Tìm \(x\in Z\) để \(\dfrac{2x-1}{x+1}\) nguyên

Những câu hỏi liên quan
1.tìm \(x\in Z\) sao cho \(\dfrac{2x+1}{x+3}\) là 1 số nguyên
1.tìm \(x\in Z\) sao cho \(\dfrac{x-1}{x+5}\) là 1 số nguyên
1.tìm \(x,y\in Z\) sao cho \(\left(x-1\right).\left(y-3\right)=7\) là 1 số nguyên
325253737747⁸⁹⁰⁷⁶⁵⁴³ chuyển đổi sang STN là?
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
1, để \(\dfrac{2x+1}{x+3}\) là 1 số nguyên
= > 2x + 1 chia hết cho x + 3 ( x thuộc Z và x \(\ne3\) )
= > 2 ( x + 3 ) - 5 chia hết cho x + 3
=> -5 chia hết cho x + 3
hay x + 3 thuộc Ư(-5 ) \(\in\left\{\pm1;\pm5\right\}\)
Đến đây em tự tìm các giá trị của x
2, Tương tự câu 1, x - 1 chia hết cho x + 5 ( x thuộc Z và x khác - 5 )
= > - 6 chia hết cho x + 5
= > \(x+5\in\left\{\pm1;\pm2;\pm3;\pm6\right\}\)
....
3, ( x - 1 ) ( y - 3 ) = 7
x,y thuộc Z = > x - 1 ; y - 3 thuộc Ư(7)
và ( x - 1 )( y - 3 ) = 7
( 1 ) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-1=1\\y-3=7\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\y=10\end{matrix}\right.\)
(2) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-1=7\\y-3=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=8\\y=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
( 3) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-1=-1\\y-3=-7\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\y=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
( 4 ) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-1=-7\\y-3=-1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-6\\y=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Từ ( 1 ) , ( 2 ) , ( 3 ) , ( 4 ) các cặp giá trị ( x,y ) nguyên cần tìm là ....
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
1) Cho a, b, c là hằng số và a+b+c2018.Tính giá trị của các biểu thức sau:Aax^3y^3+bx^3y+cxy^2 tại x1 ,y1Bax^2y^2-bx^4y+cxy^6 tại x1, y-12) Biết x+y-20. Tính giá trị của các biểu thức :Mx^3+x^2y-2x^2-xy-y^2+3y+x-1Nx^3-2x^2-xy^2+2xy+2x-2Px^4+2x^3y-2x^3+x^2y^3-2x^2y-xleft(x+yright)+2x+33) Có Adfrac{3a+2}{x-3} và Bdfrac{x^2+3x-7}{x+3}a) Tính A khi x1,x2,xdfrac{5}{2}b) Tìm x in Z để A số nguyên.c) Tìm x in Z để B số nguyên.d) Tìm x in Z để A và B cùng là số nguyên.4) Cho Cdfrac{2x-1}{x+2} và Ddfrac{...
Đọc tiếp
1) Cho a, b, c là hằng số và a+b+c=2018.Tính giá trị của các biểu thức sau:
A=\(ax^3y^3+bx^3y+cxy^2\) tại x=1 ,y=1
B=\(ax^2y^2-bx^4y+cxy^6\) tại x=1, y=-1
2) Biết x+y-2=0. Tính giá trị của các biểu thức :
M=\(x^3+x^2y-2x^2-xy-y^2+3y+x-1\)
N=\(x^3-2x^2-xy^2+2xy+2x-2\)
P=\(x^4+2x^3y-2x^3+x^2y^3-2x^2y-x\left(x+y\right)+2x+3\)
3) Có A=\(\dfrac{3a+2}{x-3}\) và B=\(\dfrac{x^2+3x-7}{x+3}\)
a) Tính A khi x=1,x=2,x=\(\dfrac{5}{2}\)
b) Tìm x \(\in\) Z để A số nguyên.
c) Tìm x \(\in\) Z để B số nguyên.
d) Tìm x \(\in\) Z để A và B cùng là số nguyên.
4) Cho C=\(\dfrac{2x-1}{x+2}\) và D=\(\dfrac{x^2-2x+1}{x+1}\)
a) Tìm x\(\in\)Z để C là số nguyên.
b) Tìm x\(\in\)Z để D là số nguyên.
c) Tìm x\(\in\)Z để C và D cùng là số nguyên.
