A= (5x+2/x2-10x+5x-2/x2+10x).x2-100/x2+4
a, rút gọn
b,tính giá trị của A biết x =20040
.Cho biểu thức A = ( x - 5 ) ( x2 + 5x + 25) - ( x – 2)(x+ 2) + x.(x2 + x + 4)
a) Rút gọn biểu thức A
b) Tính giá trị biểu thức A biết x = -2
b) Tính giá trị biểu thức A biết x2 – 1 = 0
a) A = (x - 5)(x² + 5x + 25) - (x - 2)(x + 2) + x(x² + x + 4)
= x³ - 125 - x² + 4 + x³ + x² + 4x
= (x³ + x³) + (-x² + x²) + 4x + (-125 + 4)
= 2x³ + 4x - 121
b) Tại x = -2 ta có:
A = 2.(-2)³ + 4.(-2) - 121
= 2.(-8) - 8 - 121
= -16 - 129
= -145
c) x² - 1 = 0
x² = 1
x = -1; x = 1
*) Tại x = -1 ta có:
A = 2.(-1)³ + 4.(-1) - 121
= 2.(-1) - 4 - 121
= -2 - 125
= -127
*) Tại x = 1 ta có:
A = 2.1³ + 4.1 - 121
= 2.1 + 4 - 121
= 2 - 117
= -115
Chứng minh rằng:
a) x2 + 10x + 100 > 0 ∀ x
b) -x2 + 4x - 100 < 0 ∀ x
c) x2 - 5x + 6 > 0 ∀ x
a: x^2+10x+100
=x^2+10x+25+75=(x+5)^2+75>0 với mọi x
b: -x^2+4x-100
=-(x^2-4x+100)
=-(x^2-4x+4+96)
=-(x-2)^2-96<0 với mọi x
c: x^2-5x+6
=x^2-5x+25/4-1/4
=(x-5/2)^2-1/4 chưa chắc lớn hơn 0 đâu nha bạn
Cho các biểu thức sau
A = \(\dfrac{4}{x+2}+\dfrac{2}{x-2}+\dfrac{5x-6}{4-x^2}\)
B = \(\dfrac{x+1}{x^2+3x+2}\)
a. Rút gọn A, B
b. tính giá trị của A biết x2 + x = 0
Tính giá trị của B biết x2 + 2x = 0
\(a,ĐK:x\ne\pm2\\ A=\dfrac{4x-8+2x+4-5x+6}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{x+2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{1}{x-2}\\ ĐK:x\ne-1;x\ne-2\\ B=\dfrac{x+1}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{1}{x+2}\\ b,x^2+x=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(tm\right)\\x=-1\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\\ \forall x=0\Leftrightarrow A=\dfrac{1}{0-2}=-\dfrac{1}{2}\\ \forall x=-1\Leftrightarrow A=\dfrac{1}{-1-2}=-\dfrac{1}{3}\)
\(x^2+2x=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(tm\right)\\x=-2\left(ktm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x=0\\ \Leftrightarrow B=\dfrac{1}{0+2}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
câu 2: bậc của đa thức M=x8+x2y7-y5+x là?
A.1 B.5 C.8 D.9
c6: biết x3+125=A.B và A là đa thức có bậc =1 . Khi đó biểu thức B là?
A. x2-5x+25 B.x2+5x+25 C.x2-10x+25 D. x2+10x+25
2D
6
\(x^3+125=\left(x+5\right)\left(x^2-5x+25\right)\)
A là đa thức bậc 1
=>A=x+5
=>B=x^2-5x+25
=>Chọn A
Câu 2. M có bậc 2 + 7 = 9
Chọn D
Câu 6. x³ + 125 = x³ + 5³ = (x + 5)(x² - 5x + 25)
Chọn A
Tìm x biết:
a) (x+5).(2x+1)=0
b) x.(x+2)-3.(x+2)=0
c) 2x.(x-5)-x.(3+2x)=26
d) x2-10x-8x+16=0
e) x2-10x=25
f) 5x.(x-1)=x-1
g) 2.(x+5)-x2-5x=0
h) x2+5x-6=0
i) (2x-3)2-4.(x+1).(x-1)=49
j) x3+x2+x+1=0
k) x3-x2=4x2-8x+4
Mn ơi giúp em vs ạ,em cảm ơn trc ạ
\(a,\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+5=0\\2x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-5\\x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\\ b,\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-2\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\\ c,\Leftrightarrow2x^2-10x-3x-2x^2=26\\ \Leftrightarrow-13x=26\Leftrightarrow x=-2\\ d,\Leftrightarrow x^2-18x+16=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-18x+81\right)-65=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-9\right)^2-65=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-9+\sqrt{65}\right)\left(x-9-\sqrt{65}\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=9-\sqrt{65}\\9+\sqrt{65}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(e,\Leftrightarrow x^2-10x-25=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)^2-50=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-5-5\sqrt{2}\right)\left(x-5+5\sqrt{2}\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5+5\sqrt{2}\\x=5-5\sqrt{2}\end{matrix}\right.\\ f,\Leftrightarrow5x\left(x-1\right)-\left(x-1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(5x-1\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=\dfrac{1}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\\ g,\Leftrightarrow2\left(x+5\right)-x\left(x+5\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2-x\right)\left(x+5\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=-5\end{matrix}\right.\\ h,\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x+3x+6=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x+3\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\\ i,\Leftrightarrow4x^2-12x+9-4x^2+4=49\\ \Leftrightarrow-12x=36\Leftrightarrow x=-3\)
\(j,\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x+1\right)+\left(x+1\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2=-1\left(vô.lí\right)\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x=-1\\ k,\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x-1\right)=4\left(x-1\right)^2\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x-1\right)-4\left(x-1\right)^2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2-4x+4\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)^2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Tìm giá trị nguyên của x để giá trị phân thức P = x 2 - 10 x + 25 x 2 - 5 x là nguyên
Hướng dẫn giải:
Điều kiện xác định của phân thức: x ≠ 0 , x ≠ 5
Ta có 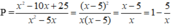
Để P nhận giá trị nguyên thì  nguyên. Hay x là ước của 5. Ta có Ư(5) = { 1;-1;5;-5}.
