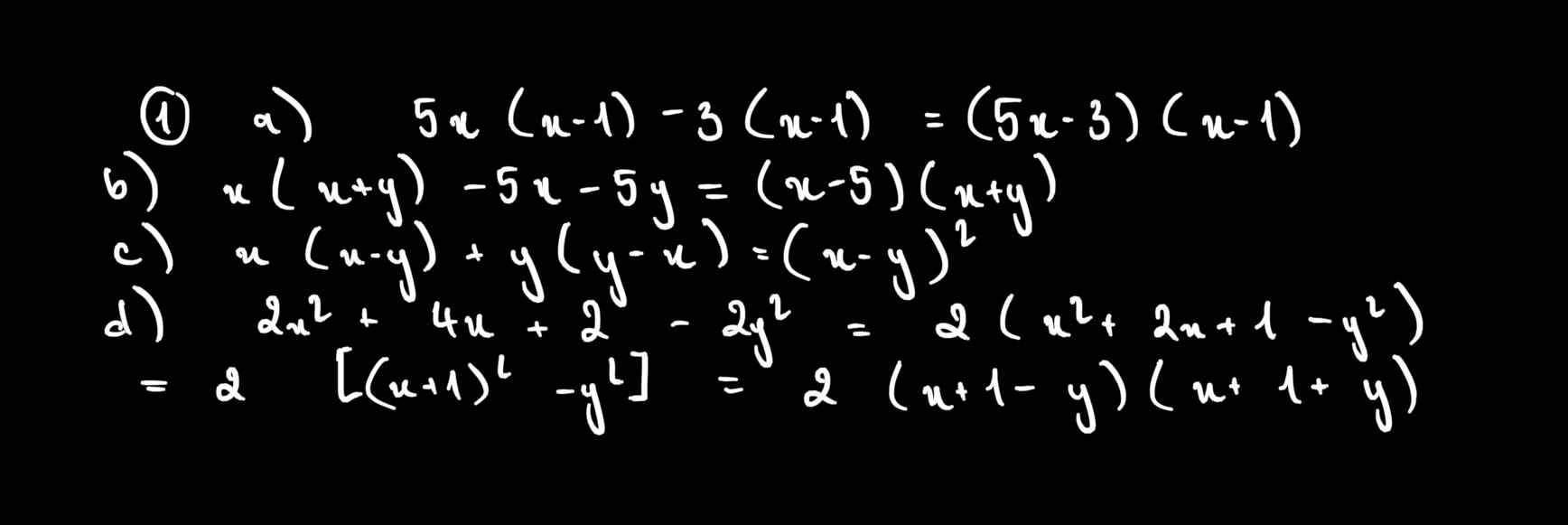Tìm x,y nguyên tố x2-5x-2=2y2-5x-1

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Bài 1: Rút gọn rồi tính giá trị biểu thức:a) A 4x2.(-3x2 + 1) + 6x2.( 2x2 – 1) + x2 khi x -1b) B x2.(-2y3 – 2y2 + 1) – 2y2.(x2y + x2) khi x 0,5 và y -1/2Bài 2: Tìm x, biết:a) 2(5x - 8) – 3(4x – 5) 4(3x – 4) +11b) 2x(6x – 2x2) + 3x2(x – 4) 8c) (2x)2(4x – 2) – (x3 – 8x2) 15Bài 3: Chứng tỏ rằng giá trị của biểu thức sau không phụ thuộc vào giá trị của biến x:P x(2x + 1) – x2(x+2) + x3 – x +3
Đọc tiếp
Bài 1: Rút gọn rồi tính giá trị biểu thức:
a) A = 4x2.(-3x2 + 1) + 6x2.( 2x2 – 1) + x2 khi x = -1
b) B = x2.(-2y3 – 2y2 + 1) – 2y2.(x2y + x2) khi x = 0,5 và y = -1/2
Bài 2: Tìm x, biết:
a) 2(5x - 8) – 3(4x – 5) = 4(3x – 4) +11
b) 2x(6x – 2x2) + 3x2(x – 4) = 8
c) (2x)2(4x – 2) – (x3 – 8x2) = 15
Bài 3: Chứng tỏ rằng giá trị của biểu thức sau không phụ thuộc vào giá trị của biến x:
P = x(2x + 1) – x2(x+2) + x3 – x +3
\(1,\\ a,A=4x^2\left(-3x^2+1\right)+6x^2\left(2x^2-1\right)+x^2\\ A=-12x^4+4x^2+12x^2-6x^2+x^2=-x^2=-\left(-1\right)^2=-1\\ b,B=x^2\left(-2y^3-2y^2+1\right)-2y^2\left(x^2y+x^2\right)\\ B=-2x^2y^3-2x^2y^2+x^2-2x^2y^3-2x^2y^2\\ B=-4x^2y^3-4x^2y^2+x^2\\ B=-4\left(0,5\right)^2\left(-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^3-4\left(0,5\right)^2\left(-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\left(0,5\right)^2\\ B=\dfrac{1}{8}-\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{1}{4}=\dfrac{1}{8}\)
Đúng 3
Bình luận (0)
\(2,\\ a,\Leftrightarrow10x-16-12x+15=12x-16+11\\ \Leftrightarrow-14x=-4\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{2}{7}\\ b,\Leftrightarrow12x^2-4x^3+3x^3-12x^2=8\\ \Leftrightarrow-x^3=8=-2^3\\ \Leftrightarrow x=2\\ c,\Leftrightarrow4x^2\left(4x-2\right)-x^3+8x^2=15\\ \Leftrightarrow16x^3-8x^2-x^3+8x^2=15\\ \Leftrightarrow15x^3=15\\ \Leftrightarrow x^3=1\Leftrightarrow x=1\)
Đúng 3
Bình luận (0)
\(P=x\left(2x+1\right)-x^2\left(x+2\right)+x^3-x+3\\ P=2x^2+x-x^3-2x^2+x^3-x+3\\ P=3\left(đfcm\right)\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
tìm các nguyên tố x,y thỏa mãn x2-2y2=1
:Các biểu thức sau không phụ thuộc vào giá trị của biến đúng hay sai :
a/ 2(2x+x2)-x2(x+2)+(x3-4x+3) b/ x(x2+x+1)-x2(x+1) –x+5
c/ 3x(x-2)-5x(x-1)-8(x2-3) d/ 2y(y2+y+1)-2y2(y+1)-2(y+10)
Tìm tất cả các bội số nguyên (x;y) thỏa mãn phương trình:
a) x2 - 2x + 2y2 = 2(xy +1)
b) x2 + 2y2 + 2xy - 2x = 7
a.
