education after receiving their vocational qualifications.
Alternatively, students can go toa sixth-form college or stay at their secondary school if it offers a sixth form for two more years. Students usually focus on three or four subjects that they are interested in or related to the degree they want to study at university. Exams are taken at the end of the two-year course, and the grades are used to apply for university courses. Not all students leaving sixth form go to university. Some prefer to get into a vocational course or find a job.
At university, students study for at least three years in order to get a bachelor’s degree. After the first degree, they can study for one to two years to get a master’s degree, and three to five years to get a doctorate.
UK education after secondary school | |
Age at end of formal education | - 16 in the UK - stay until the age of (1) ________ in full-time education or do training in England |
Vocational education | - lats up to three years - also called career education or (2) _________ - some students still go on to (3) _________ |
Sixth form | - lasts two years - students study subjects they are interested in or subjects related to higher education. - grades are used to apply for (4) _________ |
University education | Students study to get a (5) ________, a master’s degree, or a doctorate |
1 - 18 | 2 - technical education | 3 - higher education |
4 - university courses | 5 - bachelor’s degree |
1. 18
Thông tin: but in England they must stay in full-time education or do a training course until the age of 18.
(nhưng ở Anh, học sinh phải tiếp tục học toàn thời gian hoặc tham gia một khóa đào tạo cho đến năm 18 tuổi.)
2. technical education
Thông tin: That is why vocational education is often referred to as career education or technical education.
(Đó là lý do tại sao giáo dục nghề nghiệp thường được gọi là giáo dục nghề nghiệp hoặc giáo dục kỹ thuật.)
3. higher education
Thông tin: Many students still go on to higher education after receiving their vocational qualifications.
(Nhiều sinh viên vẫn tiếp tục học cao hơn sau khi nhận được bằng cấp nghề.)
4. university courses
Thông tin: Exams are taken at the end of the two-year course, and the grades are used to apply for university courses.
(Các kỳ thi được thực hiện vào cuối khóa học hai năm và điểm số được sử dụng để nộp đơn vào các khóa học đại học.)
5. bachelor’s degree
Thông tin: At university, students study for at least three years in order to get a bachelor’s degree.
(Tại trường đại học, sinh viên học ít nhất ba năm để lấy bằng cử nhân.)