CÁC BẠN LÀM NGAY GIÚP MÌNH VỚI MÌNH RẤT RẤT VỘI
Tìm giá trị nguyên của x để \(\dfrac{x+3}{2x}\)\(\in\) Z
Để: \(\dfrac{x+3}{2x}\) ∈ Z thì:
x + 3 ⋮ 2x
=> 2. (x + 3) ⋮ 2x
=> 2x + 6 ⋮ 2x
=> 6 ⋮ 2x
=> 2x ∈ Ư (6)
=> 2x ∈ {1; -1; 2; -2; 3; -3; 6; -6}
Mà x ∈ Z => 2x ⋮ 2
=> 2x ∈ {2; -2; 6; -6}
=> x ∈ {1; -1; 3; -3}
Đúng 2
Bình luận (1)
Cho M= \(\dfrac{x^2+x}{x^2-2x+1}\):\(\left(\dfrac{x+1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{1-x}+\dfrac{2-x^2}{x^2-x}\right)\)
a, Rút gọn M
b, Tìm x để M>1
c, Tìm x\(\in\)Z để M\(\in\)Z
d, Tìm M khi |x+1|=2
a: Ta có: \(M=\dfrac{x^2+x}{x^2-2x+1}:\left(\dfrac{x+1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{1-x}+\dfrac{2-x^2}{x^2-x}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)^2}:\dfrac{x^2-1+x+2-x^2}{x\left(x-1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\cdot\dfrac{x\left(x-1\right)}{x+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2}{x-1}\)
b: Để M>1 thì M-1>0
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2-x+1}{x-1}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1>0\)
hay x>1
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
a) ĐKXĐ: x # 0; x # 1; x# -1
M = (x^2)/(x-1)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
A = \(\dfrac{x^2-2x+1}{x+1}\)
Tìm x \(\in\) Z để A \(\in\) Z
Giúp mk với !
Ta có : \(A=\dfrac{x^2+2x+1-4x-4+4}{x+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2-4\left(x+1\right)+4}{x+1}=x+1-4+\dfrac{4}{x+1}\)
- Để A là số nguyên
\(\Leftrightarrow x+1\inƯ_{\left(4\right)}\) ( Do x là số nguyên )
\(\Leftrightarrow x+1\in\left\{1;-1;2;-2;4;-4\right\}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{0;-2;1;-3;3;-5\right\}\)
Vậy ....
Đúng 2
Bình luận (1)
Tìm \(x\in Z\) để biểu thức \(A=\dfrac{x^2-2x+5}{x-1}\) có giá trị nguyên.
Cho C =\(\left(\dfrac{1}{x-1}-\dfrac{2x}{x^3-x^2+x-1}\right):\left(\dfrac{x^2+2}{x^3+x^2+x+1}+\dfrac{1}{x+1}\right)\)
a) Tìm đkxđ của C
b) Rút gọn C
c) Tìm x để C =\(\dfrac{2}{5}\)
d) Tìm x ϵ Z để giá trị C là số nguyên
Bổ sung phần c và d luôn:
c, C = \(\dfrac{2}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\dfrac{x^2-1}{2x^2+3}\) = \(\dfrac{2}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) 5(x2 - 1) = 2(2x2 + 3)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) 5x2 - 5 = 4x2 + 6
\(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 = 11
\(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 - 11 = 0
\(\Leftrightarrow\) (x - \(\sqrt{11}\))(x + \(\sqrt{11}\)) = 0
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-\sqrt{11}=0\\x+\sqrt{11}=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\sqrt{11}\left(TM\right)\\x=-\sqrt{11}\left(TM\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