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-4x+4y^2=4xy+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-4xy+4y^2\right)+\left(x^2-4x+4\right)=8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2y\right)^2+\left(x-2\right)^2=8\) (1)
Do \(\left(x-2y\right)^2\ge0;\forall x;y\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2\le8\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2=\left\{0;1;4\right\}\)
TH1: \(\left(x-2\right)^2\Rightarrow x=2\) thế vào (1)
\(\Rightarrow\left(2-2y\right)^2=8\Rightarrow\left(1-y\right)^2=2\) (ko tồn tại y nguyên t/m do 2 ko phải SCP)
TH2: \(\left(x-2\right)^2=1\Rightarrow\left(x-2y\right)^2=8-1=7\), mà 7 ko phải SCP nên pt ko có nghiệm nguyên
TH3: \(\left(x-2\right)^2=4\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\x=0\end{matrix}\right.\) thế vào (1):
- Với \(x=0\Rightarrow\left(-2y\right)^2+4=8\Rightarrow y^2=1\Rightarrow y=\pm1\)
- Với \(x=2\Rightarrow\left(2-2y\right)^2+4=8\Rightarrow\left(1-y\right)^2=1\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\y=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy pt có các cặp nghiệm là:
\(\left(x;y\right)=\left(0;1\right);\left(0;-1\right);\left(2;0\right);\left(2;2\right)\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
b.
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+4y^2+4xy-4x=14\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+4xy+4y^2\right)+\left(x^2-4x+4\right)=18\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2y\right)^2+\left(x-2\right)^2=18\) (1)
Lý luận tương tự câu a ta được
\(\left(x-2\right)^2\le18\Rightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2=\left\{0;1;4;9;16\right\}\)
Với \(\left(x-2\right)^2=\left\{0;1;4;16\right\}\) thì \(18-\left(x-2\right)^2\) ko phải SCP nên ko có giá trị nguyên x;y thỏa mãn
Với \(\left(x-2\right)^2=9\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\) thế vào (1)
- Với \(x=5\Rightarrow\left(5+2y\right)^2+9=18\Rightarrow\left(5+2y\right)^2=9\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}5+2y=3\\5+2y=-3\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}y=-1\\y=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
- Với \(x=-1\Rightarrow\left(-1+2y\right)^2=9\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}-1+2y=3\\-1+2y=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}y=2\\y=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(5;-1\right);\left(5;-4\right);\left(-1;3\right);\left(-1;-3\right)\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Cho hai số x và y thỏa mãn x2+2y2-3xy=0 và x>y>0.