nguyên. Hay x là ước của 5. Ta có Ư(5) = { 1;-1;5;-5}.
Vì điều kiện xác định của phân thức là x ≠ 0, x≠ 5
Vậy x ∈ { 1;-1;-5} thì giá trị phân thức 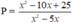 là nguyên
là nguyên
Cho \(A=\left(\frac{5x+2}{x^2-10x}+\frac{5x-2}{x^2+10x}\right).\frac{x^2-100}{x^2+4}\)
a) Tìm điều kiện của x để biểu thức xác định
b) Tính giá trị của A tại x=20040
a) ĐKXĐ:
x2-10x khác 0 và x2+10x khác 0
=>x.(x-10) khác 0 và x.(x+1) khác 0
=>x khác 0 và x khác 10 ;-10
b)\(A=\left(\frac{5x+2}{x^2-10x}+\frac{5x-2}{x^2+10x}\right).\frac{x^2-100}{x^2+4}\)
\(=\frac{5x+2}{x^2-10x}.\frac{x^2-100}{x^2+4}+\frac{5x-2}{x^2+10x}.\frac{x^2-100}{x^2+4}\)
\(=\frac{5x+2}{x.\left(x-10\right)}.\frac{\left(x-10\right)\left(x+10\right)}{x^2+4}+\frac{5x-2}{x.\left(x+10\right)}.\frac{\left(x-10\right)\left(x+10\right)}{x^2+4}\)
\(=\frac{\left(5x+2\right).\left(x+10\right)}{x.\left(x^2+4\right)}+\frac{\left(5x-2\right).\left(x-10\right)}{x.\left(x^2+4\right)}\)
\(=\frac{5x^2+52x+20+5x^2-52x+20}{x.\left(x^2+4\right)}=\frac{10x^2+40}{x.\left(x^2+4\right)}=\frac{10.\left(x^2+4\right)}{x.\left(x^2+4\right)}=\frac{10}{x}\)
Để A=20040 thì:
10/x=20040
=>x=1/2004
Tìm X:
a)(x-4)(x+4)=9
b)x2-4x+4-(5x-2)2=0
c)4x2+4+1-x2-10x-25=0
d)(x2+x+7)(x2+x-7)=(x2+x)2-7x
a)
⇔ \(x^2-16=9\)
⇔ \(x^2=25\)
⇔ \(x=\pm5\)
b)
⇔ \(x^2-4x+4-25x^2+20x-4=0\)
⇔ \(16x-24x^2=0\)
⇔ \(8x\left(2-3x\right)=0\)
⇒ \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\2-3x=0\end{matrix}\right.\) ⇔ \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=\dfrac{2}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x=0\) hoặc \(x=\dfrac{2}{3}\)
c)
⇔ \(3x^2-10x-20=0\)
⇔ \(x^2-2.x.\dfrac{5}{3}+\dfrac{25}{9}-\dfrac{205}{9}=0\)
⇔ \(\left(x-\dfrac{5}{3}\right)^2=\dfrac{205}{9}\)
⇒ \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-\dfrac{5}{3}=\sqrt{\dfrac{205}{9}}\\x-\dfrac{5}{3}=-\sqrt{\dfrac{205}{9}}\end{matrix}\right.\) ⇔ \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\sqrt{\text{205}}}{\text{3}}+\dfrac{5}{3}\\x=-\dfrac{\sqrt{\text{205}}}{\text{3}}+\dfrac{5}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\) ⇔ \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{15+\text{9}\sqrt{\text{205}}}{\text{9}}\\\text{x}=-\dfrac{15+\text{9}\sqrt{\text{205}}}{\text{9}}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy...
d)
⇔ \(\left(x^2+x\right)^2-49=\left(x^2+x\right)^2-7x\)
⇔ 7x = 49
⇔ x=7
Vậy...