d, Ta có: \(\dfrac{x^2-1}{2x^2+3}\) = \(\dfrac{x^2+\dfrac{3}{2}-\dfrac{5}{2}}{2\left(x^2+\dfrac{3}{2}\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) - \(\dfrac{5}{4\left(x^2+\dfrac{3}{2}\right)}\)
C nguyên \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\dfrac{5}{4\left(x^2+\dfrac{3}{2}\right)}\) nguyên \(\Leftrightarrow\) 5 \(⋮\) 4(x2 + \(\dfrac{3}{2}\))
\(\Leftrightarrow\) 4(x2 + \(\dfrac{3}{2}\)) \(\in\) Ư(5)
Xét các TH:
4(x2 + \(\dfrac{3}{2}\)) = 5 \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 = \(\dfrac{-1}{4}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 + \(\dfrac{1}{4}\) = 0 (Vô nghiệm)
4(x2 + \(\dfrac{3}{2}\)) = -5 \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 = \(\dfrac{-11}{4}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 + \(\dfrac{11}{4}\) = 0 (Vô nghiệm)
4(x2 + \(\dfrac{3}{2}\)) = 1 \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 = \(\dfrac{-5}{4}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 + \(\dfrac{5}{4}\) = 0 (Vô nghiệm)
4(x2 + \(\dfrac{3}{2}\)) = -1 \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 = \(\dfrac{-7}{4}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 + \(\dfrac{7}{4}\) = 0 (Vô nghiệm)
Vậy không có giá trị nào của x \(\in\) Z thỏa mãn C \(\in\) Z
Chúc bn học tốt! (Ko bt đề sai hay ko nữa :v)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Tìm x thuộc Z để M=\(\dfrac{2x+1}{x+3}\)có giá trị là số nguyên tố
Chữ hơi xấu mong bạn thông cảm 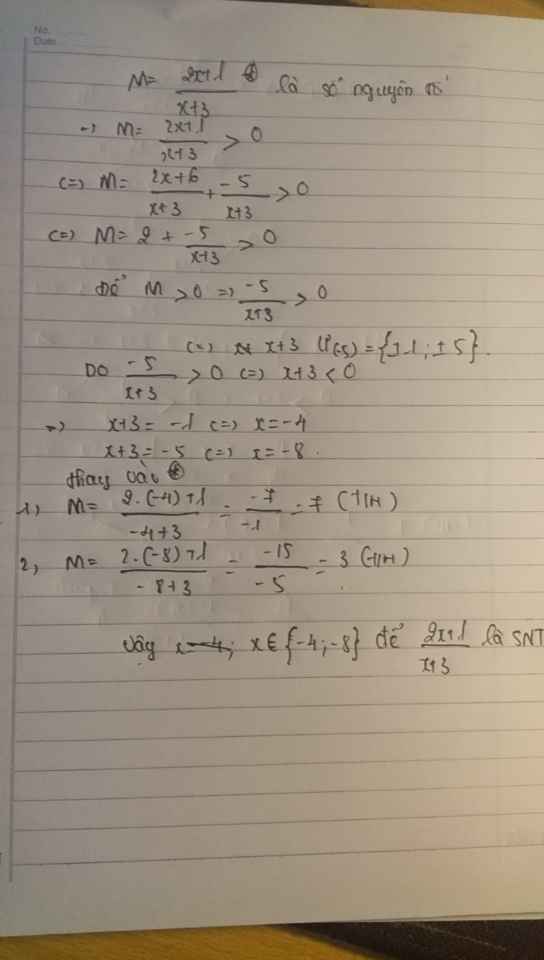
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Tìm các số nguyên x sao cho:
a) \(\dfrac{7}{x-1}\in Z\)
b) \(\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}\in Z\)
\(a,\Leftrightarrow7⋮x-1\Leftrightarrow x-1\inƯ\left(7\right)=\left\{-7;-1;1;7\right\}\\ \Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{-6;0;2;8\right\}\\ b,\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-1+2}{x-1}\in Z\Leftrightarrow1+\dfrac{2}{x-1}\in Z\\ \Leftrightarrow2⋮x-1\Leftrightarrow x-1\inƯ\left(2\right)=\left\{-2;-1;1;2\right\}\\ \Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{-1;0;2;3\right\}\)
Đúng 3
Bình luận (0)
a) để 7/x-1 thuộc Z
=> (x-1) thuộc ước 7(+-1;+-7)
x-1 -1 1 -7 7
x 0 2 -6 8
Đúng 3
Bình luận (0)
a) \(\dfrac{7}{x-1}\in Z\Leftrightarrow x-1\inƯ\left(7\right)=\left\{1;-1;7;-7\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow x\in\left\{2;0;8;-6\right\}\)
b) \(\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}\in Z\Rightarrow\dfrac{x-1}{x-1}+\dfrac{2}{x-1}=1+\dfrac{2}{x-1}\in Z\)
\(\Rightarrow x-1\inƯ\left(2\right)=\left\{1;-1;2;-2\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow x\in\left\{2;0;3;-1\right\}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)