Tính GTBT: A=\(\dfrac{6x+16y}{5x-3y}\)
\(x^2+2y^2-3xy=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-y\right)\left(x-2y\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-2y=0\) (do \(x>y\) nên \(x-y>0\))
\(\Leftrightarrow x=2y\)
\(\Rightarrow A=\dfrac{6.2y+16y}{5.2y-3y}=\dfrac{28y}{7y}=4\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
tìm gtnn (gtln) của
a) 4x2+12x+1 b) 4x2-3x+10
c)2x2+5x+10 d) x-x2+2
e) 2x-2x2 f) 4x2+2y2+4xy+4y+5
a) \(4x^2+12x+1=\left(4x^2+12x+9\right)-8=\left(2x+3\right)^2-8\ge-8\)
\(ĐTXR\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{3}{2}\)
b) \(4x^2-3x+10=\left(4x^2-3x+\dfrac{9}{16}\right)+\dfrac{151}{16}=\left(2x-\dfrac{3}{4}\right)^2+\dfrac{151}{16}\ge\dfrac{151}{16}\)
\(ĐTXR\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{3}{8}\)
c) \(2x^2+5x+10=\left(2x^2+5x+\dfrac{25}{8}\right)+\dfrac{55}{8}=\left(\sqrt{2}x+\dfrac{5\sqrt{2}}{4}\right)^2+\dfrac{55}{8}\ge\dfrac{55}{8}\)
\(ĐTXR\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{5}{4}\)
d) \(x-x^2+2=-\left(x^2-x+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)+\dfrac{9}{4}=-\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{9}{4}\le\dfrac{9}{4}\)
\(ĐTXR\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
e) \(2x-2x^2=-2\left(x^2-x+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)+\dfrac{1}{2}=-2\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{1}{2}\le\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(ĐTXR\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
f) \(4x^2+2y^2+4xy+4y+5=\left(4x^2+4xy+y^2\right)+\left(y^2+4y+4\right)+1=\left(2x+y\right)^2+\left(y+2\right)^2+1\ge1\)
\(ĐTXR\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\y=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 4
Bình luận (1)
a: Ta có: \(4x^2+12x+1\)
\(=4x^2+12x+9-8\)
\(=\left(2x+3\right)^2-8\ge-8\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi \(x=-\dfrac{3}{2}\)
b: Ta có: \(4x^2-3x+10\)
\(=4\left(x^2-\dfrac{3}{4}x+\dfrac{5}{2}\right)\)
\(=4\left(x^2-2\cdot x\cdot\dfrac{3}{8}+\dfrac{9}{64}+\dfrac{151}{64}\right)\)
\(=4\left(x-\dfrac{3}{8}\right)^2+\dfrac{151}{16}\ge\dfrac{151}{16}\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi \(x=\dfrac{3}{8}\)
c: Ta có: \(2x^2+5x+10\)
\(=2\left(x^2+\dfrac{5}{2}x+5\right)\)
\(=2\left(x^2+2\cdot x\cdot\dfrac{5}{4}+\dfrac{25}{16}+\dfrac{55}{16}\right)\)
\(=2\left(x+\dfrac{5}{4}\right)^2+\dfrac{55}{8}\ge\dfrac{55}{8}\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi \(x=-\dfrac{5}{4}\)
Đúng 3
Bình luận (1)
Bài 1 : tìm x ; y nguyên dương
2xy + x + y = 83
Bài 2 tìm nghiệm nguyên của phương trình :
a ) x2 + 2y2 + 3xy - x - y + 3 = 0
b ) 6x2y3 + 3x2 - 10y3 = -2
Bài 1: Phân tích các đa thức sau thành nhân tử:
a) 5x(x – 1) – 3(x – 1) b)x(x + y) – 5x – 5y
c) x(x – y) + y(y – x) d) 2x2 + 4x + 2 – 2y2
a) = (x - 1)(5x - 3)
b) = x(x + y) - 5(x + y)
= (x + y)(x - 5)
c) = x(x - y) - y(x - y)
= (x - y)^2
d) = 2(x2 + 2x + 1 - y2)
= 2[(x + 1)2 - y2]
= 2(x - y + 1)(x + y + 1)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
tìm các số nguyen tố x,y thỏa mãn đề bài x2-2y2-1=0
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-1=2y^2\)
Do vế phải chẵn \(\Rightarrow\) vế trái chẵn \(\Leftrightarrow x\) lẻ
\(\Rightarrow x=2k+1\)
Pt trở thành: \(\left(2k+1\right)^2-1=2y^2\Leftrightarrow2\left(k^2+k\right)=y^2\)
Vế trái chẵn \(\Rightarrow\) vế phải chẵn \(\Rightarrow y^2\) chẵn \(\Rightarrow y\) chẵn
\(\Rightarrow y=2\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2-9=0\Rightarrow x=3\)
Vậy \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(3;2\right)\)
Đúng 3
Bình luận (0)